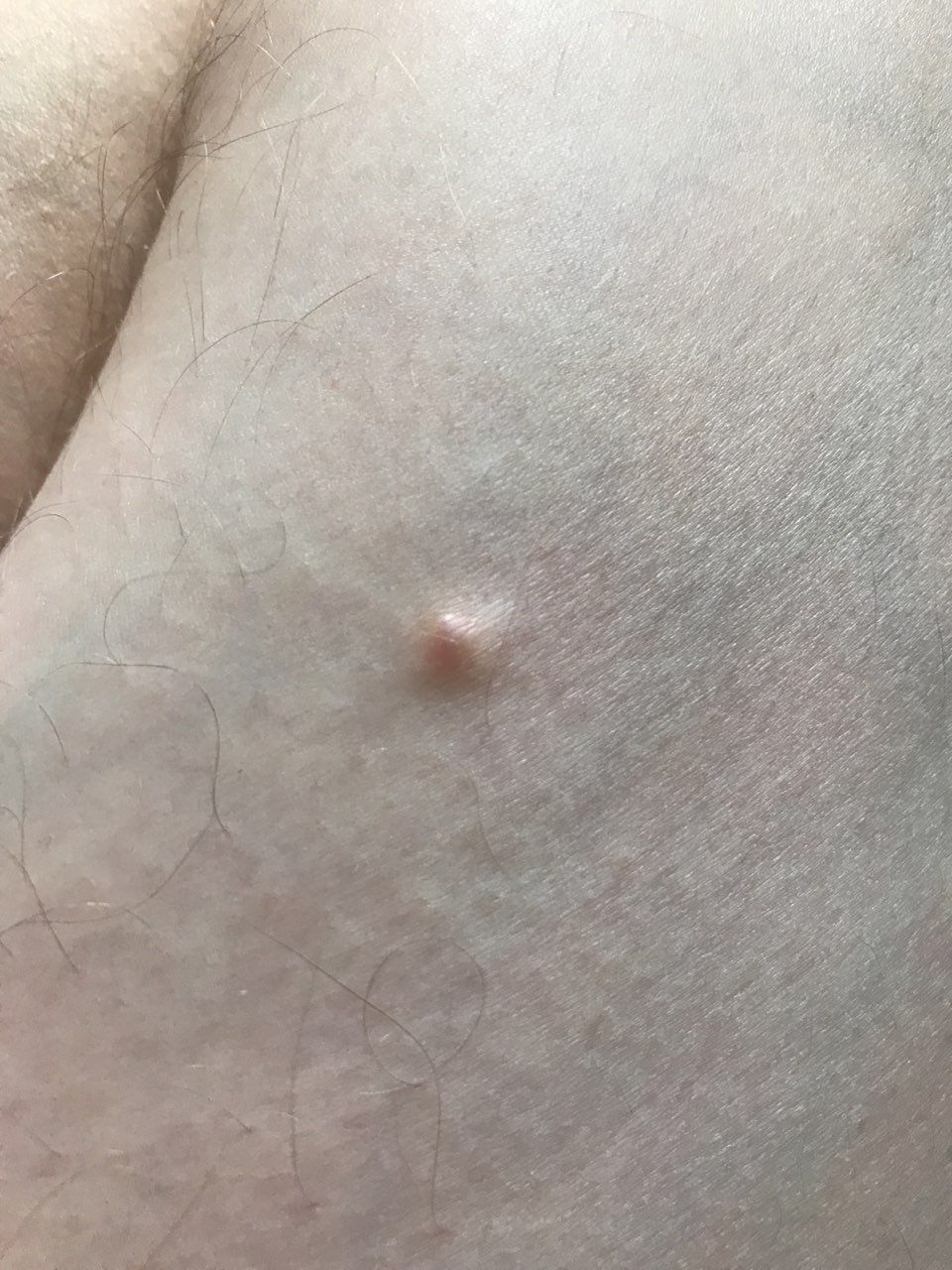
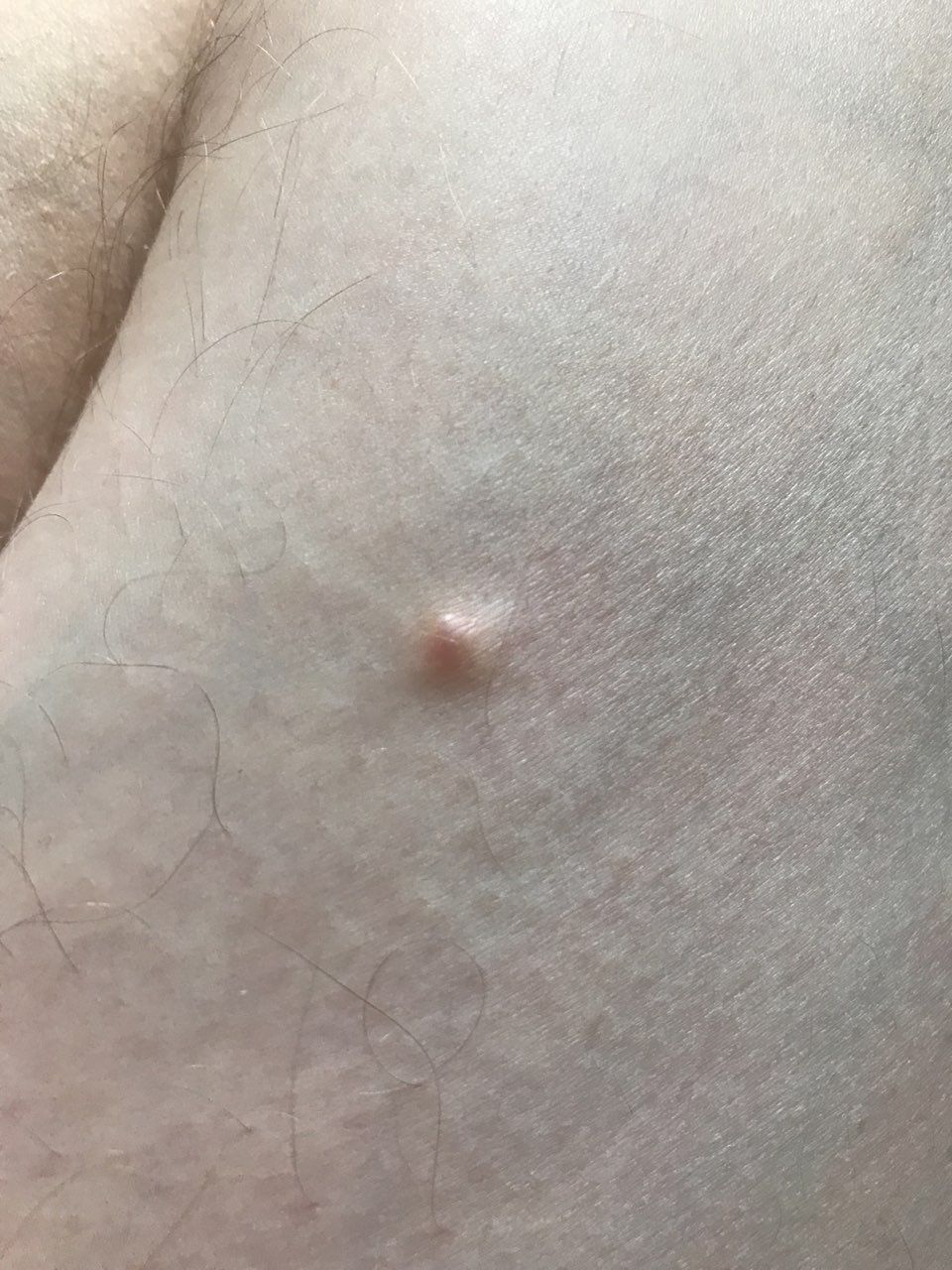
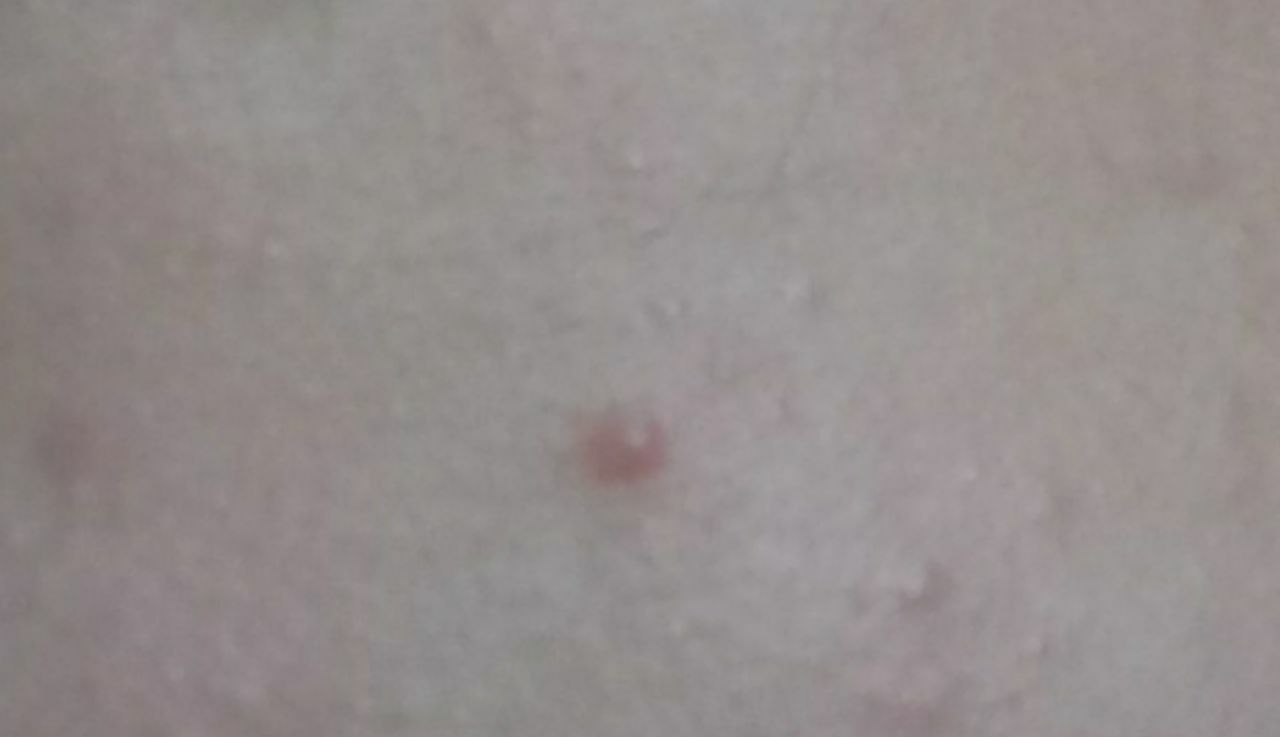
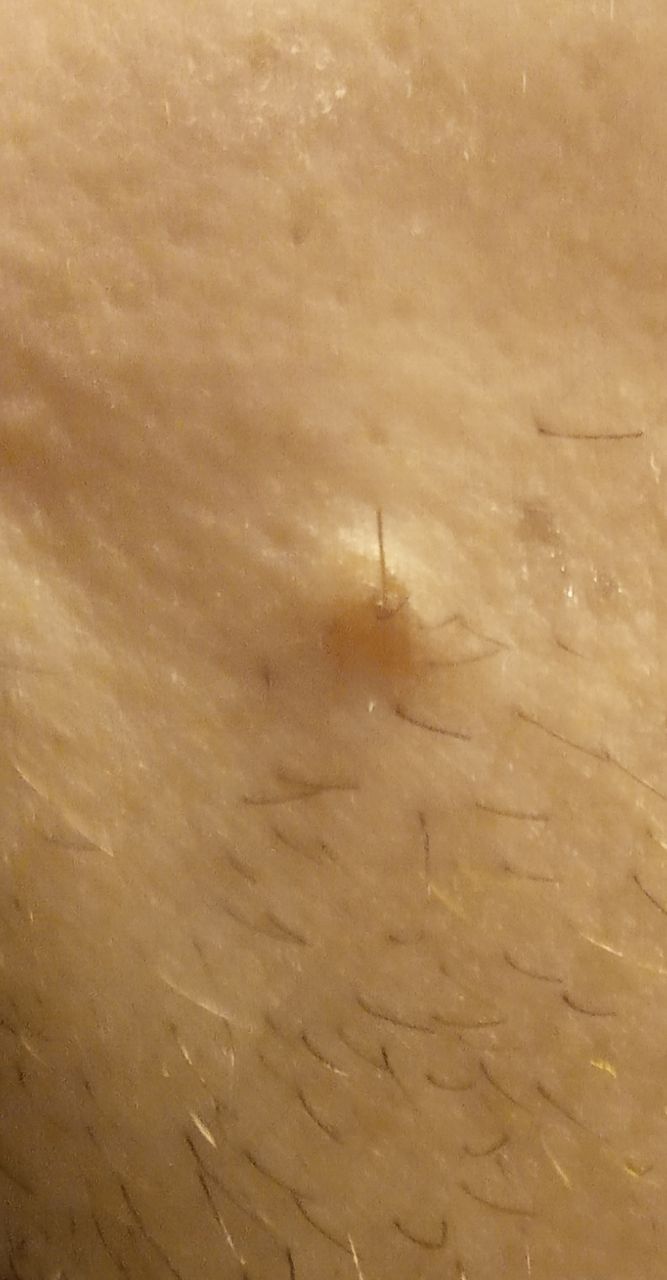
