Pityriasis versicolor is a chronic mycosis caused by fungi of the genus Malassezia, most commonly M. furfur. It can exist as a saprophyte, a yeast-like type that is a normal inhabitant of sebum-rich skin areas, and as a pathogen, an “activated” mold-like (mycelial) type that causes shingles.
Factors responsible for mycelial transformation include a warm, humid environment, use of oral contraceptives, heredity, use of systemic corticosteroids, Cushing’s disease, immunosuppression, hyperhidrosis and malnutrition.
Clinical picture
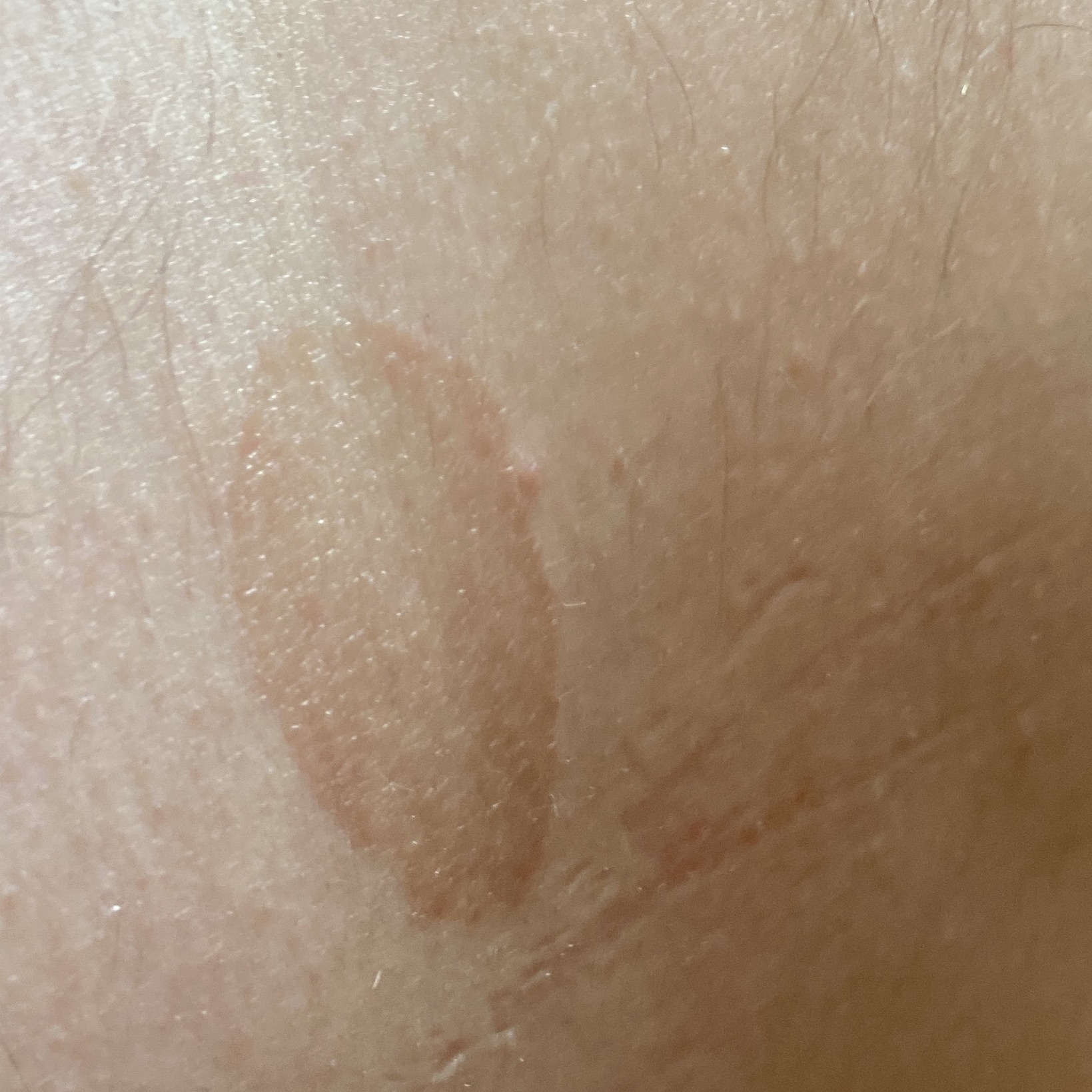
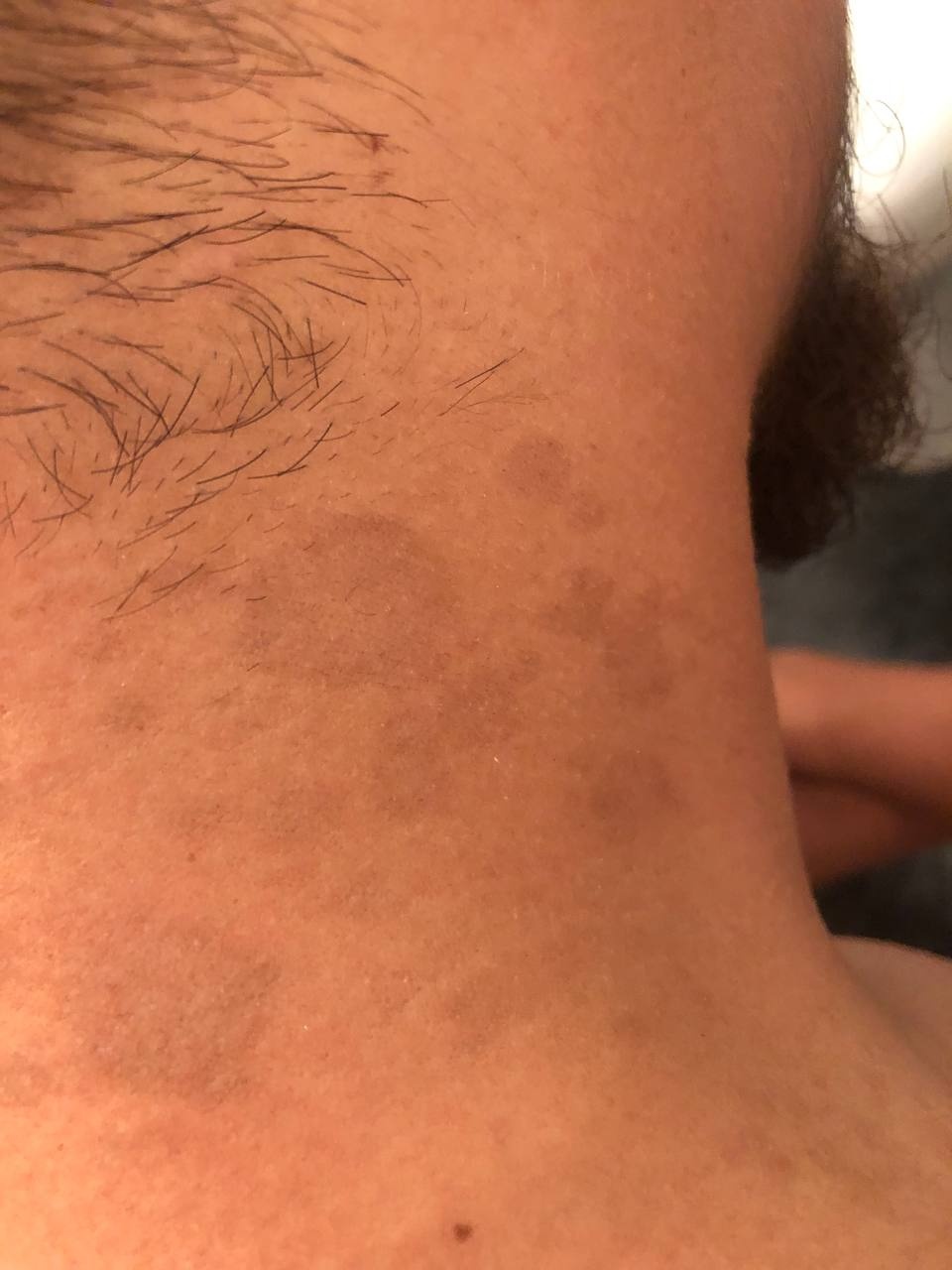
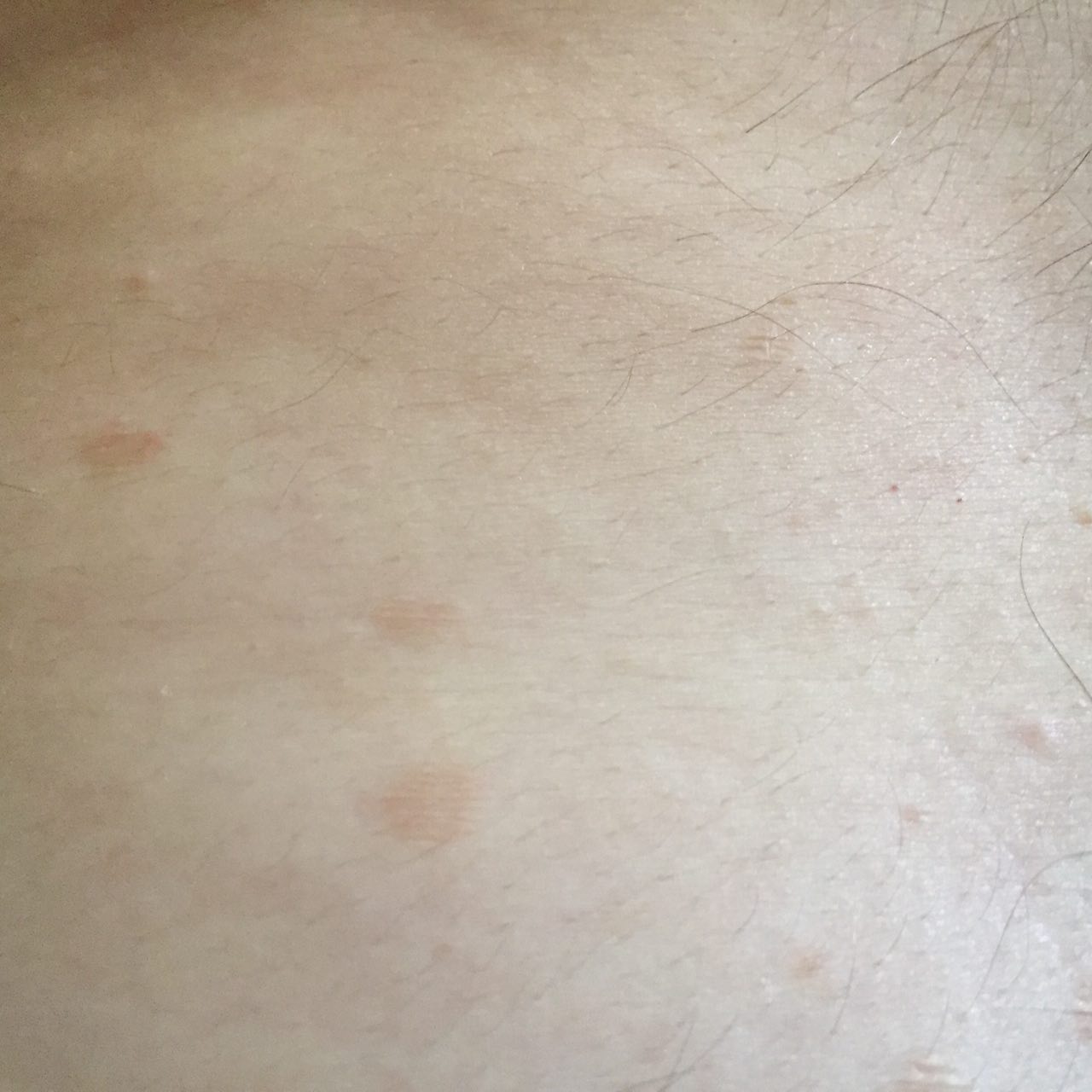
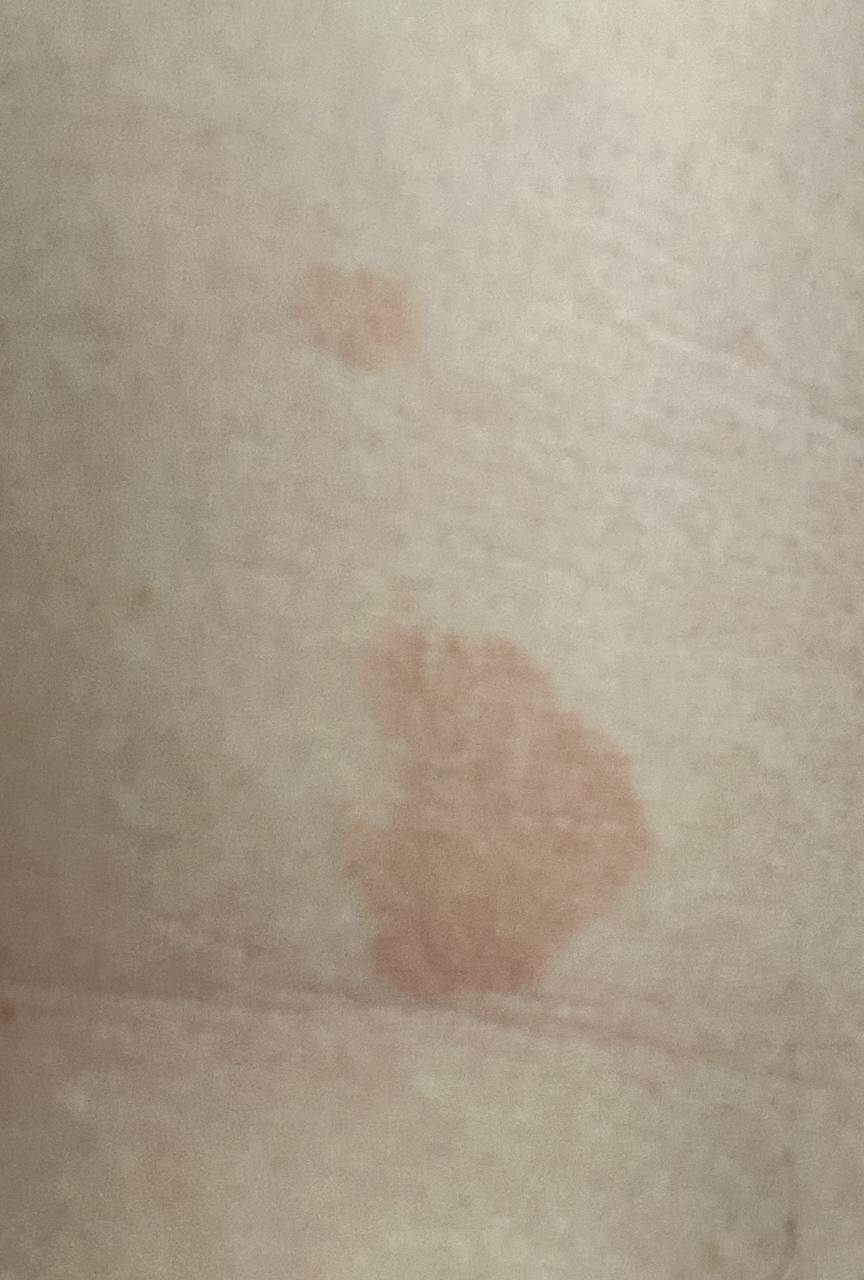
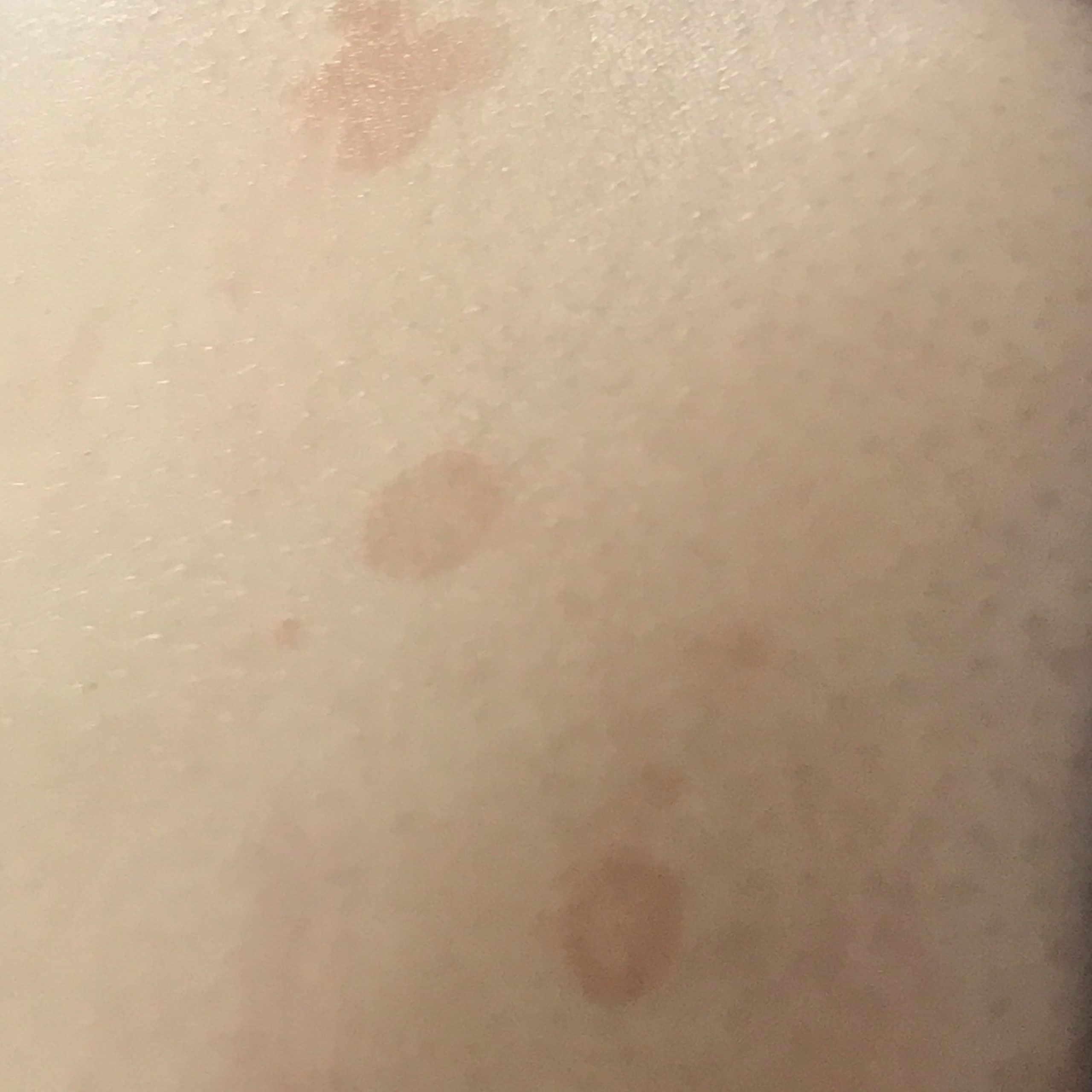
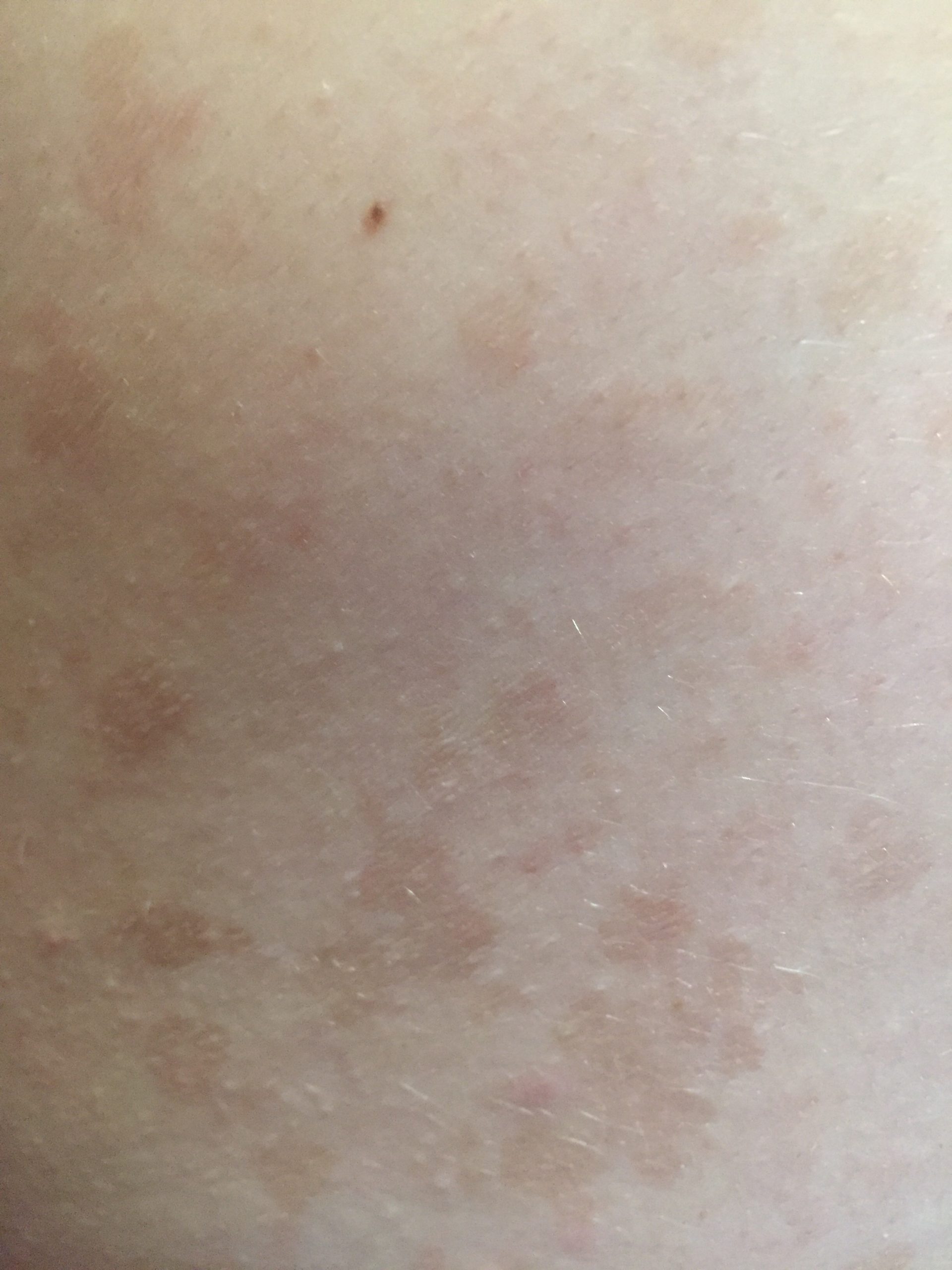
