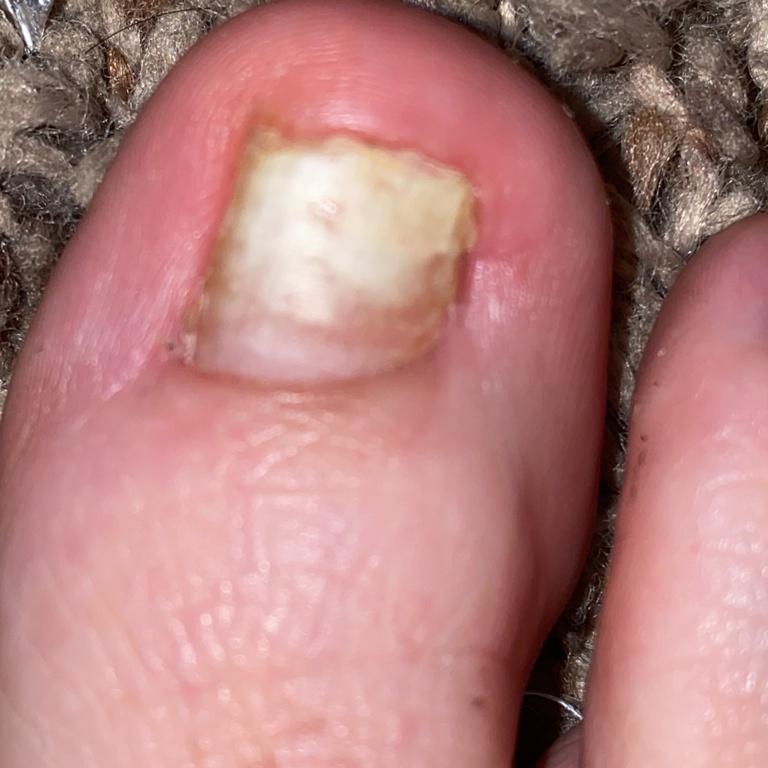
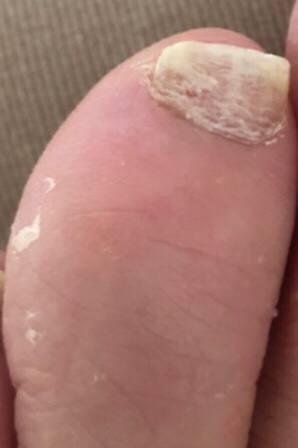
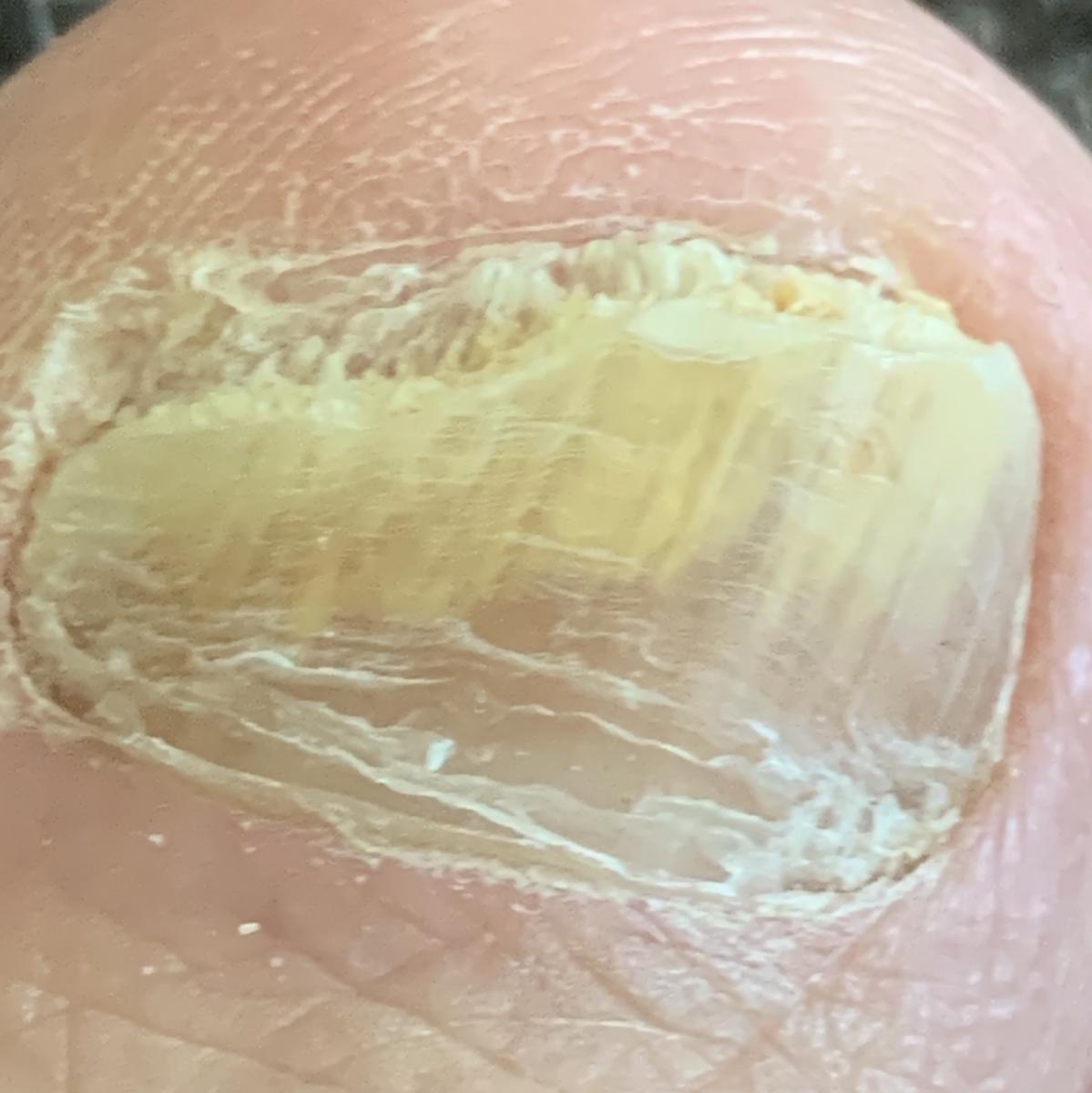
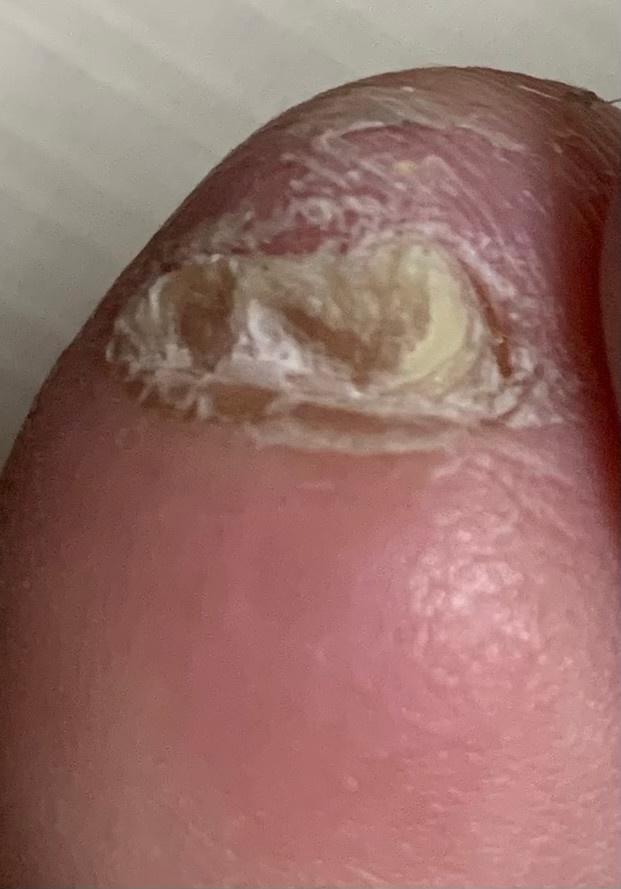
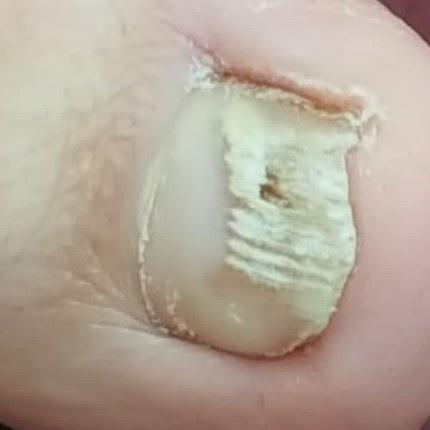
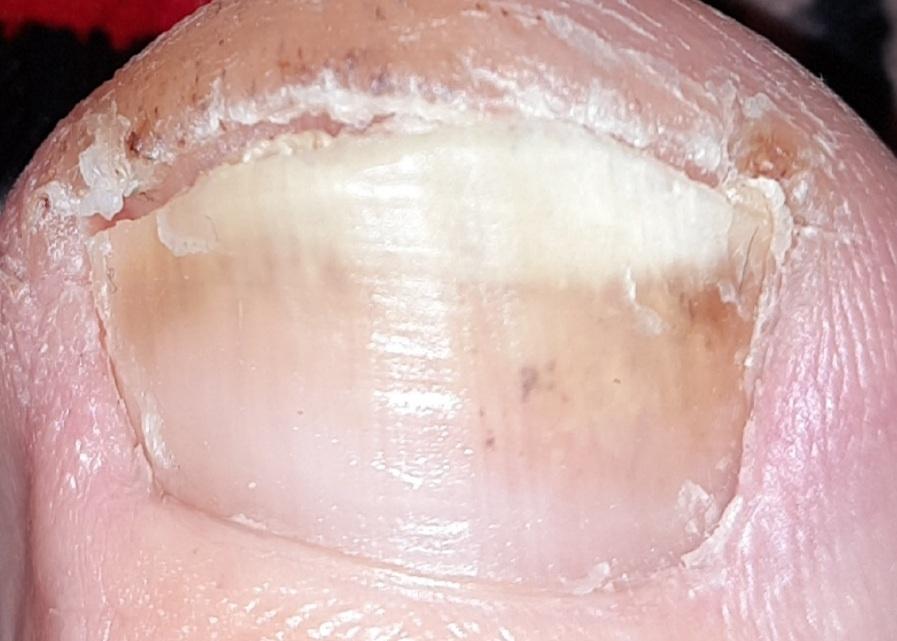
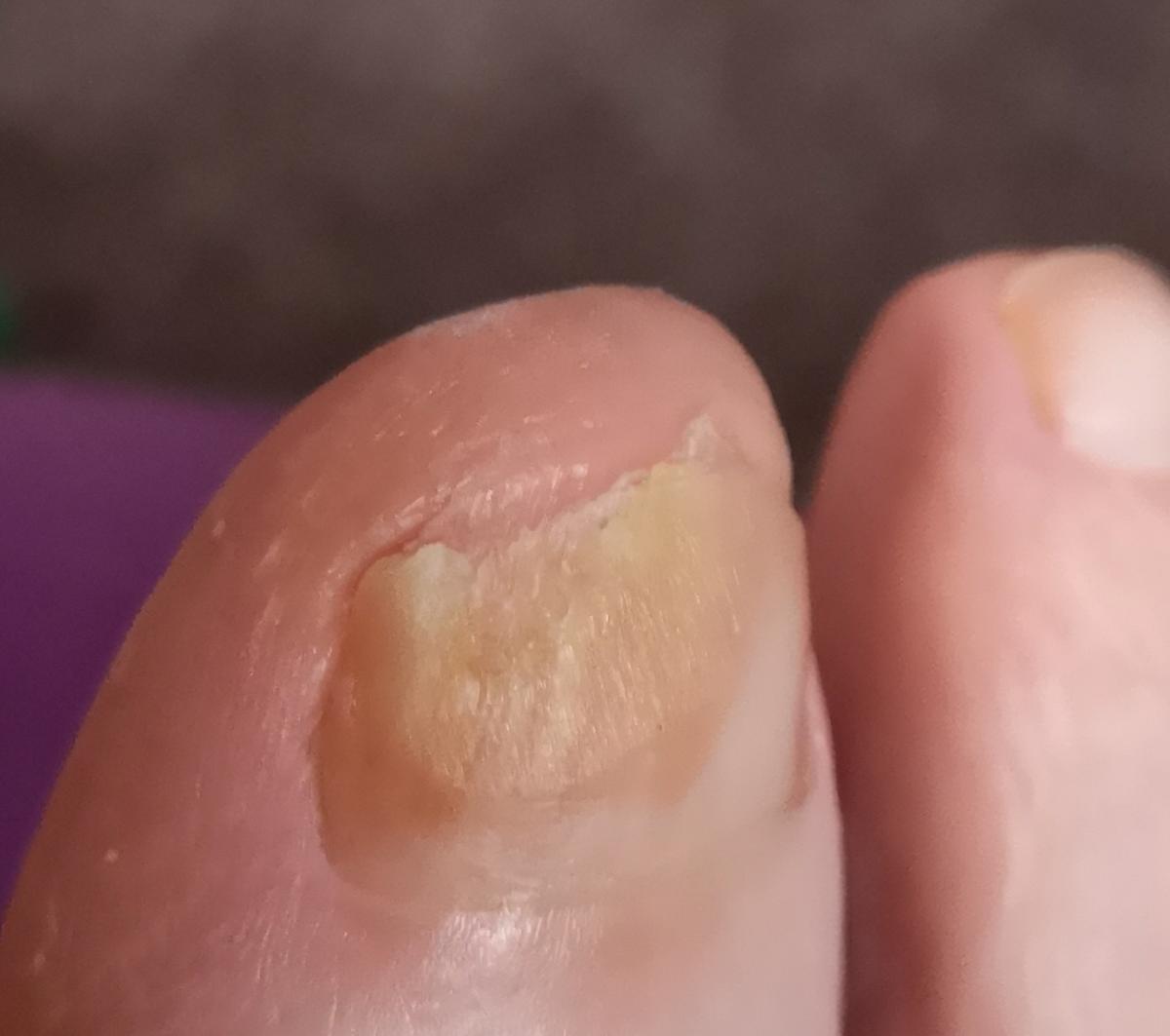