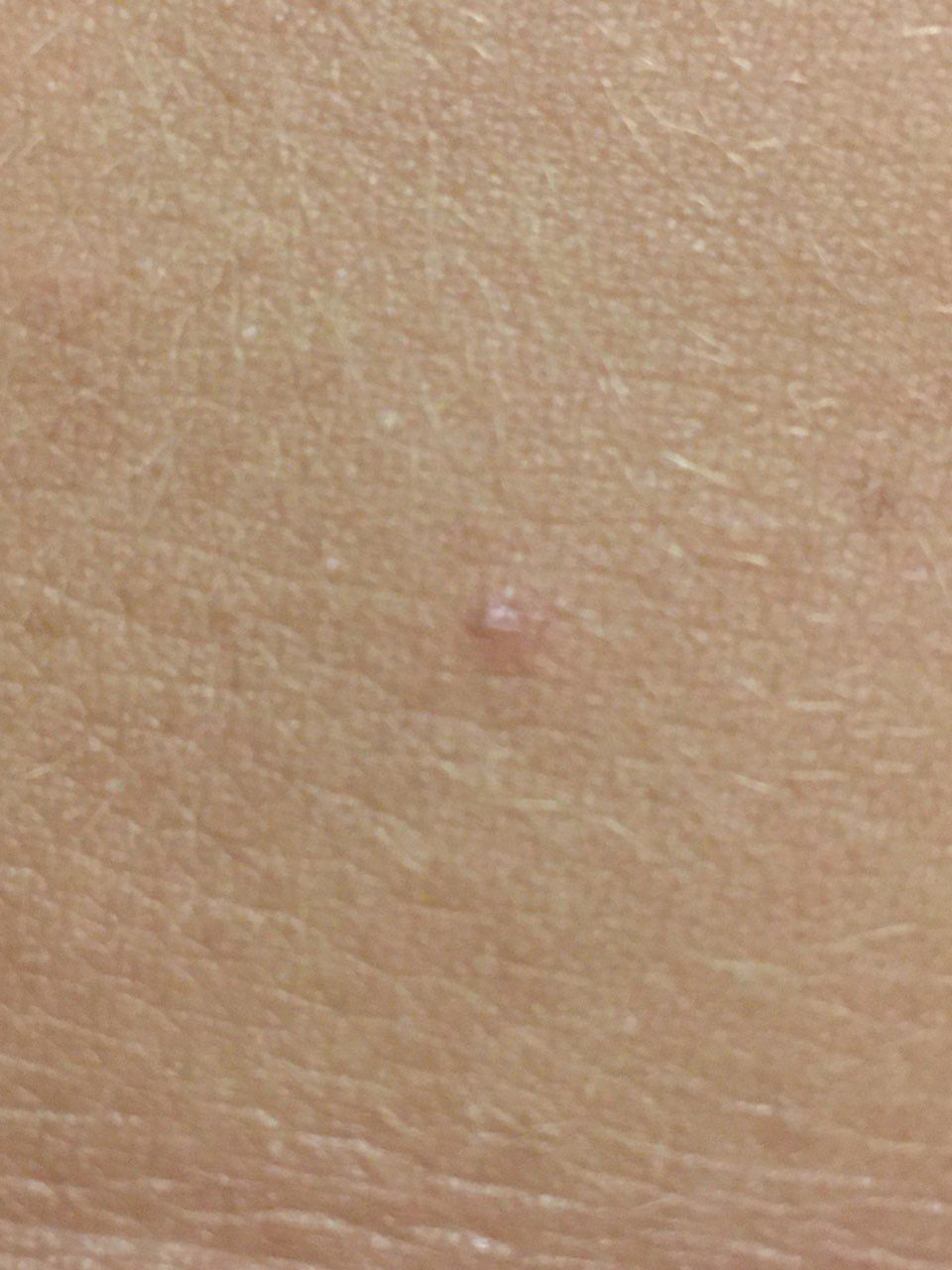
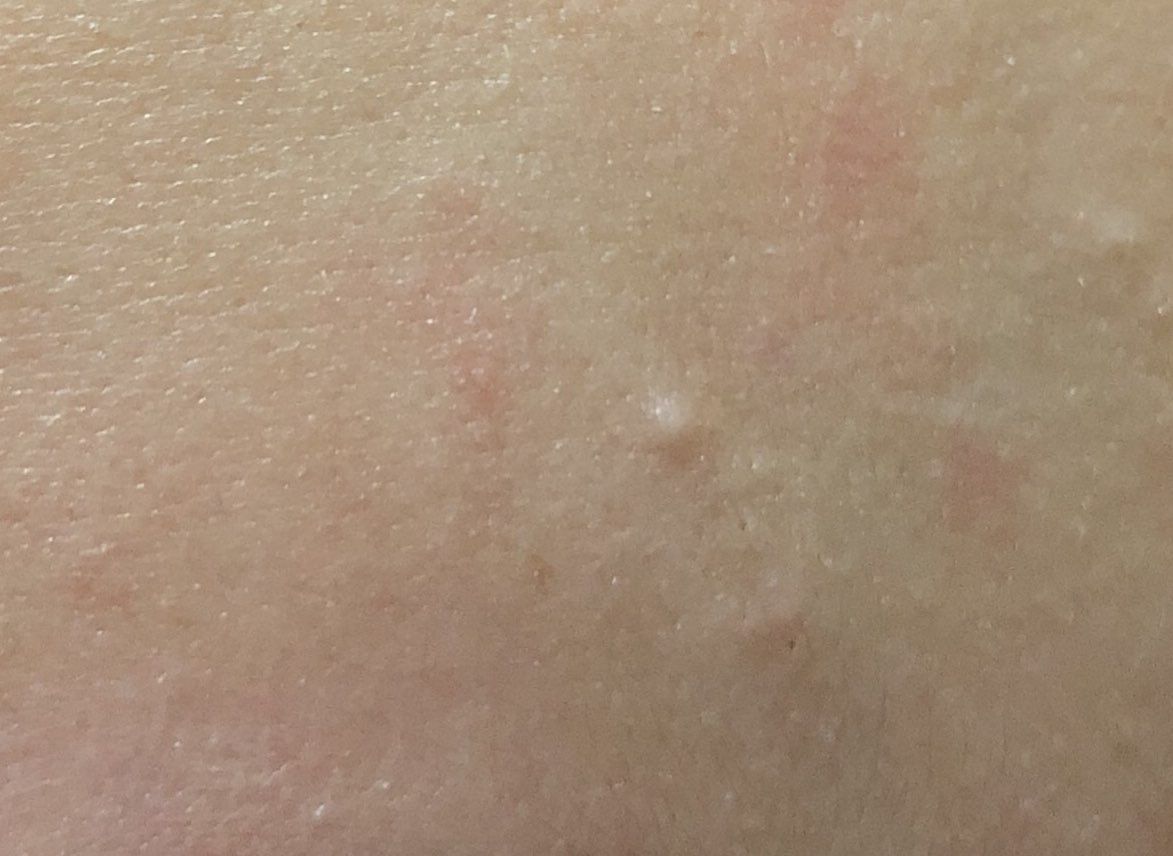
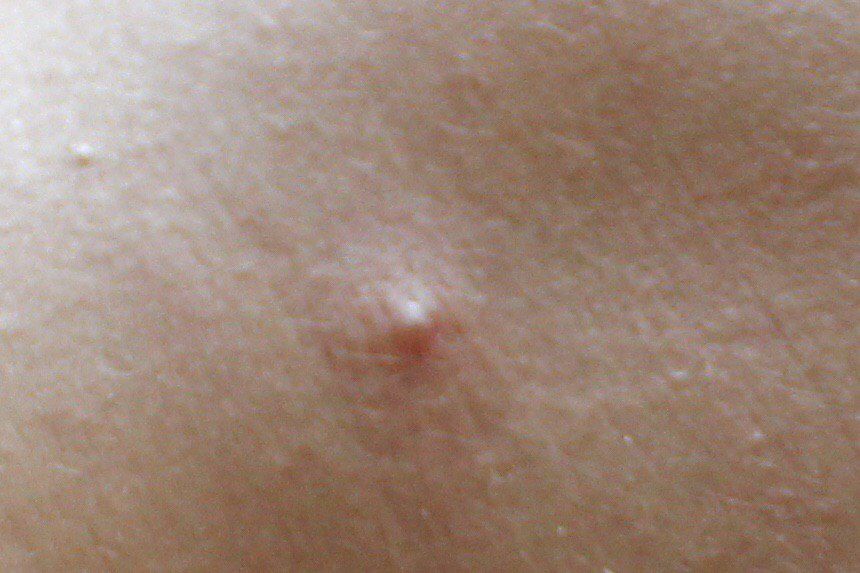
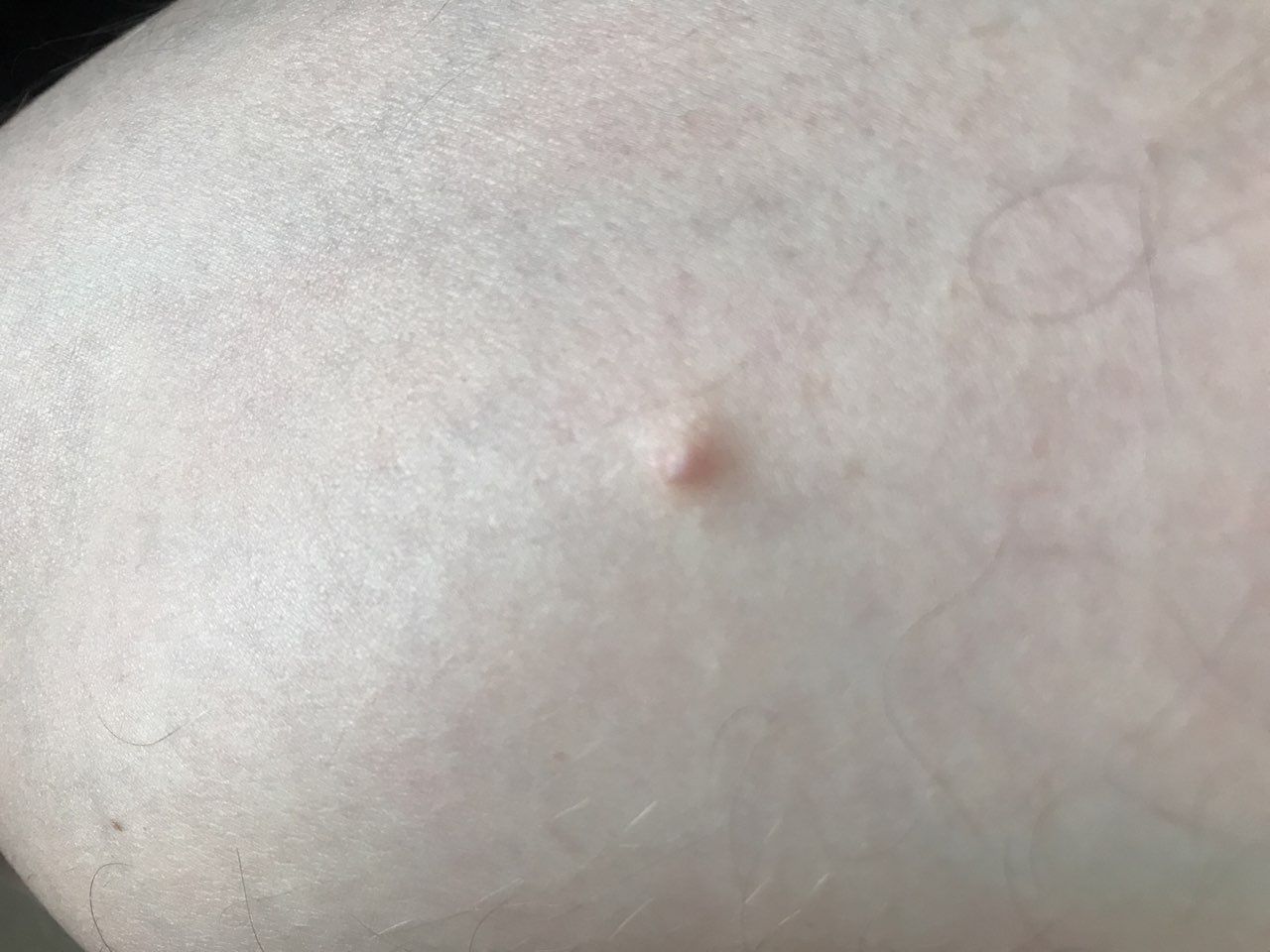