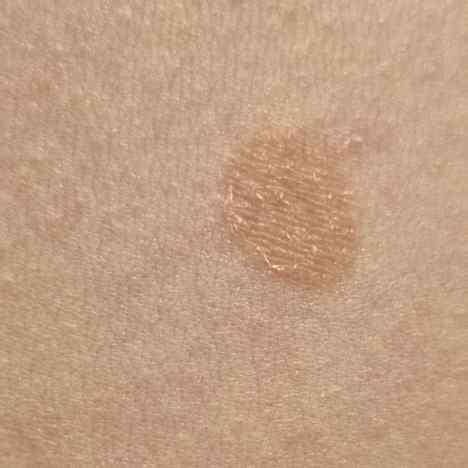
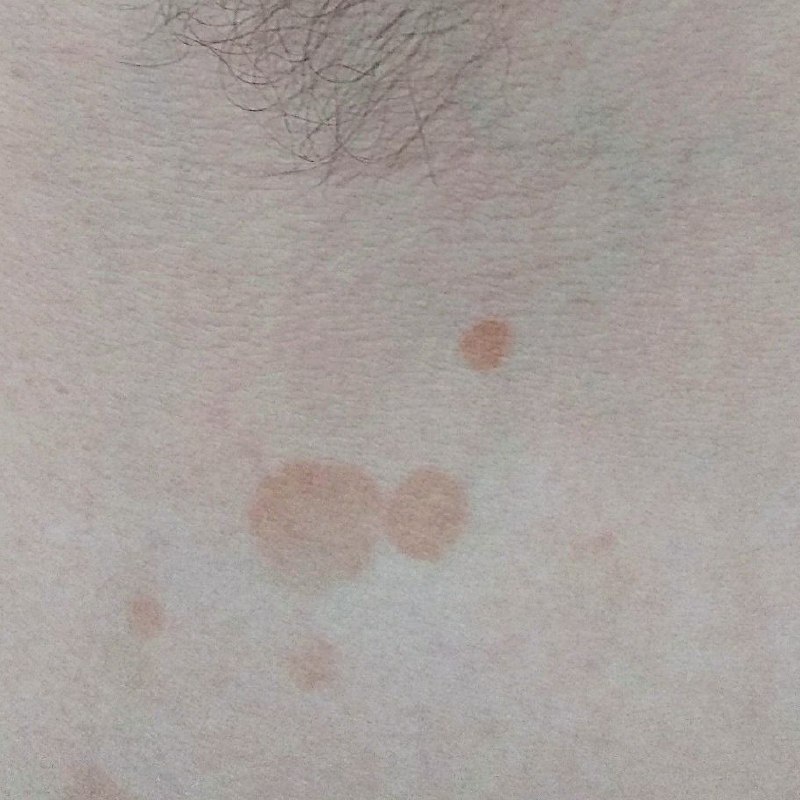
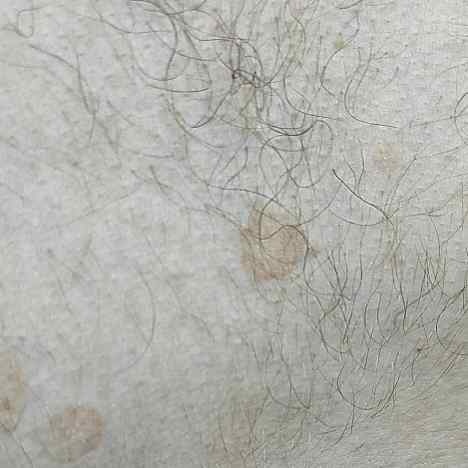
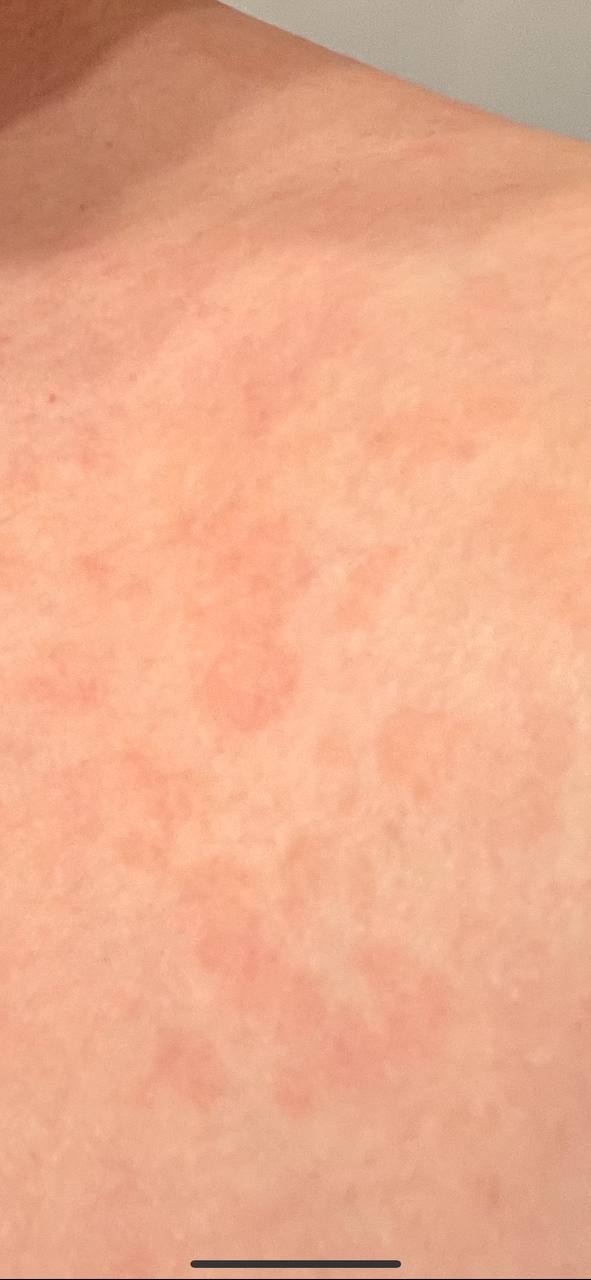
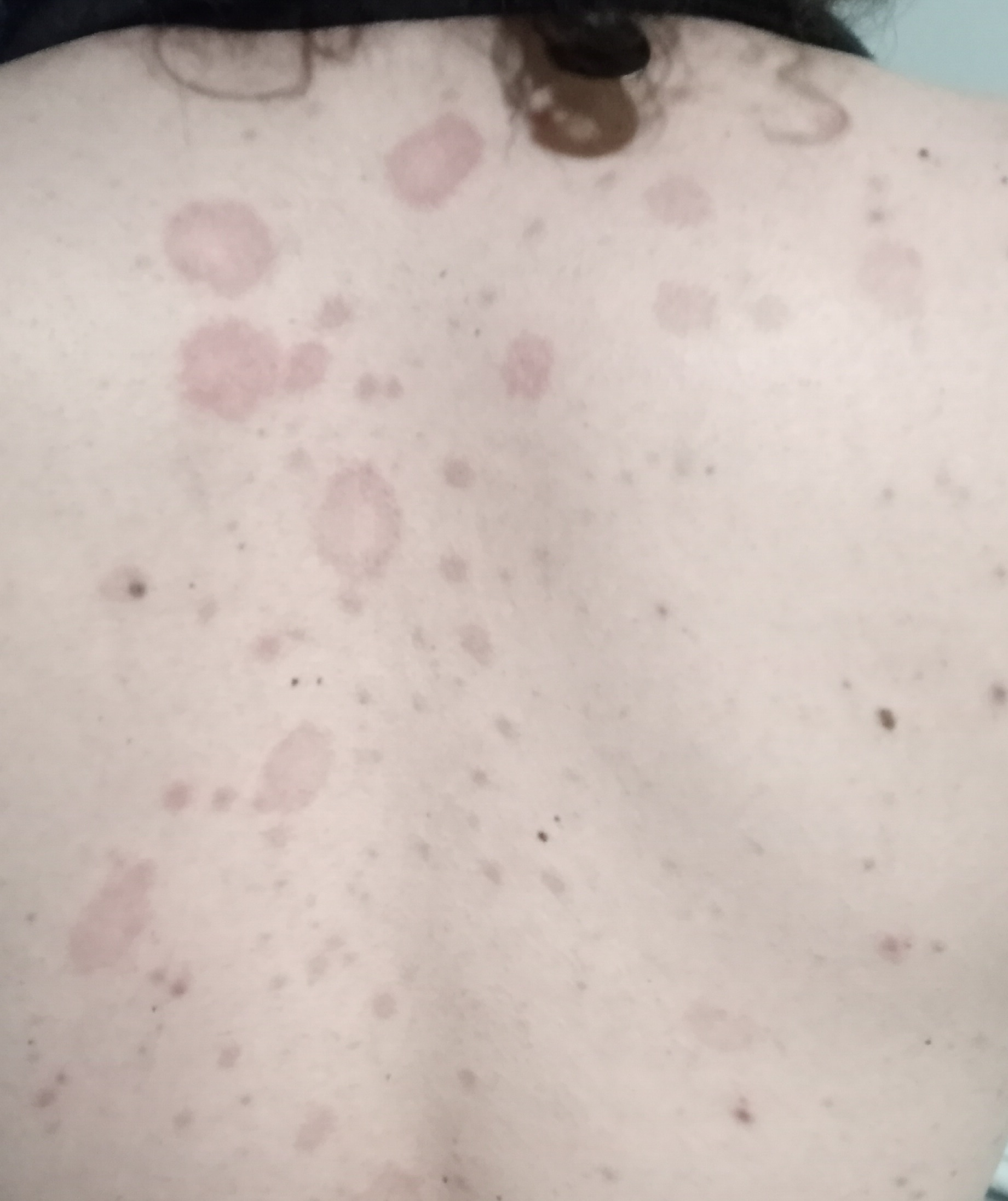
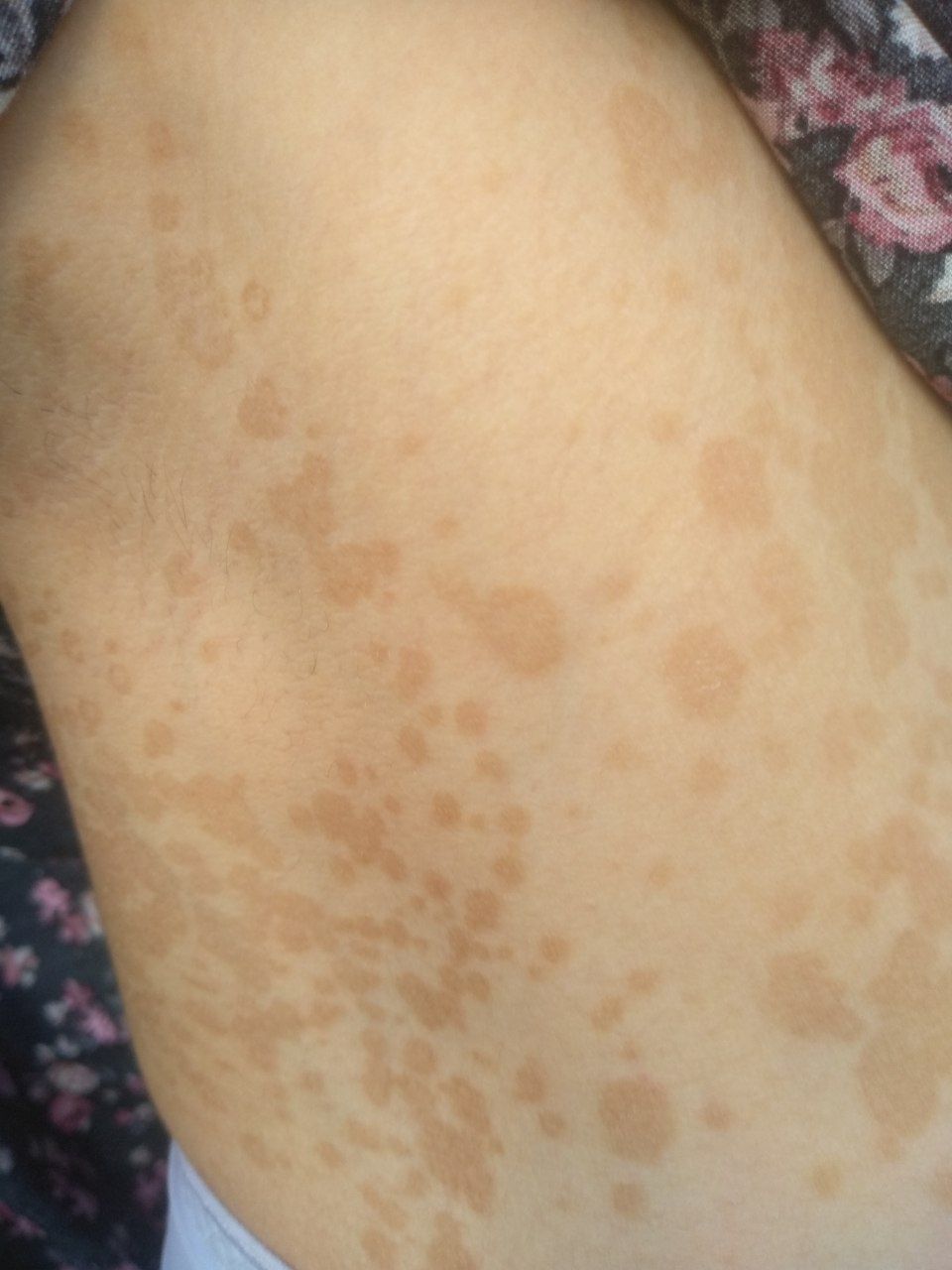
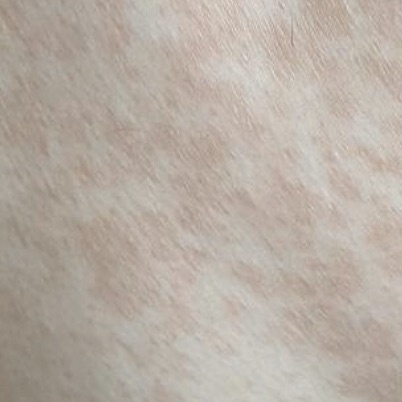
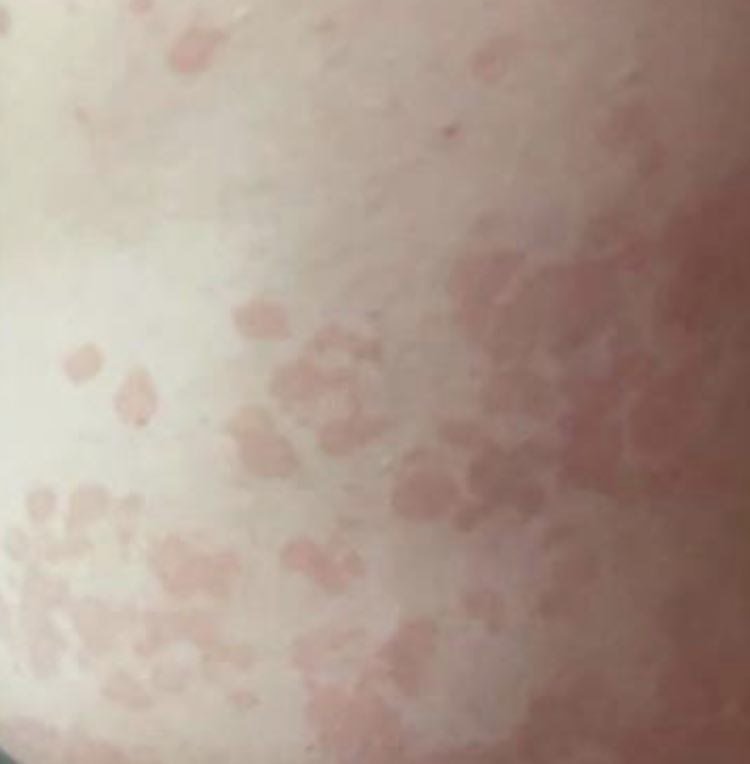
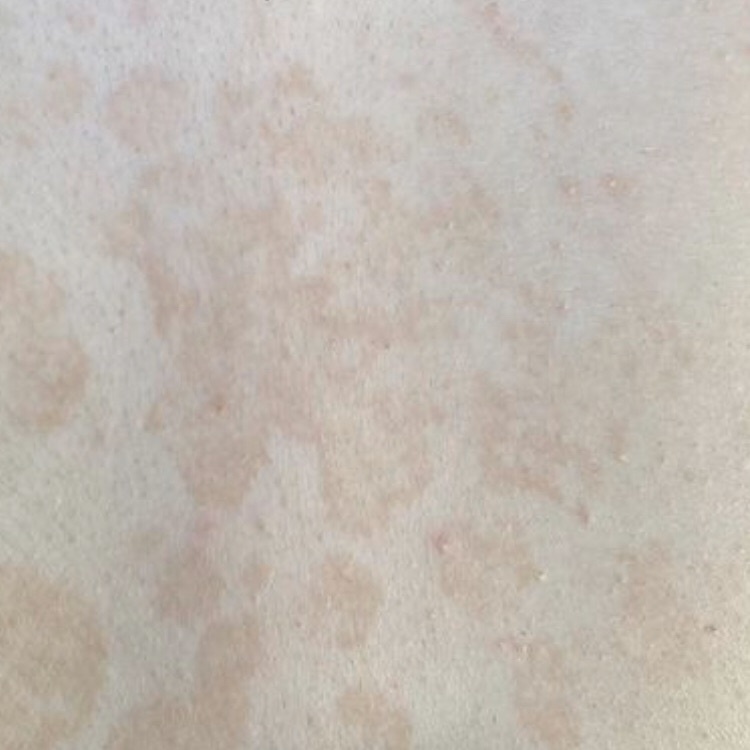
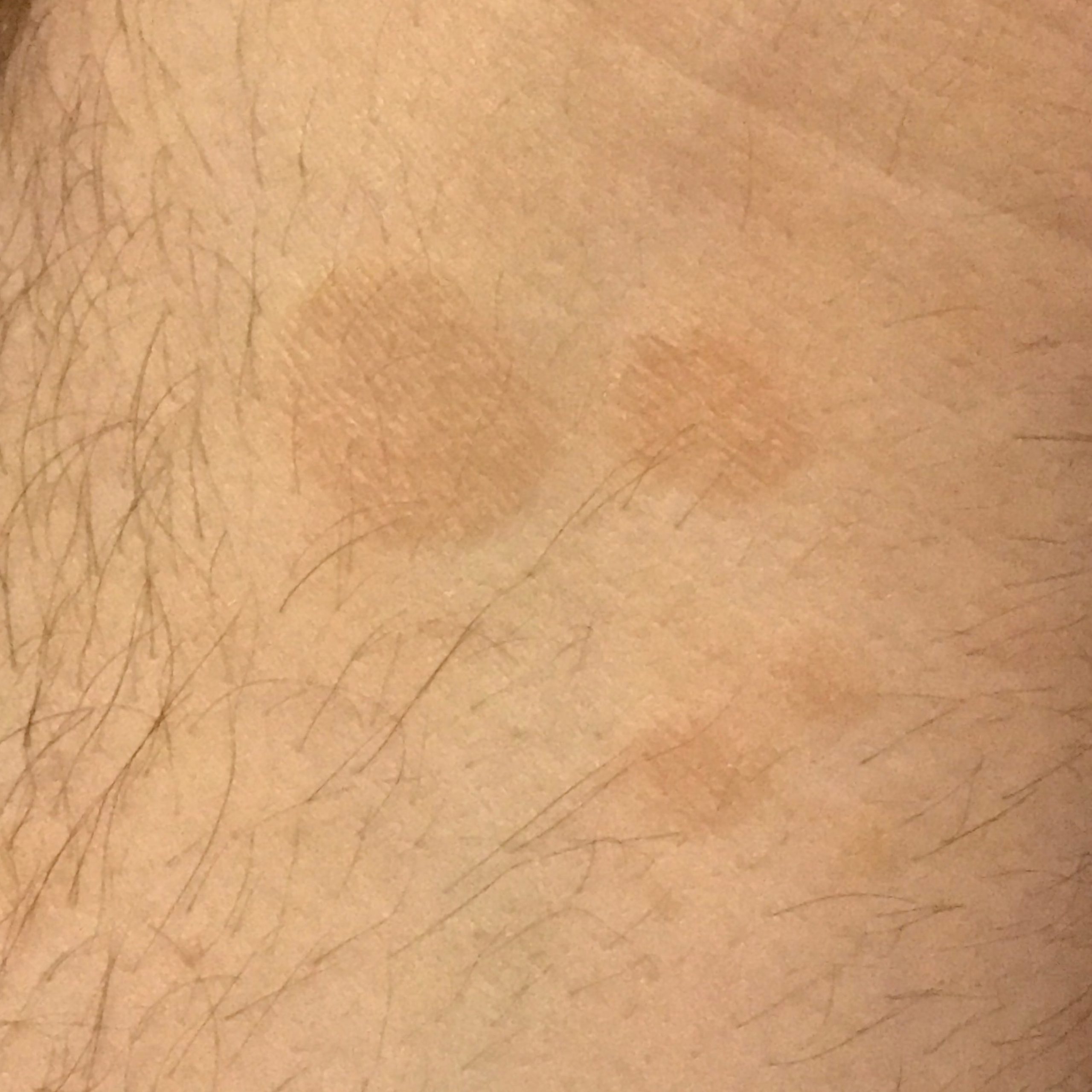