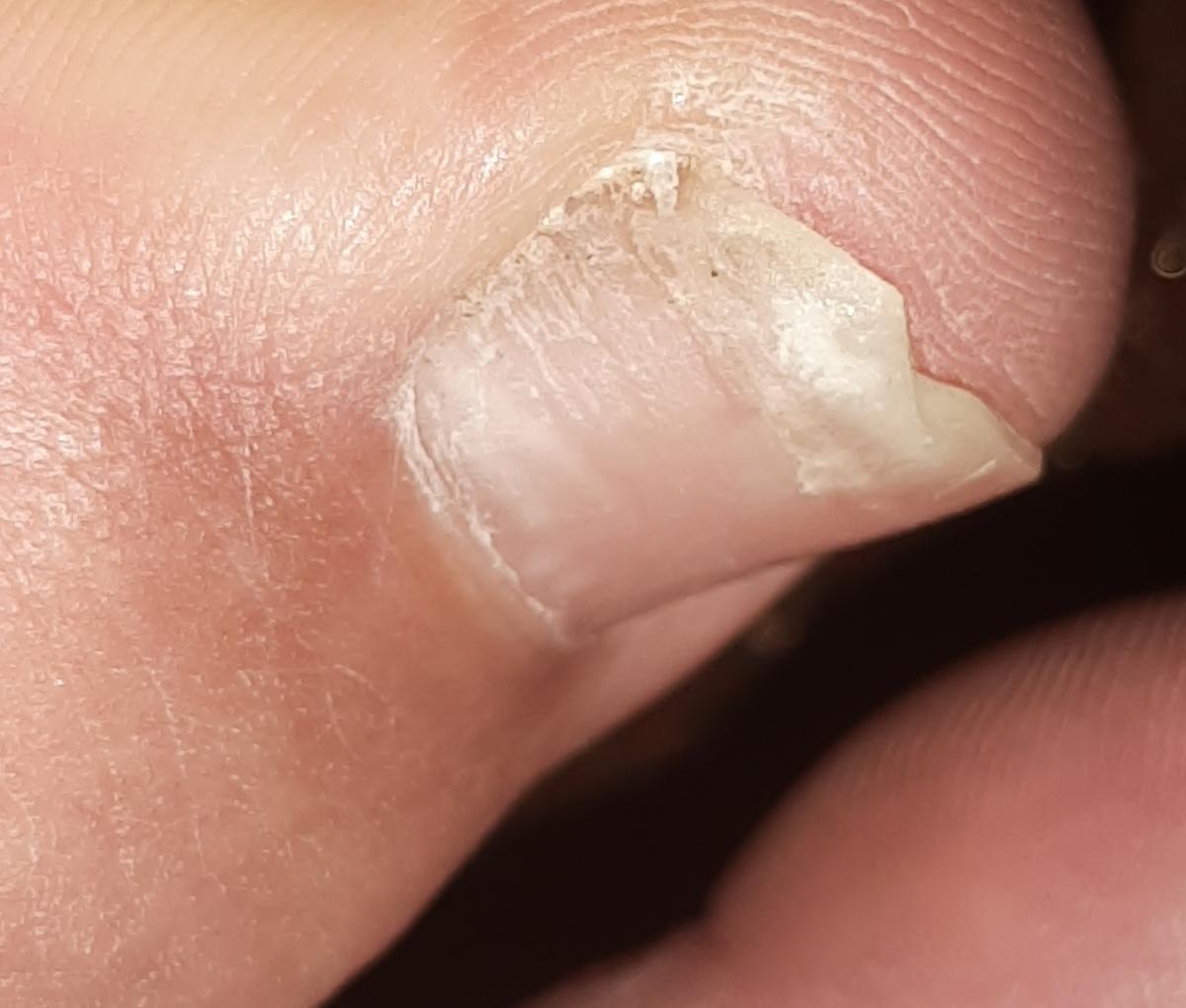
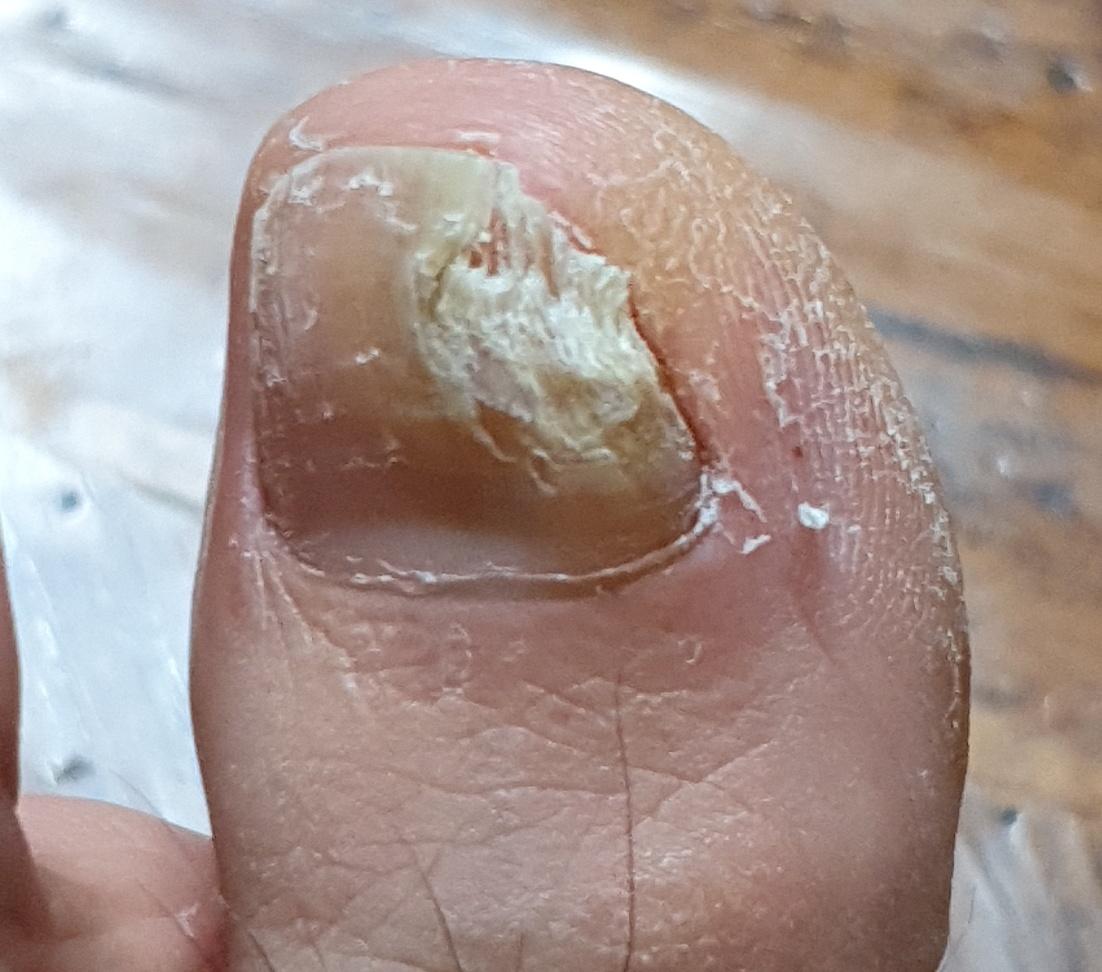
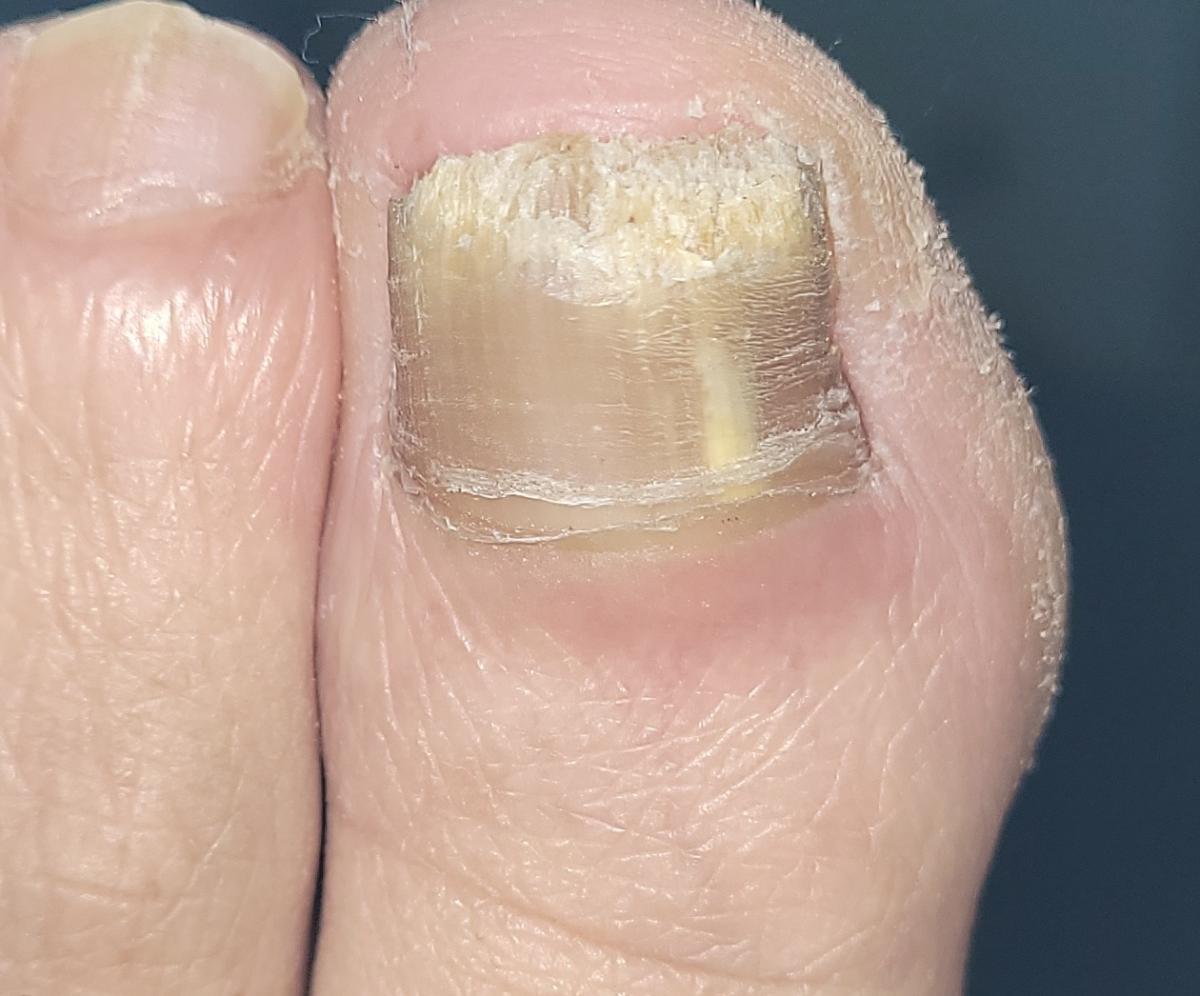
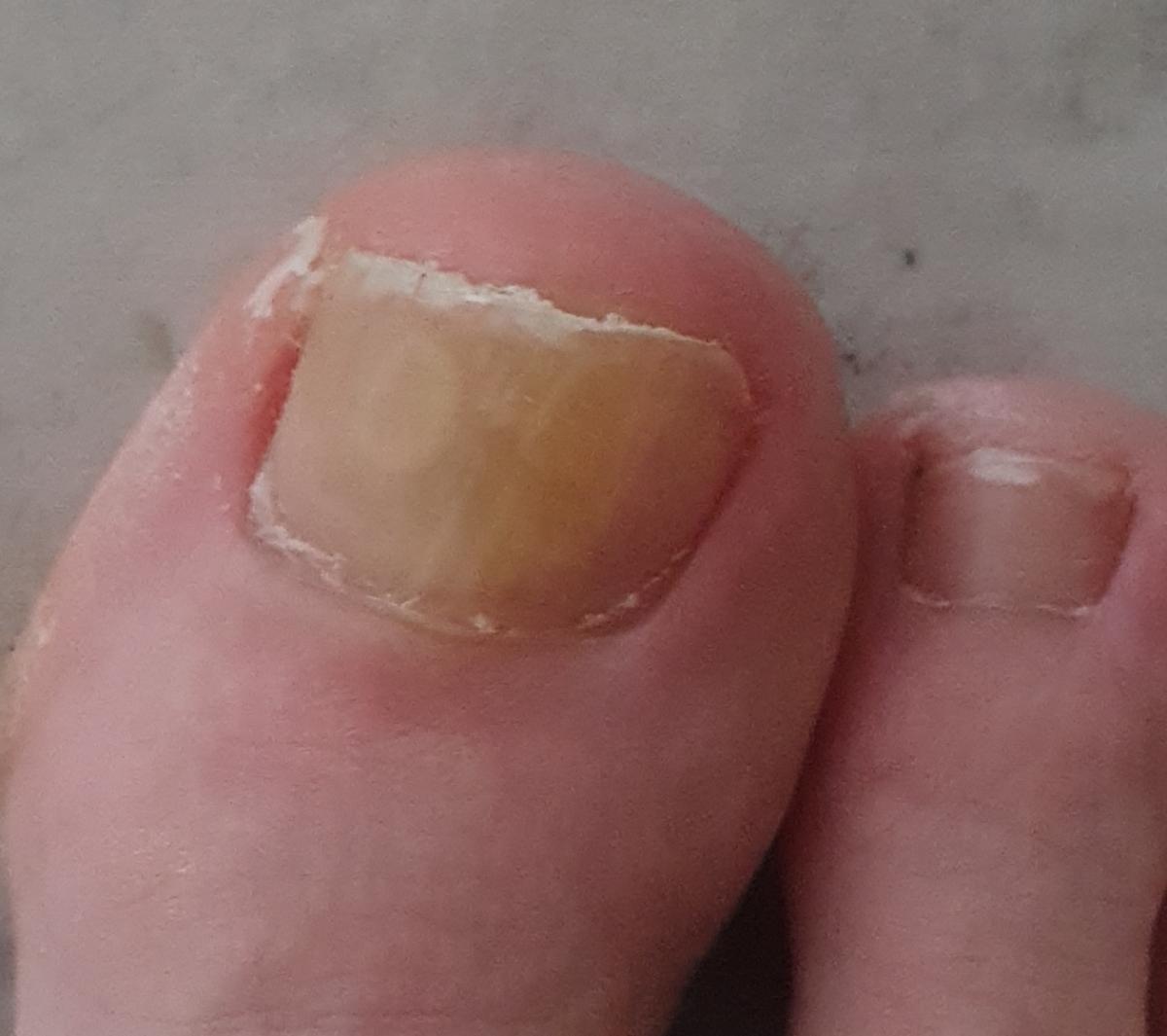
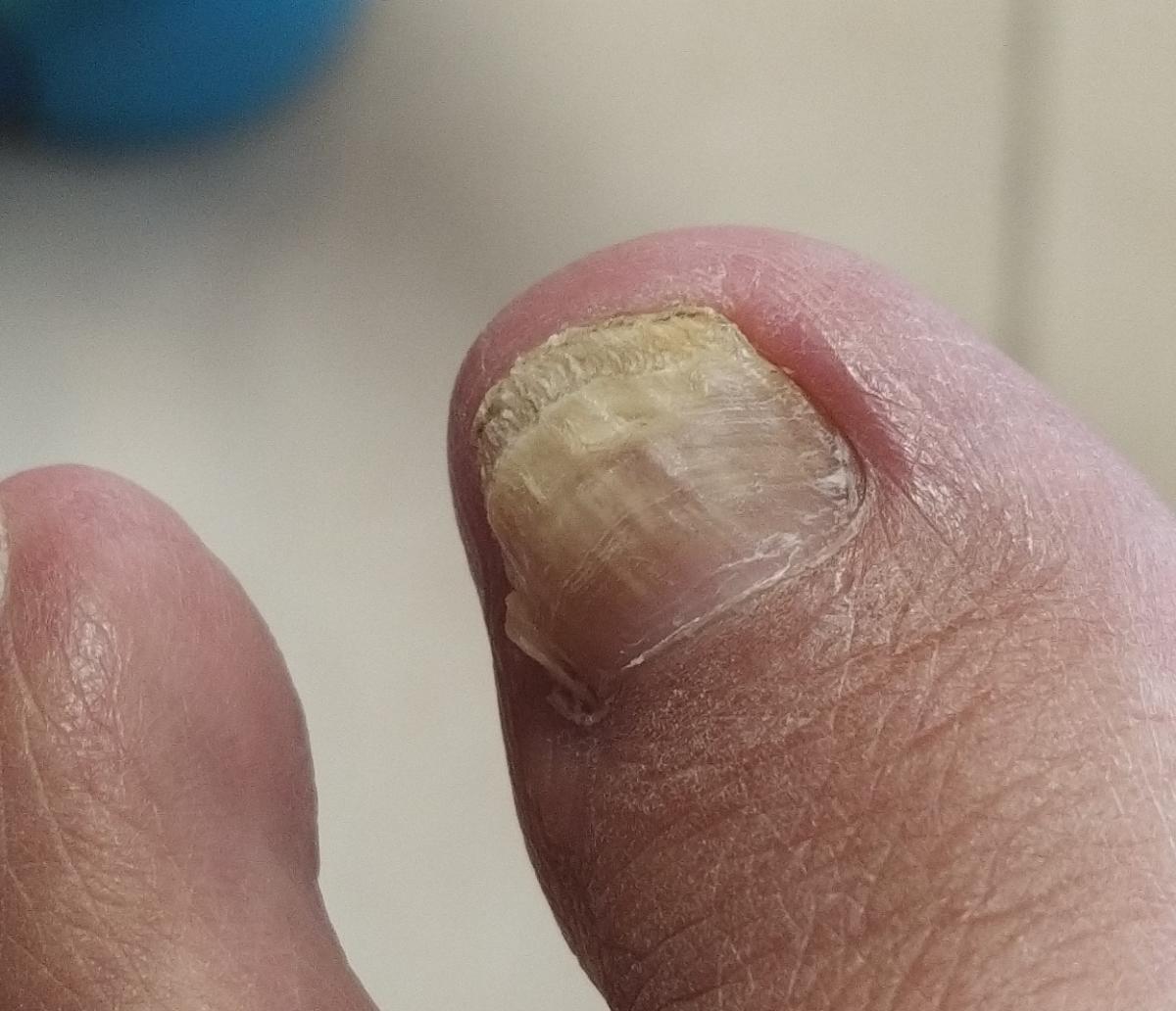
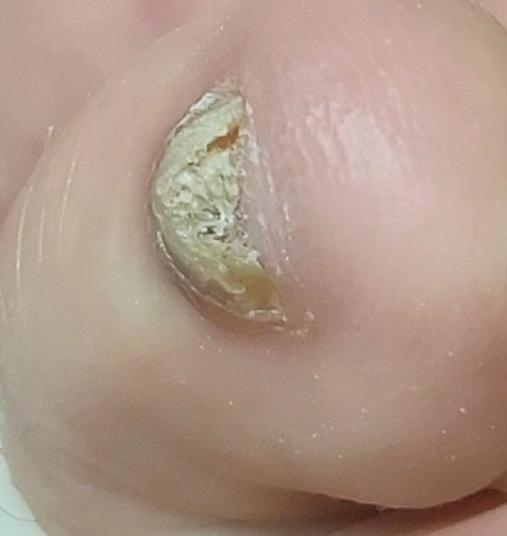
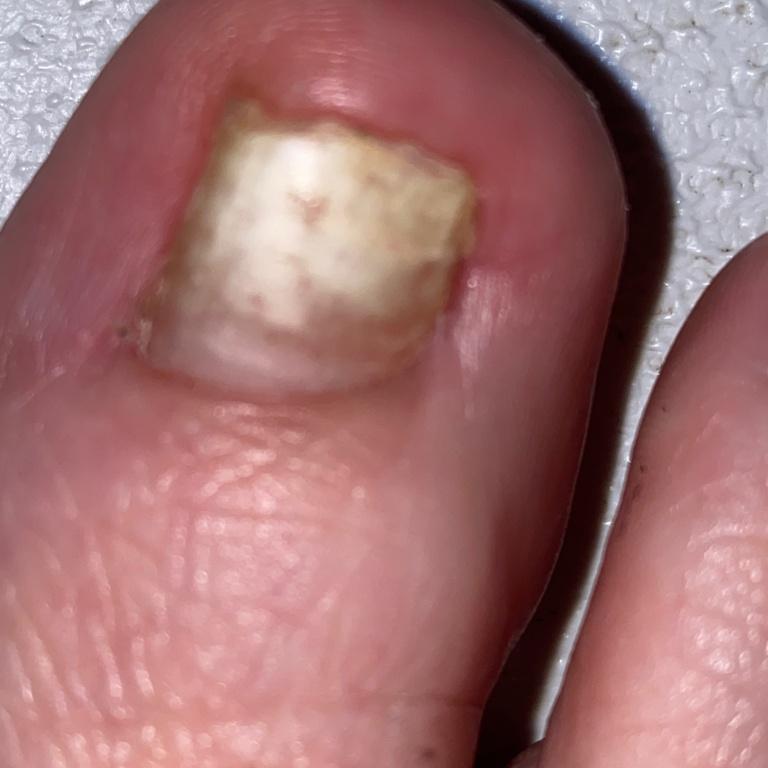
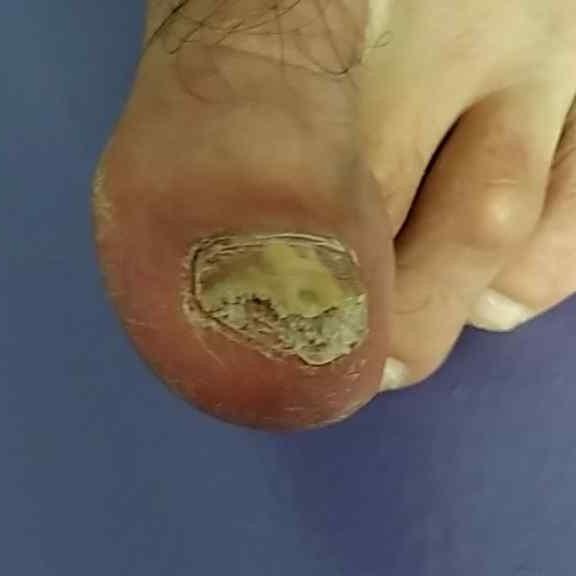