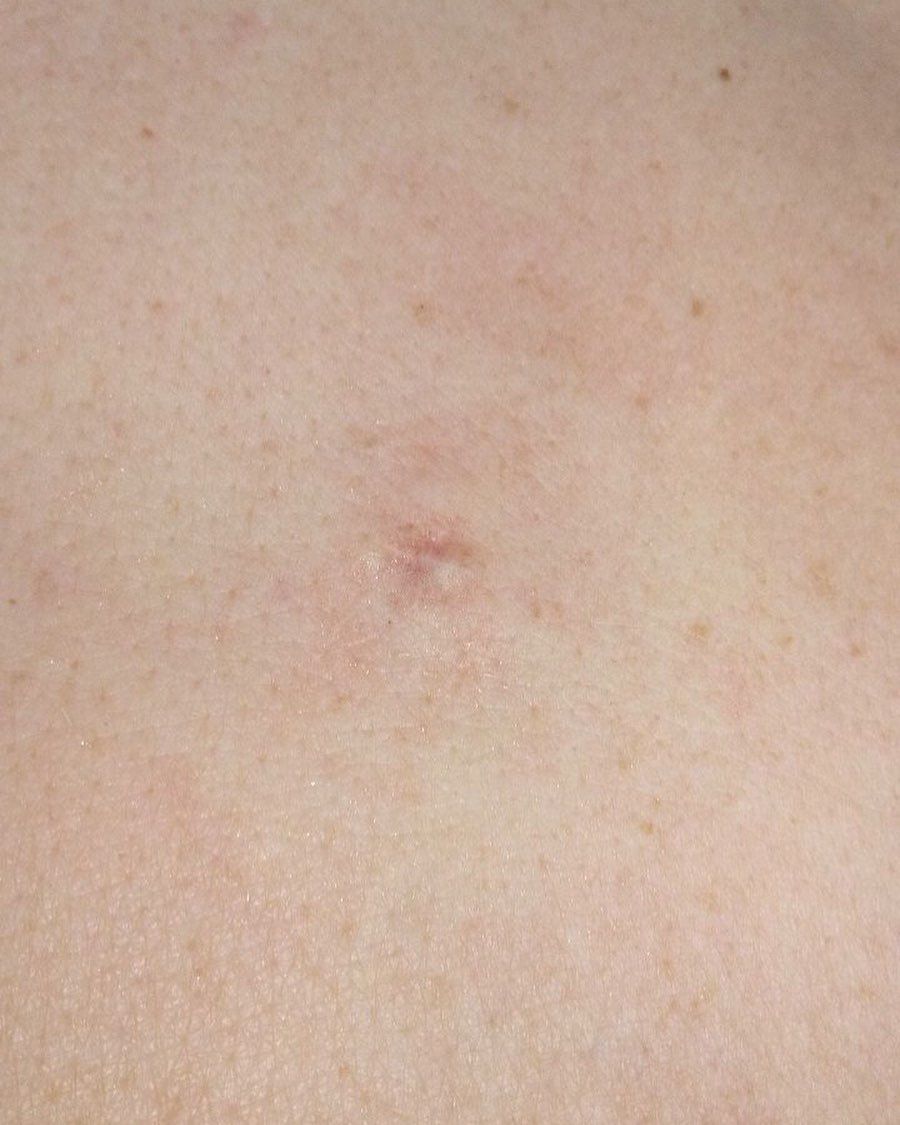
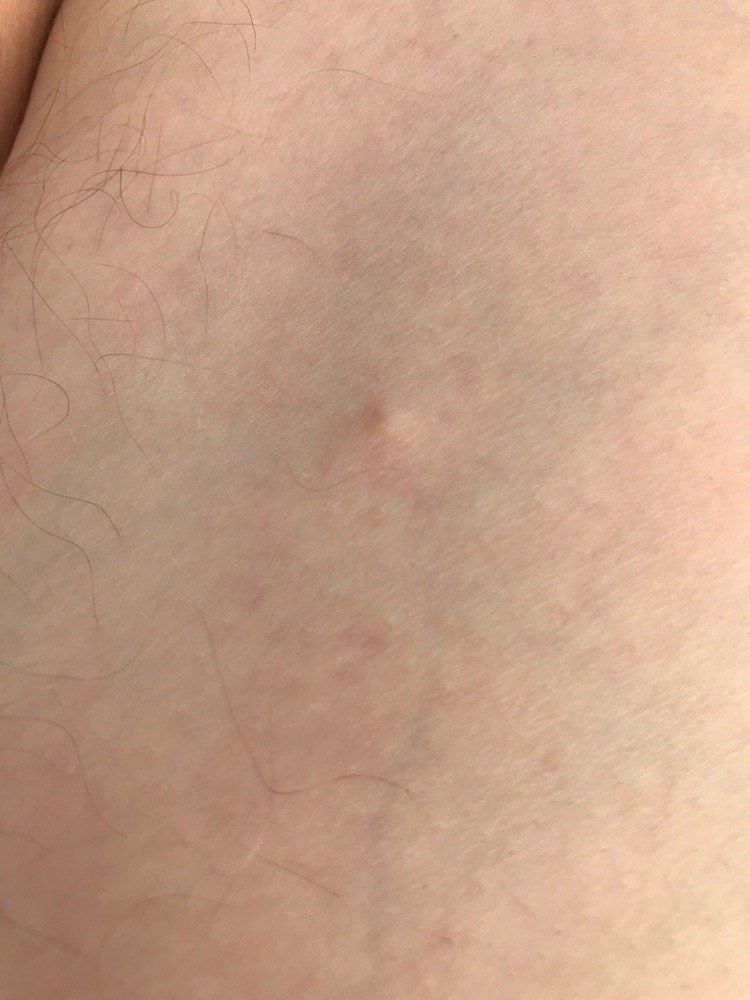
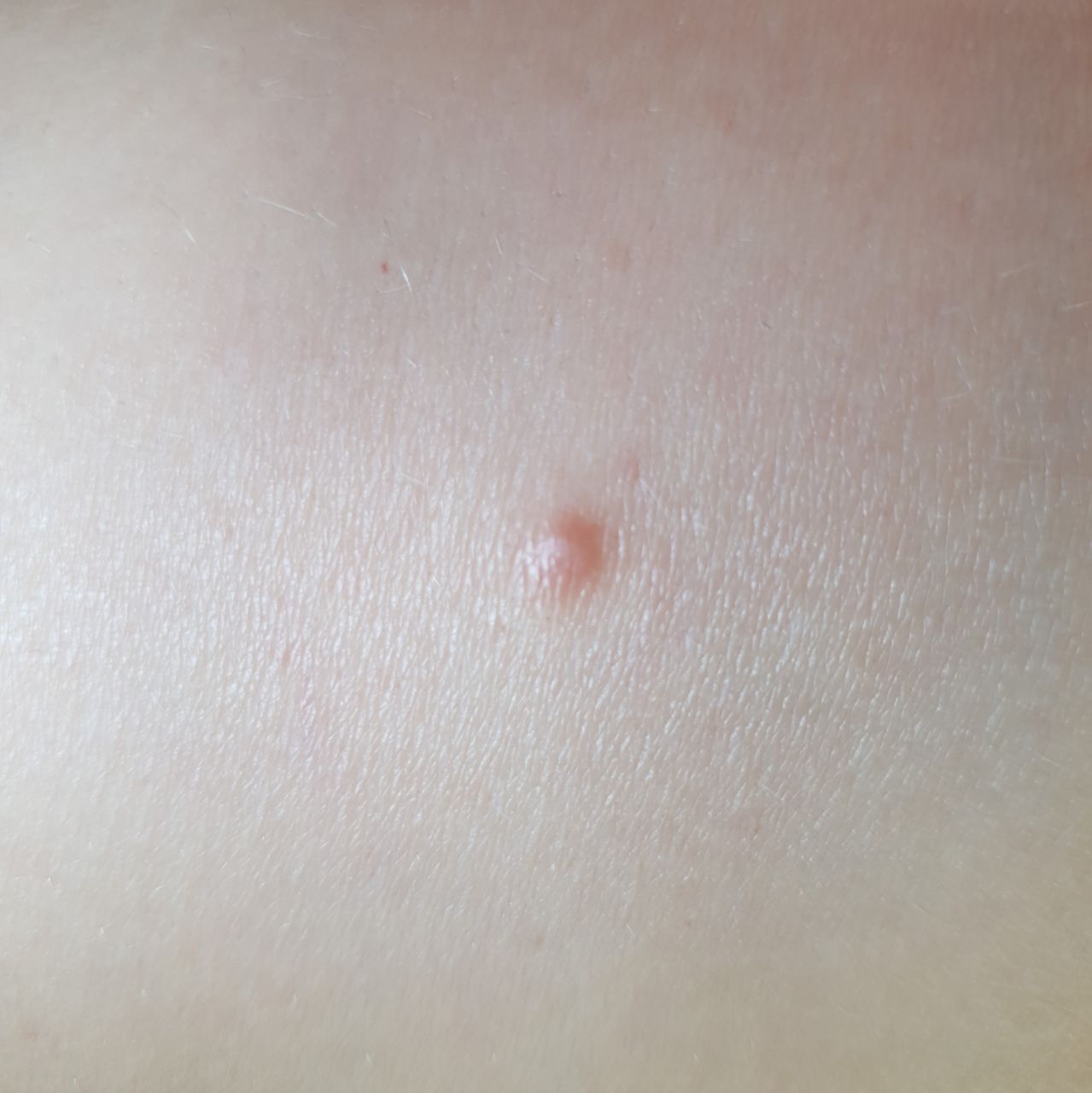