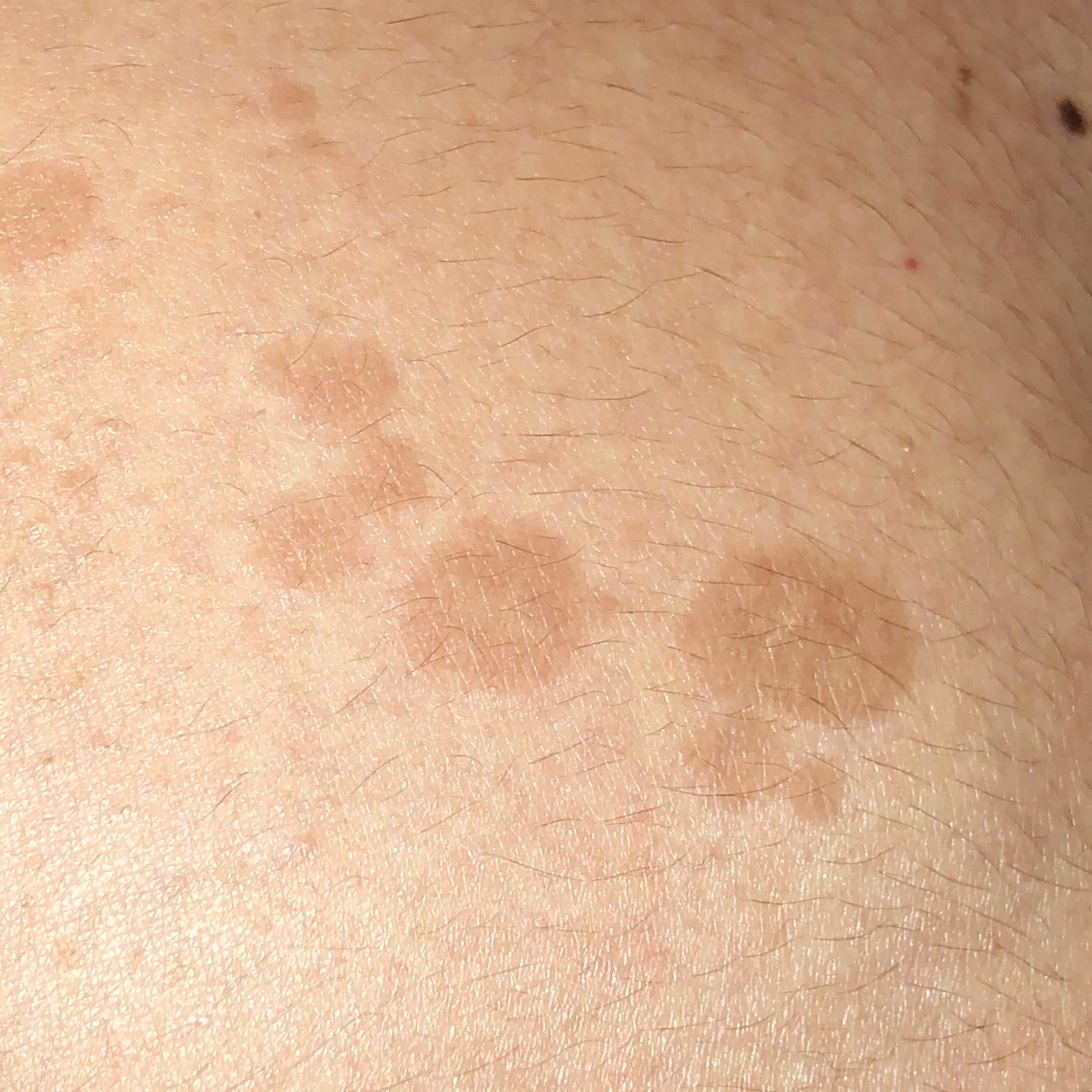
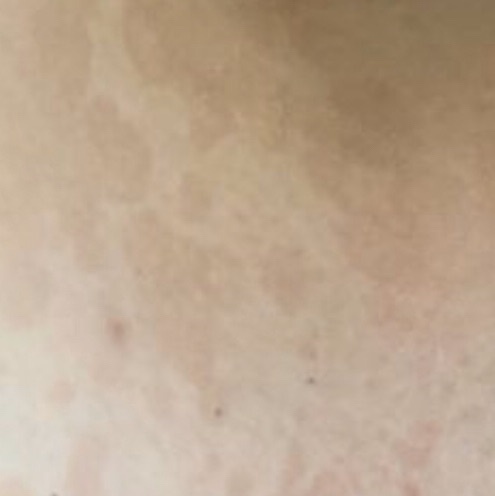
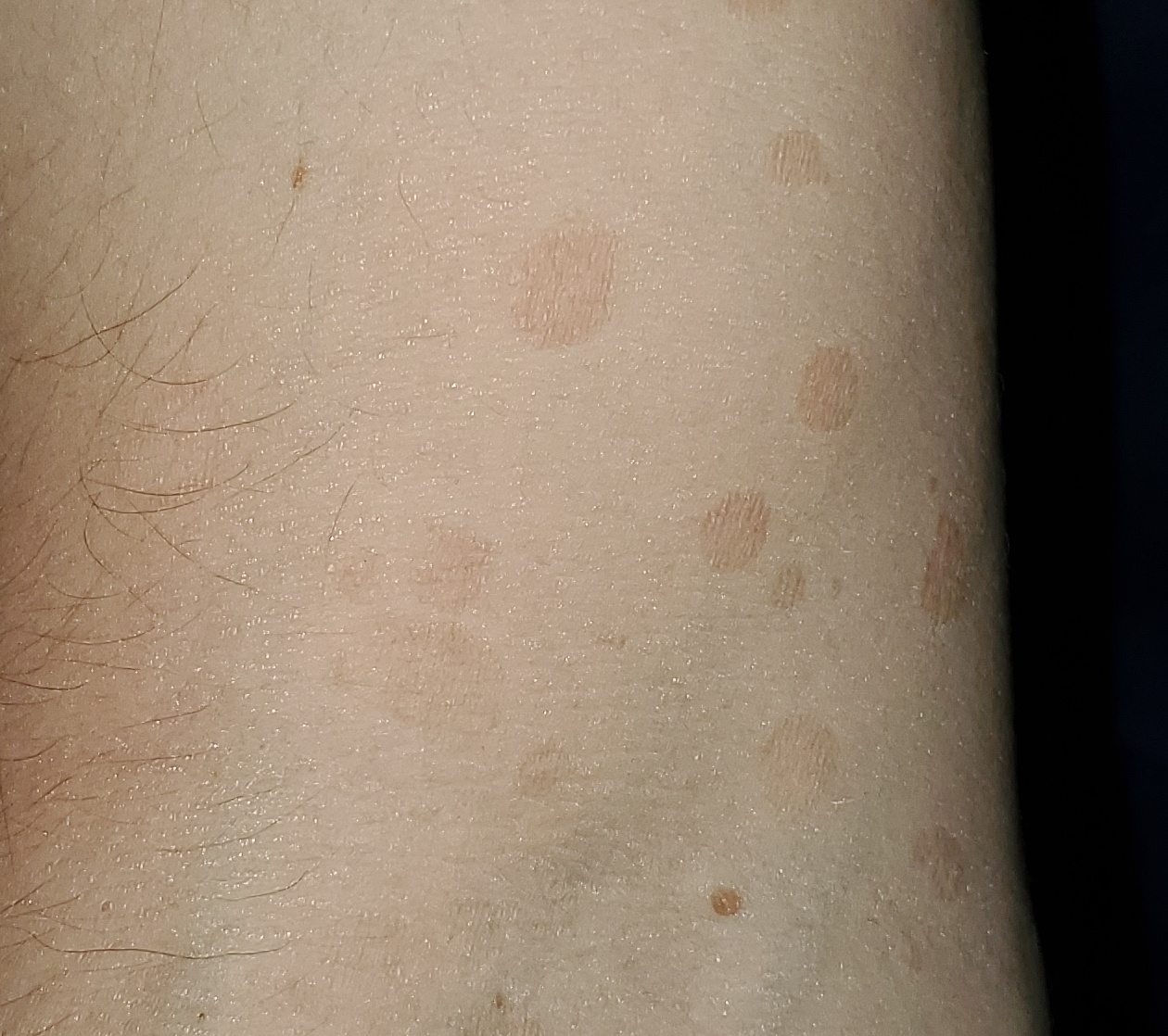
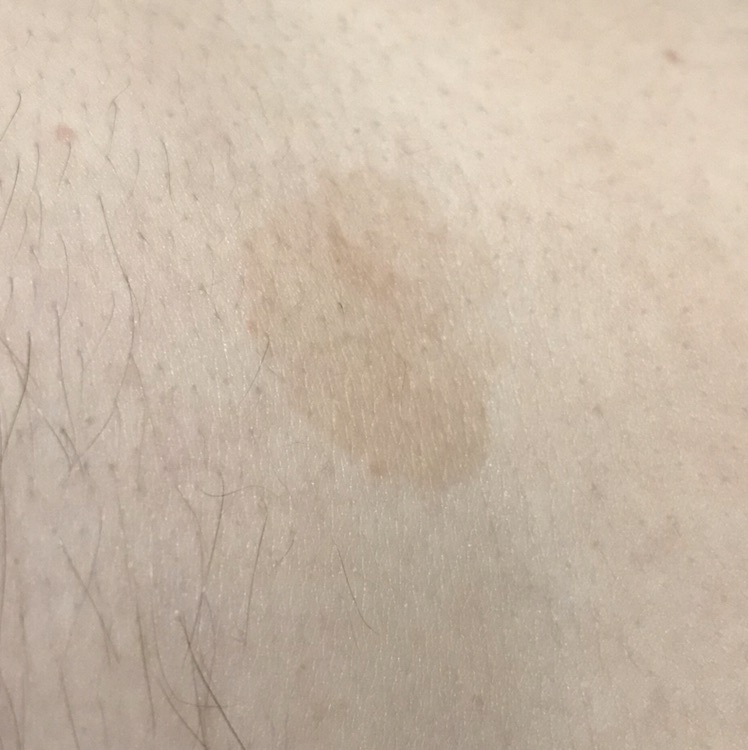
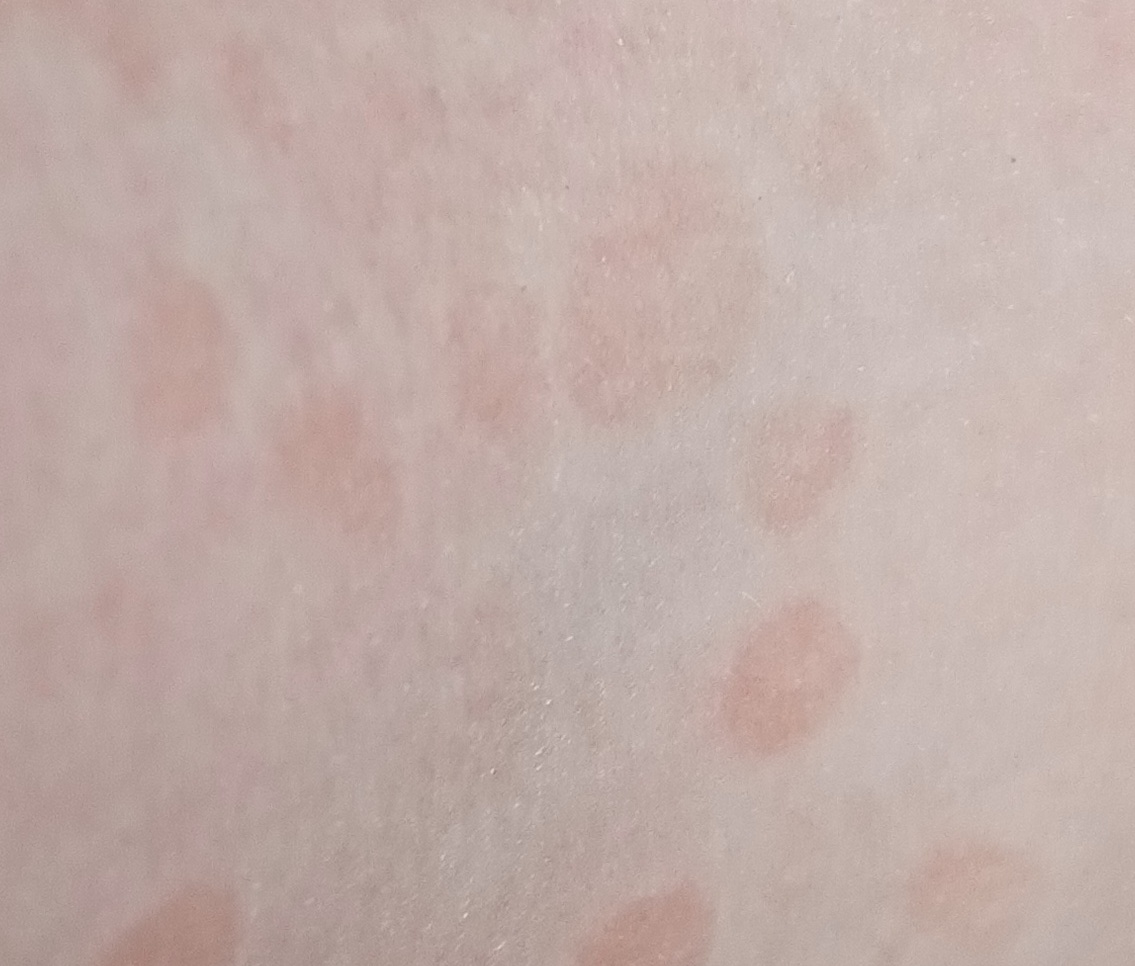
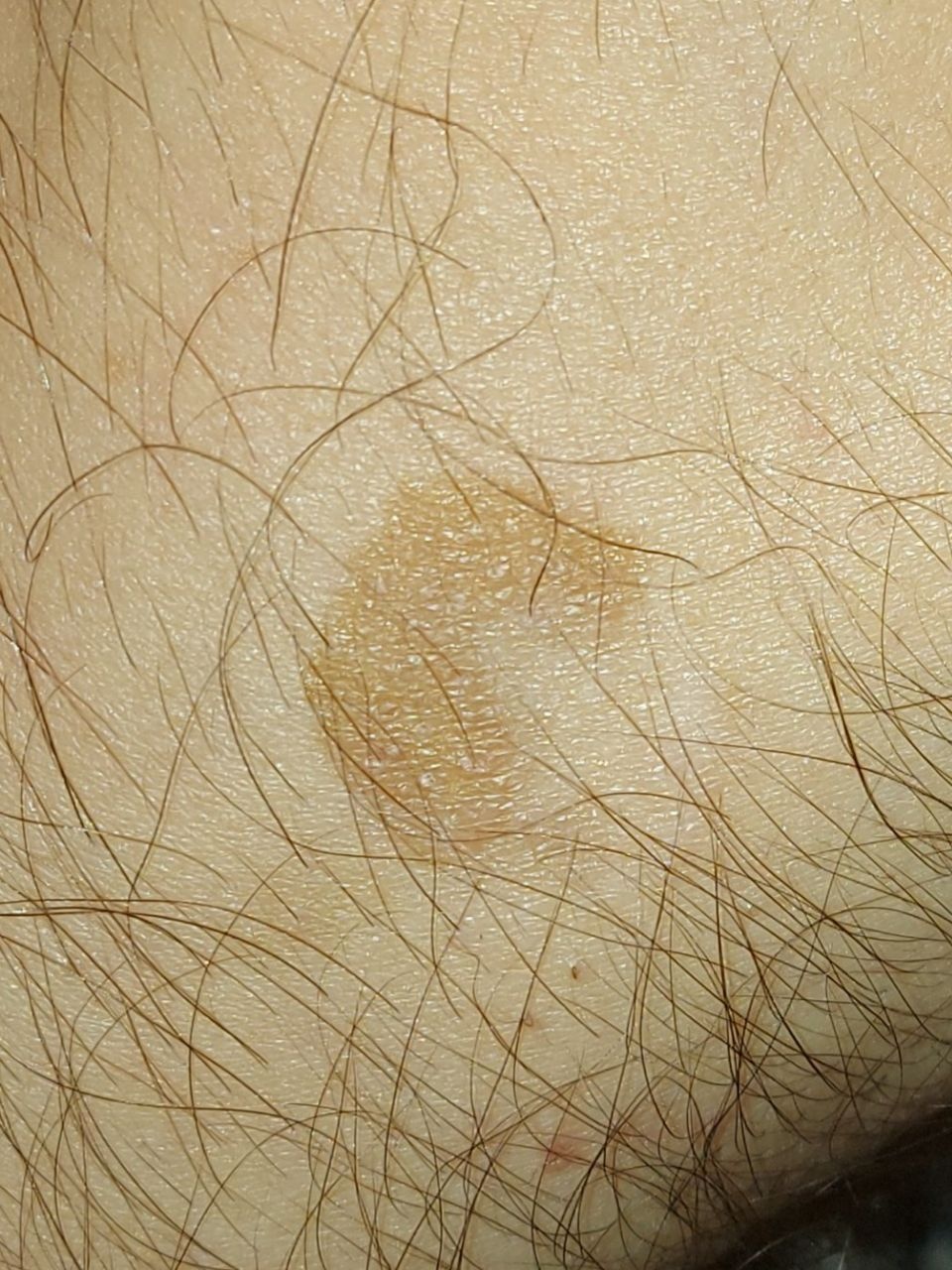
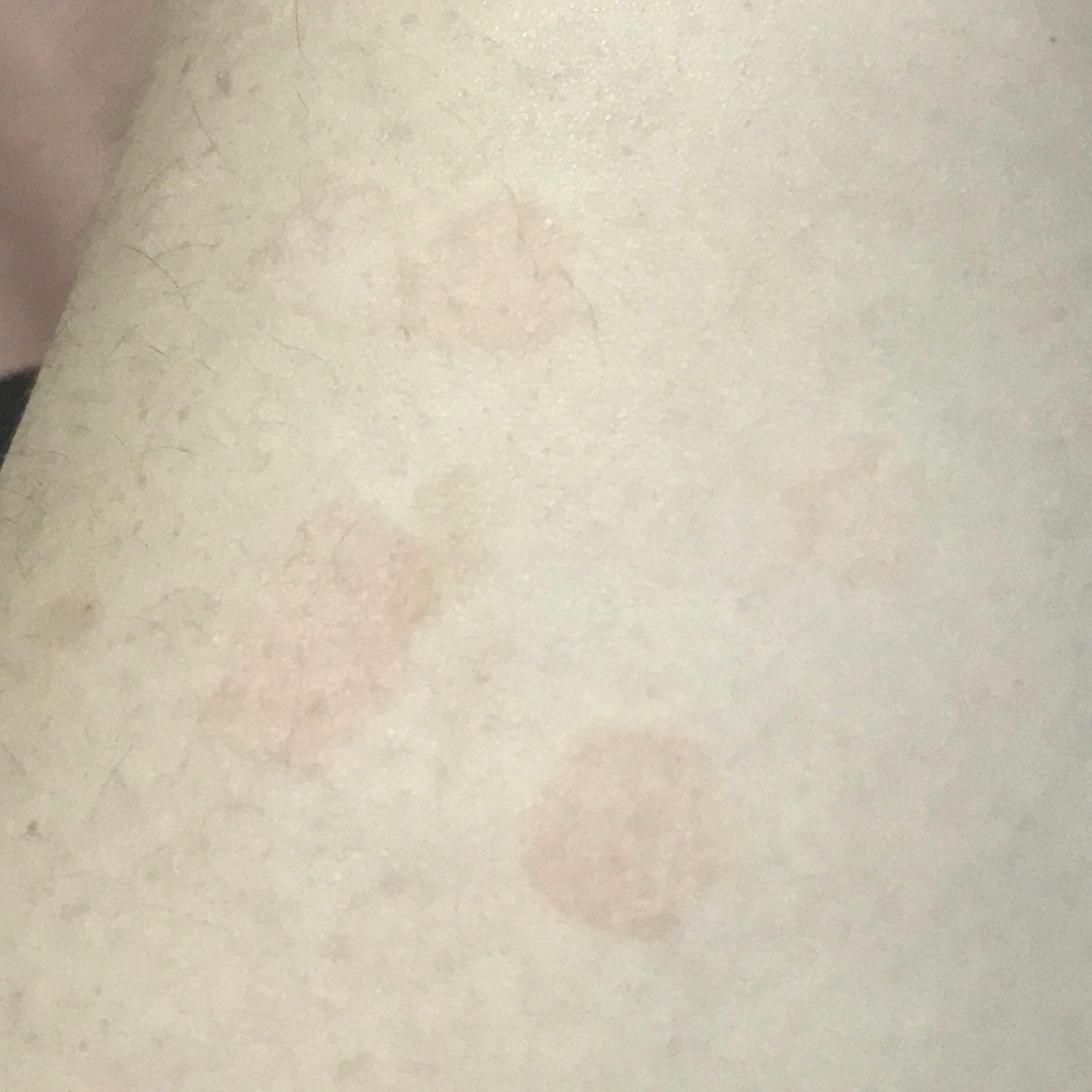
The most common manifestations of Pityriasis versicolor are flaky, pigmented (noninflammatory) patches