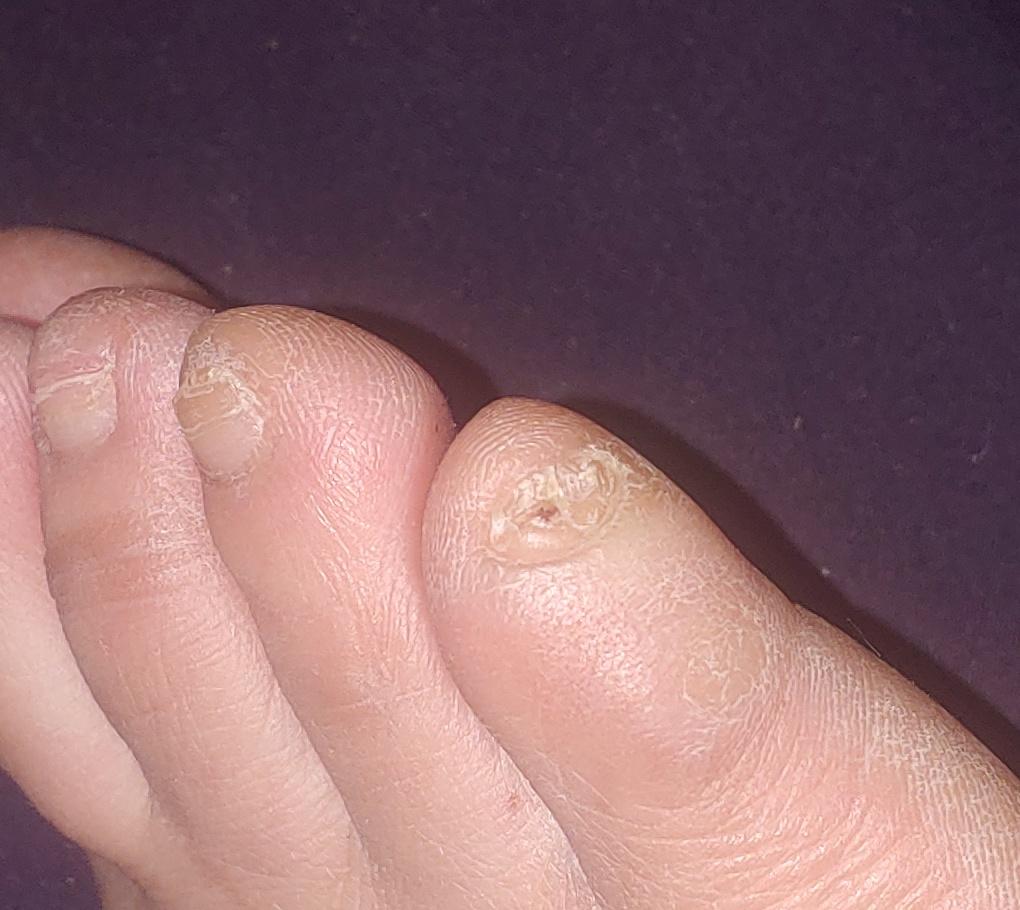
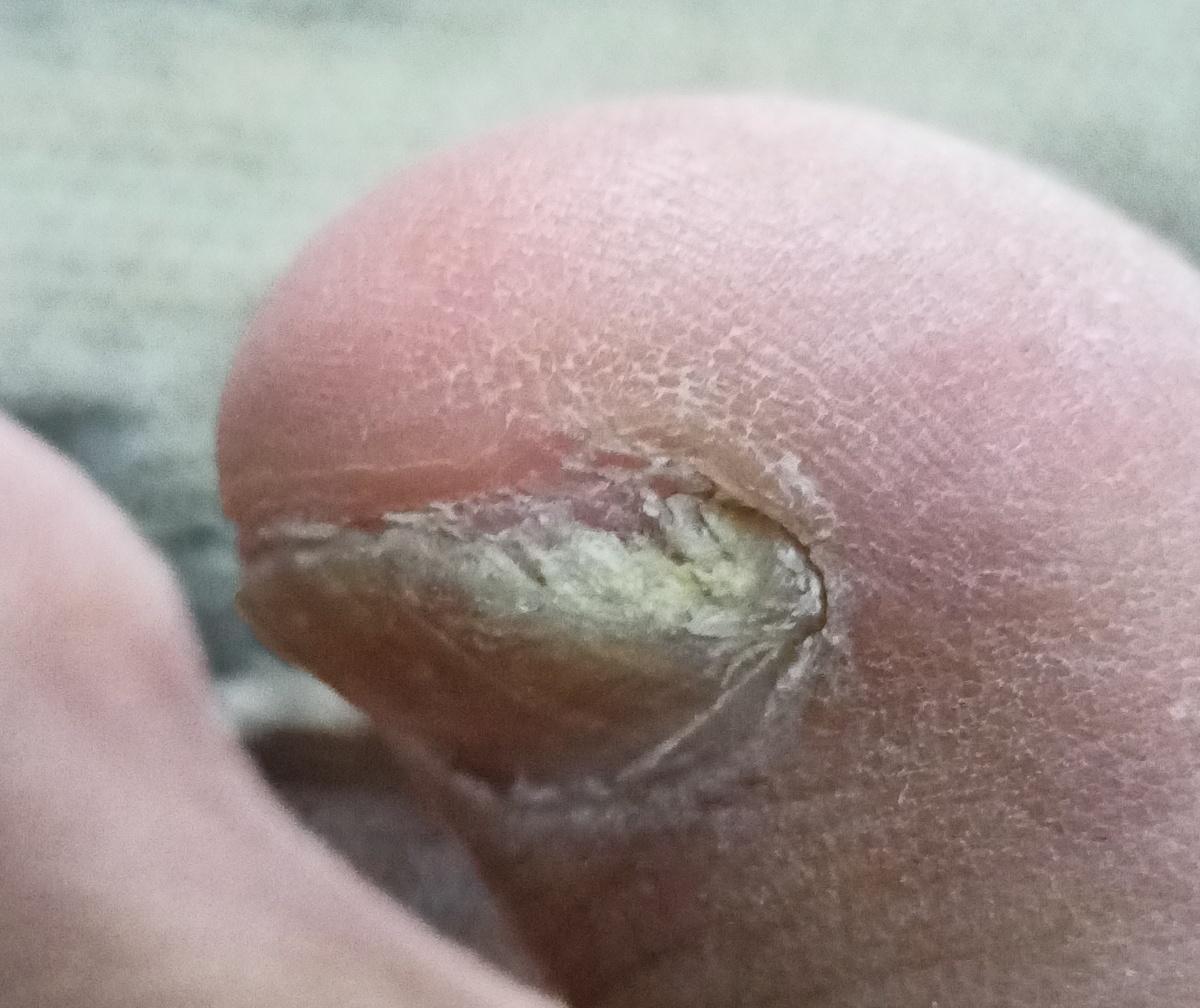
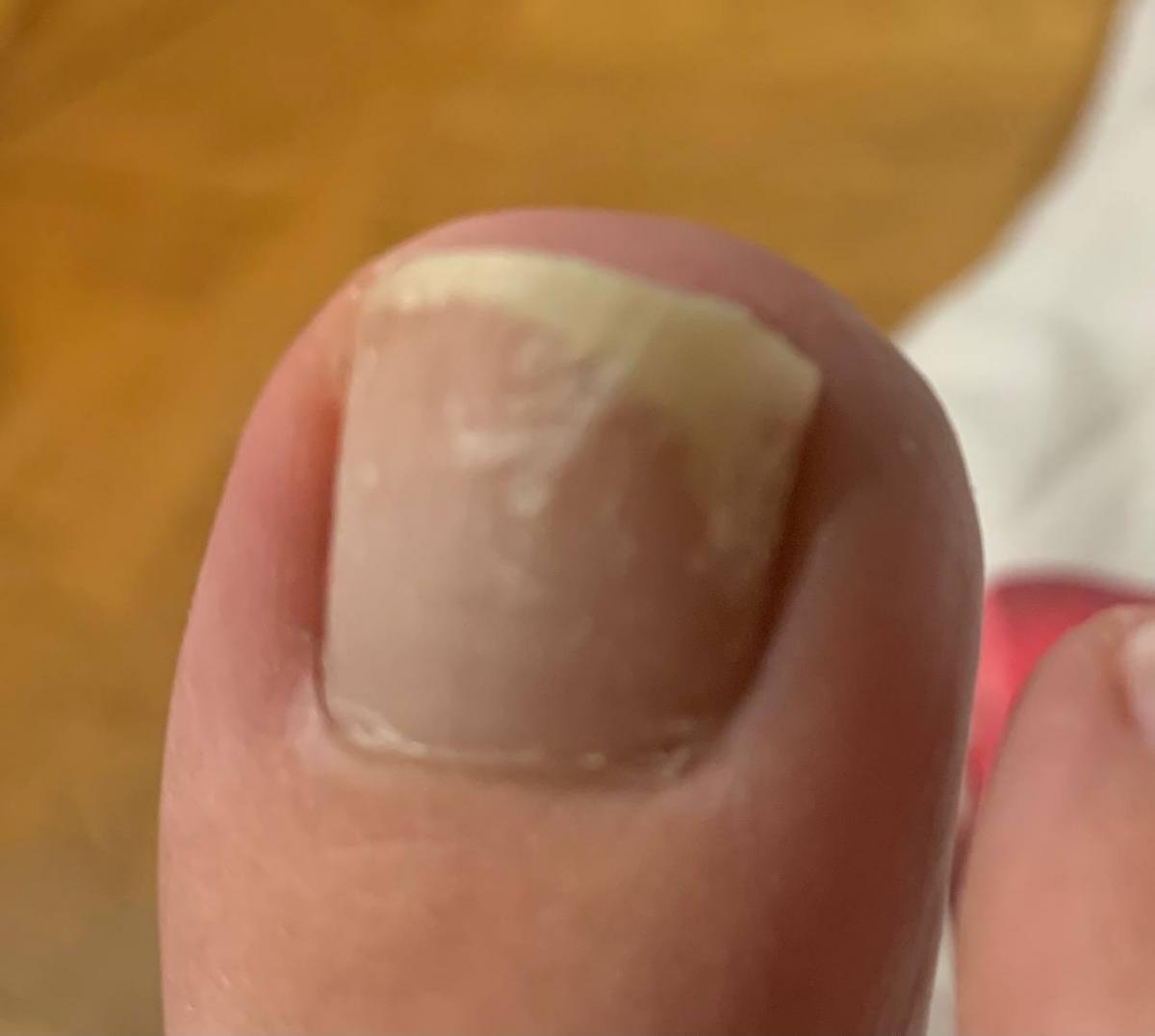
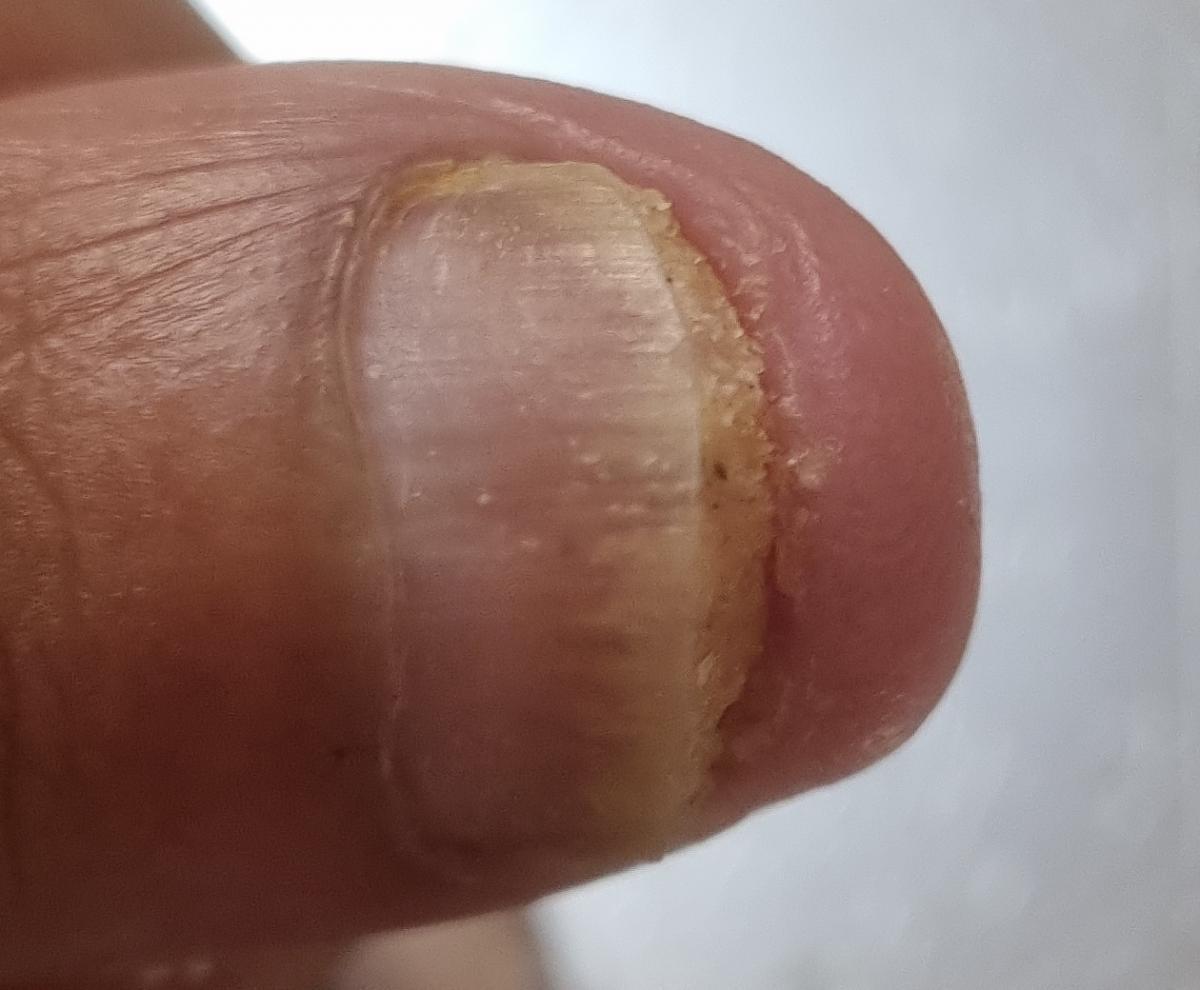
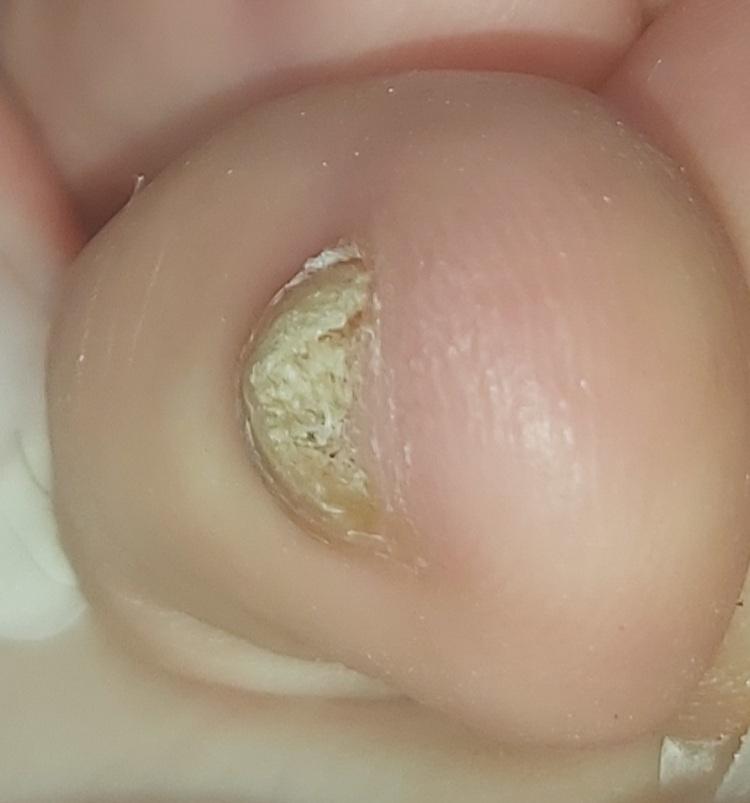
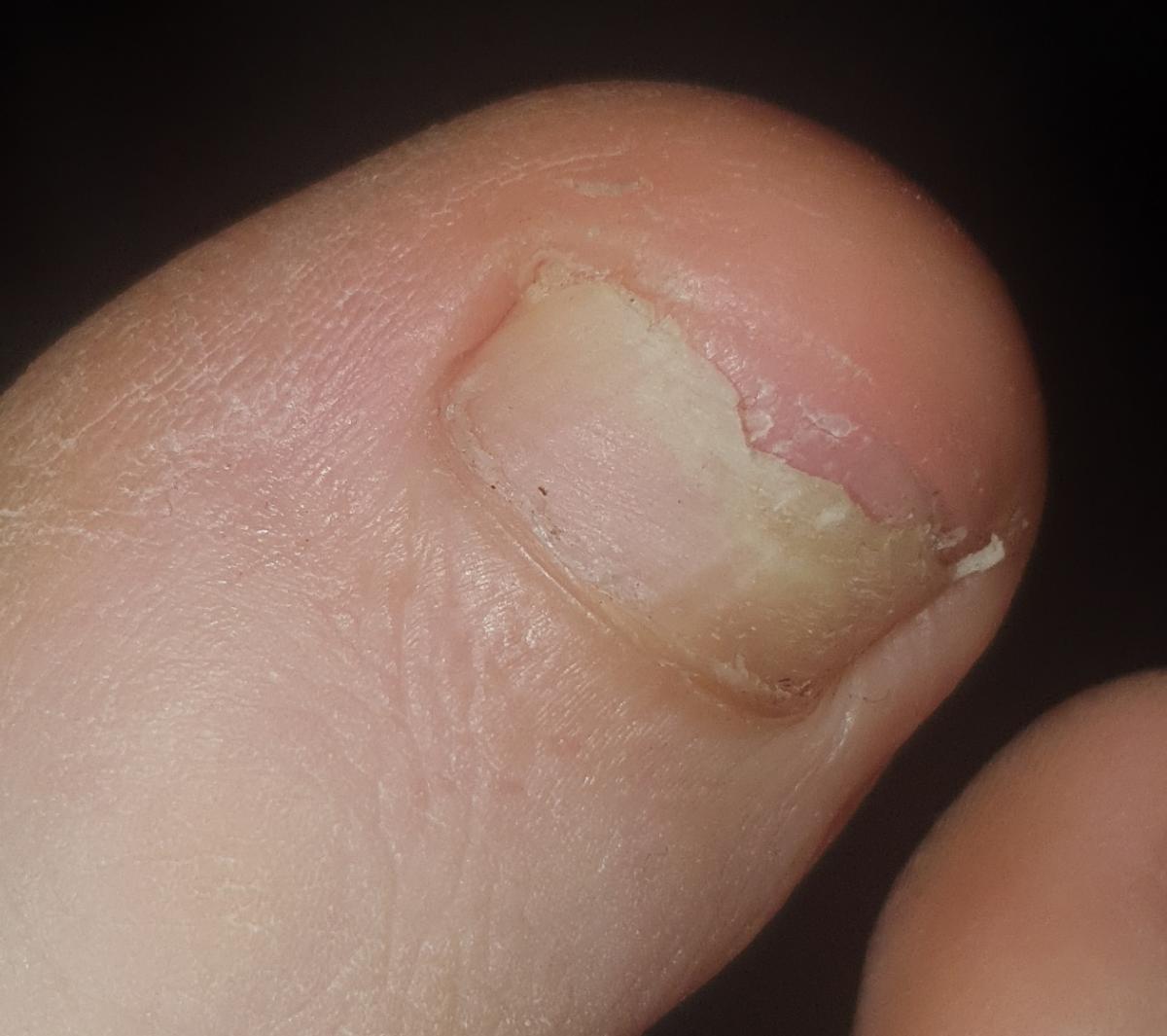
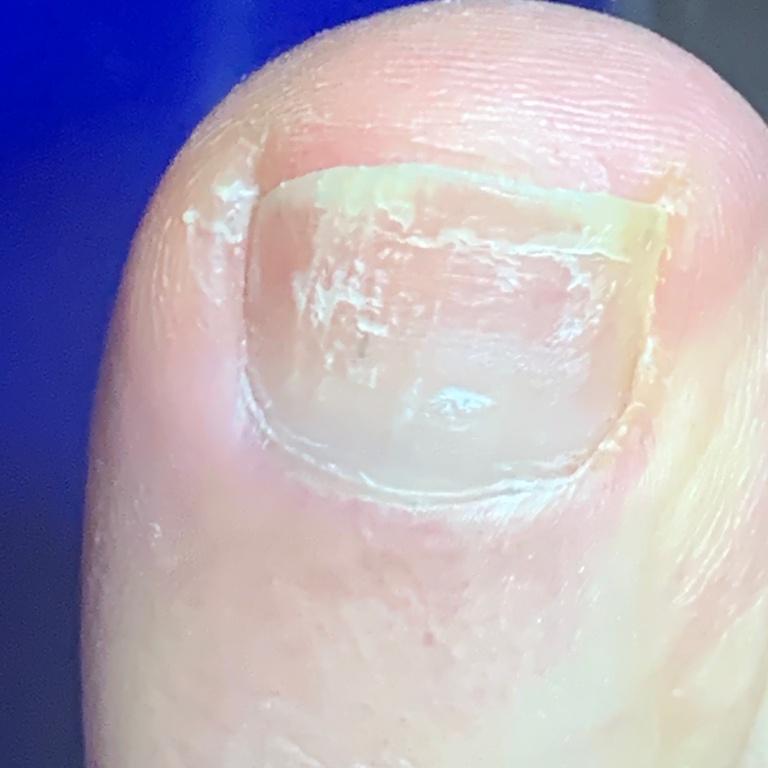