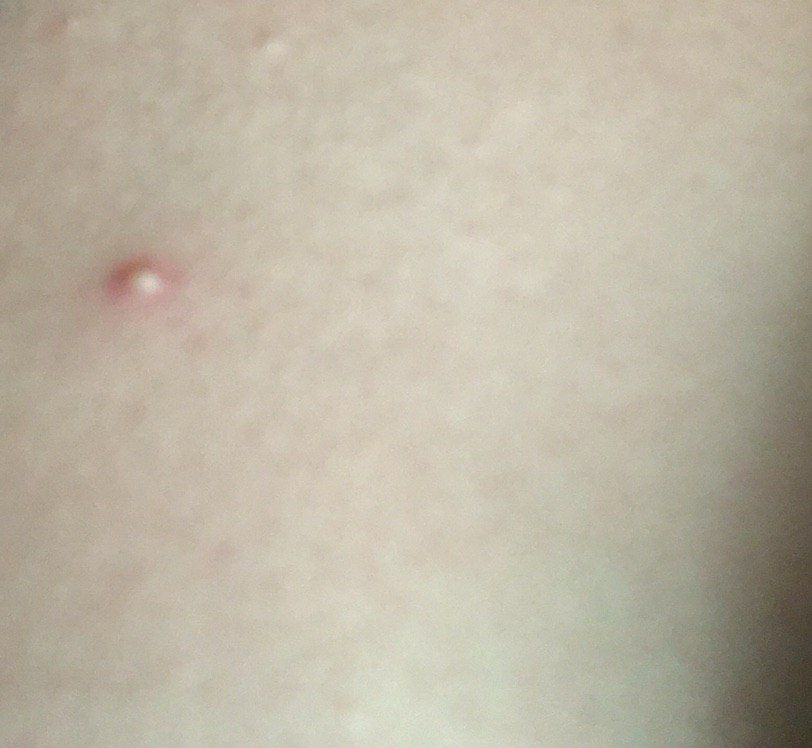
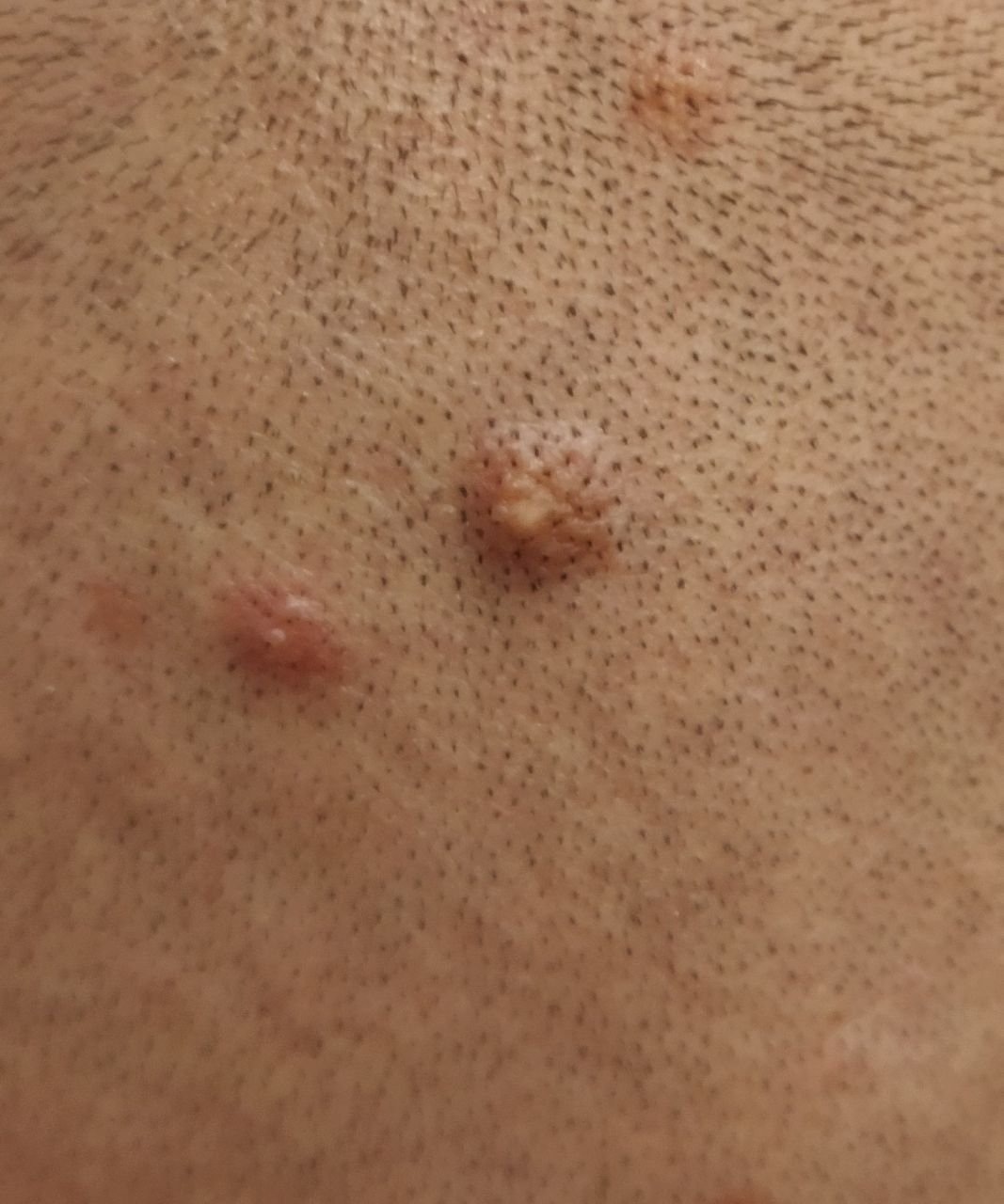
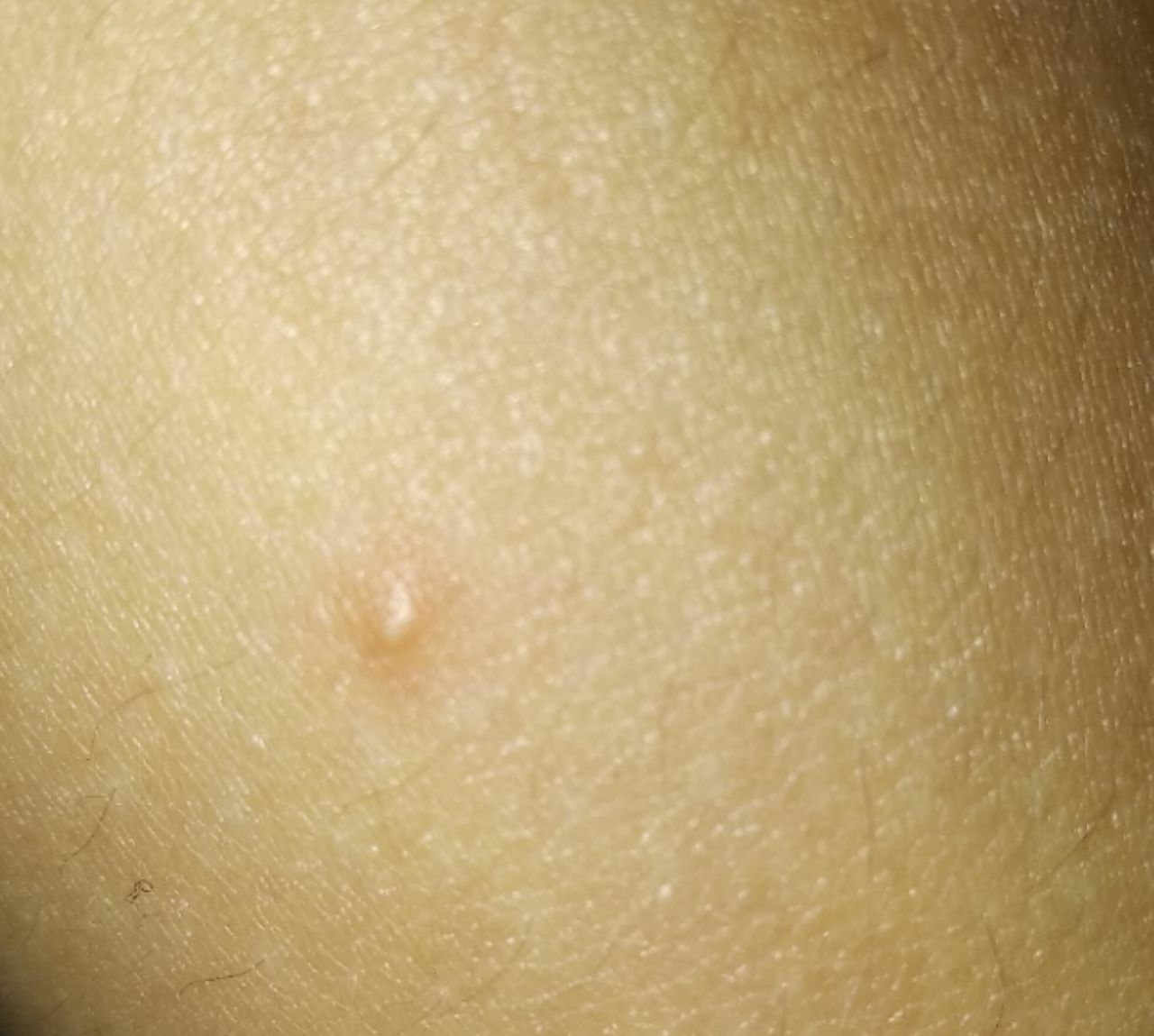
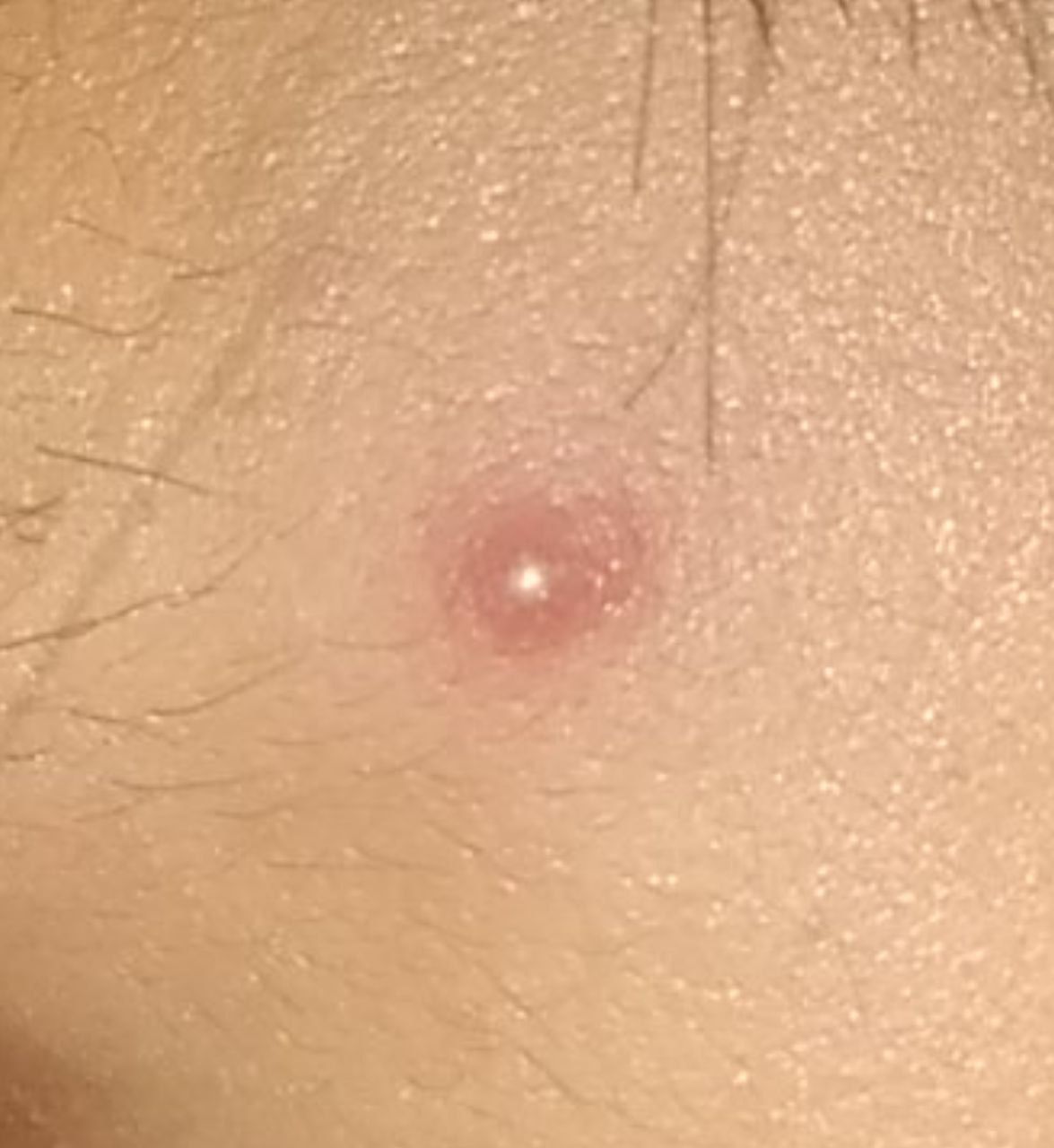