of pink, yellow, brown, and coffee and milk. In dark-skinned individuals, they are lighter in color than the surrounding skin.
Location
- Chest
- Back
- Abdomen
- Proximal limbs.
The face, scalp, and genitals are less frequently affected, and in severe cases, the process may spread to extensive areas.
Borders are clearly delineated. The spots are up to 1 cm in size, but they tend to coalesce, forming large lesion foci. Presented complaints, as a rule, have an aesthetic character. Itching is moderate or absent. A secondary hypopigmentation (reversible) remains after tanning.
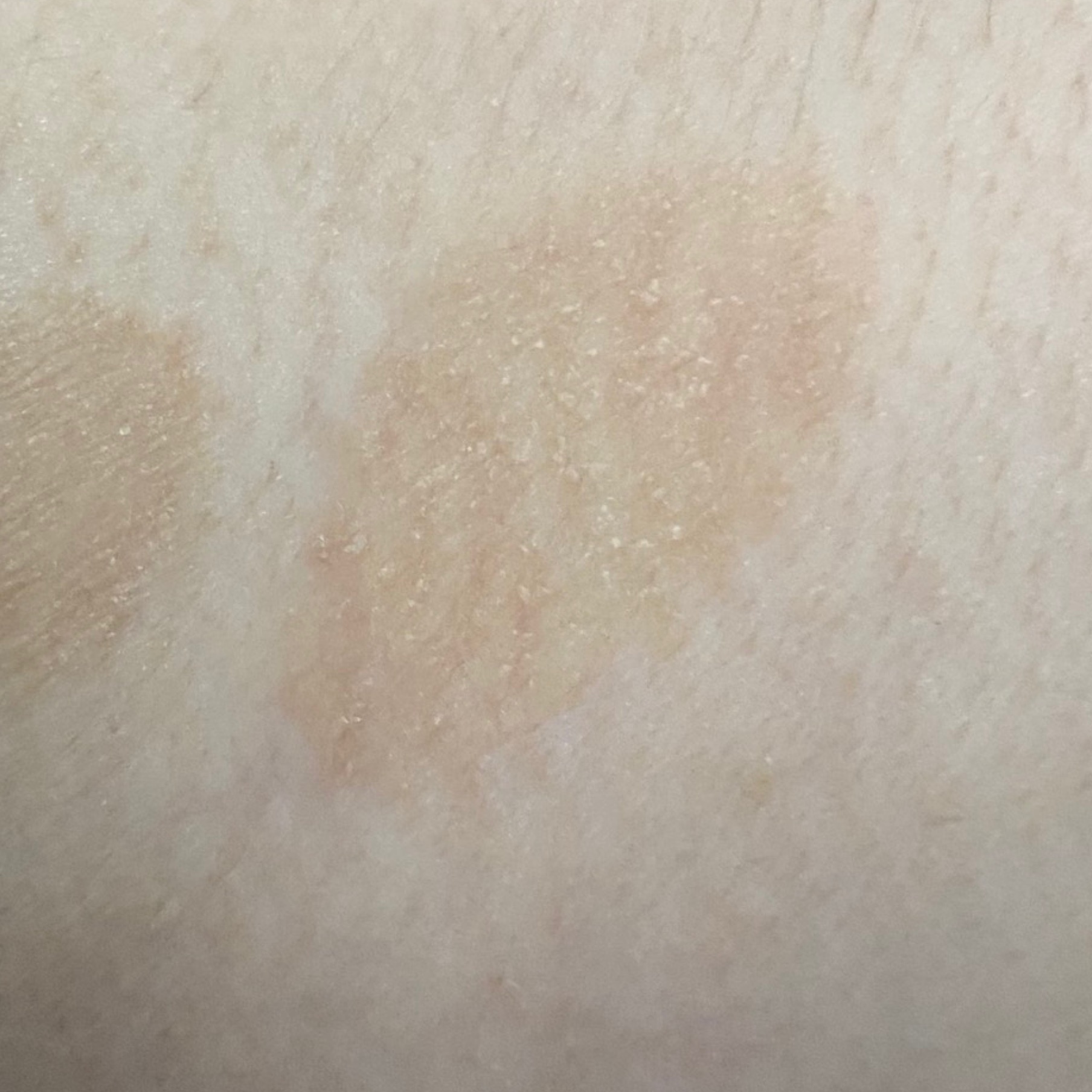
The disease may also manifest as itchy folliculitis in the back, chest, and sometimes on the extremities. The primary rashes are perfollicular, erythematous, in the form of papules or pustules 2-3 mm in diameter. Only appropriate culture and KOH (potassium hydroxide) testing can distinguish this infection from bacterial folliculitis.
Diagnosis
- Wood lamp – yellow or orange glow;
- KOH microscopy – detection of filamentous mycelium and globular pseudomycelium (a “meatball-spaghetti” appearance);
- Mucilaginous creamy colonies.
Treatment
Antiseptics and antifungal agents in the form of shampoos, solutions or creams (ketoconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine) are used to treat mild forms 2 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
Therapy for severe forms includes systemic itraconazole (100 mg twice daily) or fluconazole (50 mg once daily) or ketoconazole (200 mg twice daily) for 2-4 weeks.