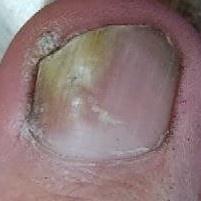
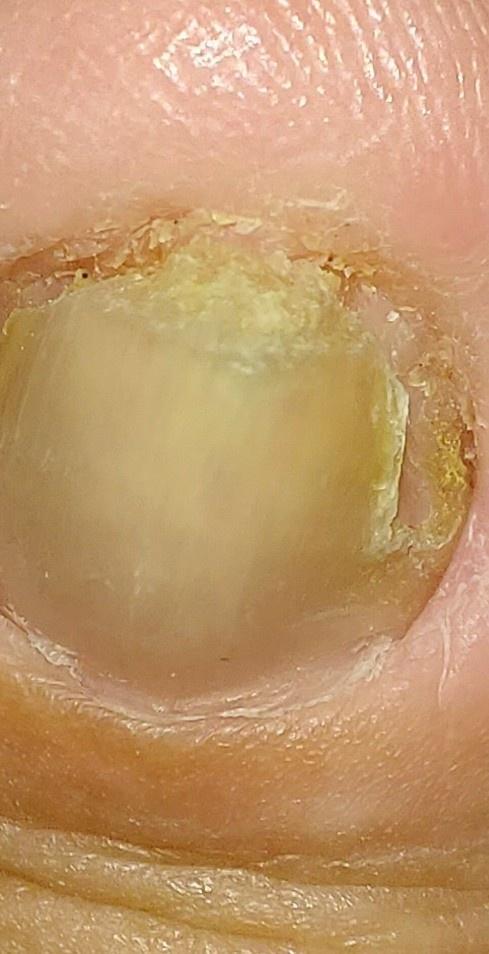
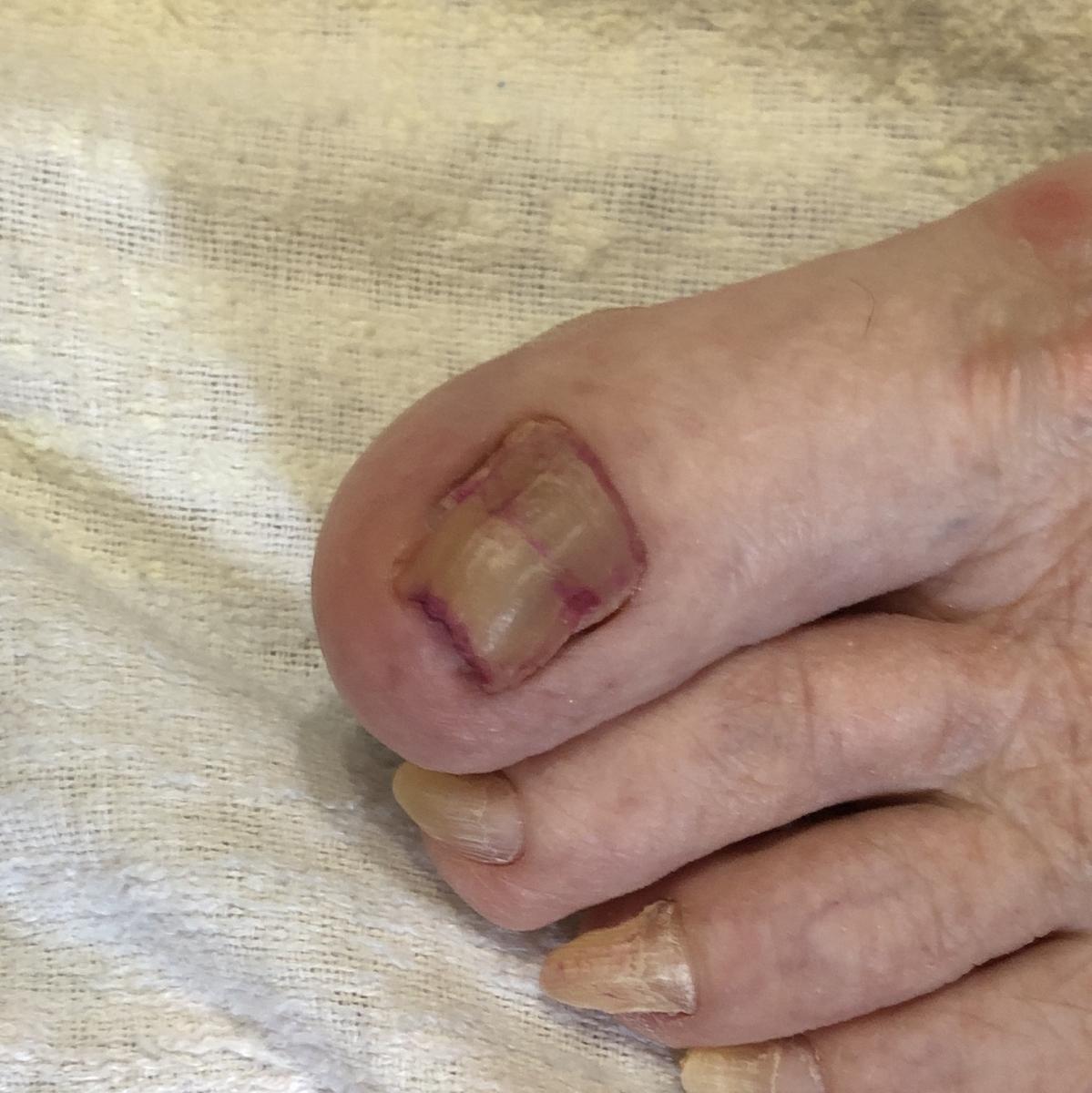
Onychomycosis refers to any nail infection caused by dermatophytes, non-dermatophytes or yeasts.
Clinical types of onychomycosis:
- Distal (lateral) subungual onychomycosis – invasion through hyponychium, affects the distal part of the nail, spreads proximally until complete defeat;
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis – invasion under the proximal nail fold with damage to the proximal part of the nail plate;
- White superficial onychomycosis – direct invasion of the nail plate: causes the appearance of white or dull yellow sharply bordered spots on the surface of the nail.
Clinical types of nail lesions, depending on the degree of thickening of the nail plate:
- Normotrophic: there is only a yellow or white discoloration of the nail plate;
- Hypertrophic: thickening and formation of ridges on the nail plate, hypertrophy of the underlying tissues (nail bed);
- Atrophic: thinning and detachment of the nail plate.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis:
- Thorough clinical examination;
- Wood’s lamp examination;
- Laboratory diagnostics: microscopy, culture method, PCR.
Various complex systemic and local antifungal agents are used to treat onychomycosis. Systemic treatment is required in all cases where there is a lesion of the scalp, beard and nails. With limited skin lesions without affecting the appendages of the skin, external monotherapy can be used.