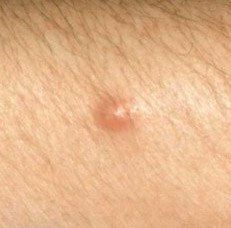
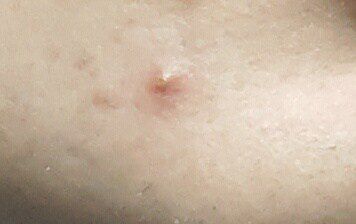
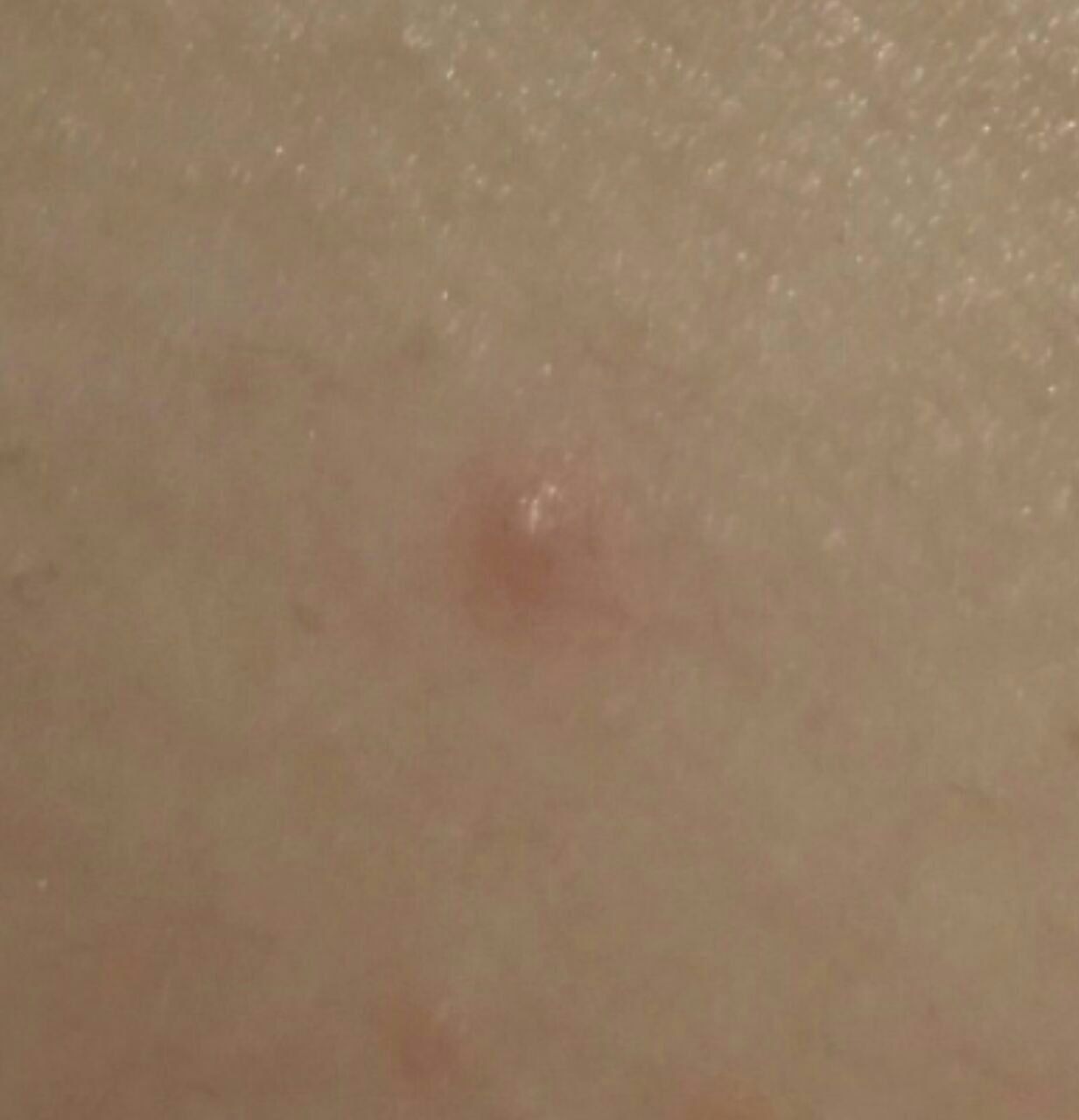
Closed comedone is a skin cyst formed as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland and covered with a thin layer of skin. A distinctive feature of a closed comedone from an open one is the absence in the center of a black point (the plug of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland oxidized under the influence of air).
Comedones belong to the group of acne, however, as such, they are not a disease due to the absence of an inflammatory process. At the same time, a large number of comedones in one anatomical region can be regarded as a non-inflammatory form of acne.
Comedones can appear at any age and on any part of the body where sebaceous glands are present. However, they most often appear during puberty, in adolescents and middle-aged people. Can be single or multiple.
Predisposing factors
The appearance of comedones is facilitated by the increased activity of the sebaceous glands of the skin with a tendency of the skin to hyperkeratosis. In the latter case, there is insufficient exfoliation of keratinized skin scales and their long-term fixation to the epidermis. The thick keratinized layer makes it difficult for the secretion of the sebaceous glands to pass through the excretory ducts and ultimately clogs them completely. At the same time, the sebaceous gland itself continues to function and produce its own secret.
Hyperkeratosis and increased activity of the sebaceous glands leads to:
-
Improper or unsatisfactory skin hygiene;
- Poor quality skin care products;
- Smoking;
- Improper nutrition;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Skin damage (including ultraviolet light);
- Diseases of internal organs (metabolic and endocrine disorders).
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of closed comedones is based on a clinical examination, which includes a routine examination of the formation and dermatoscopy. In case of an ambiguous clinical picture, a biopsy can be performed, followed by a histological examination.
Symptoms
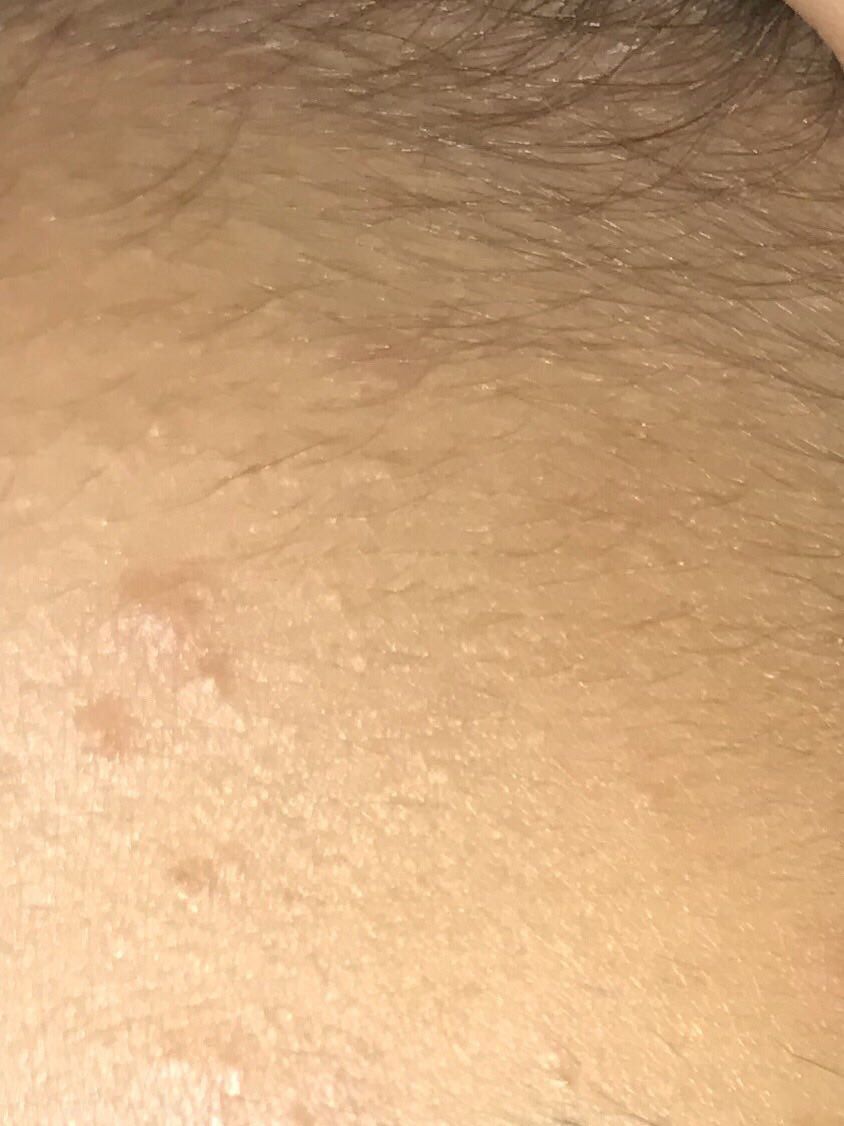
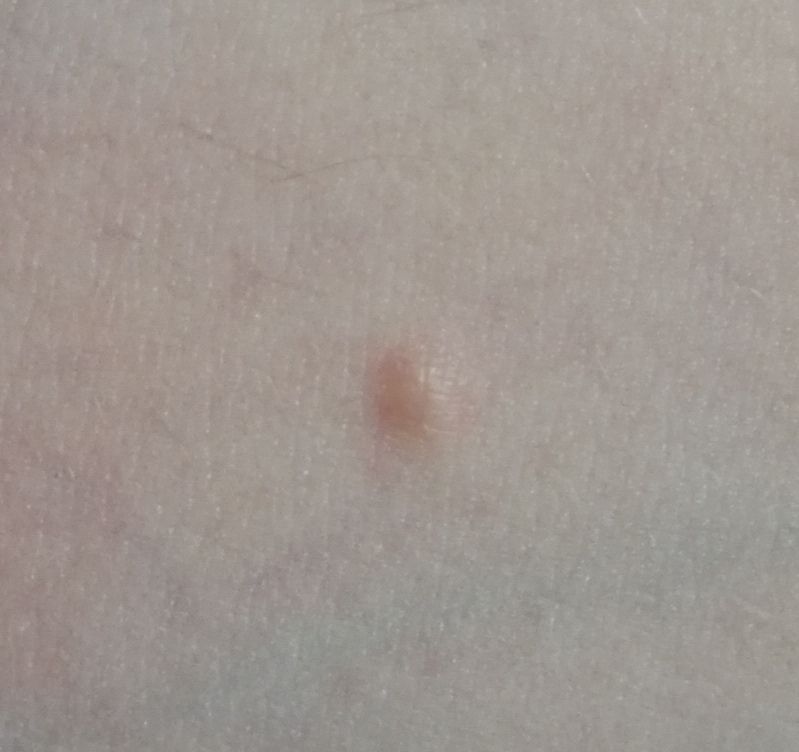
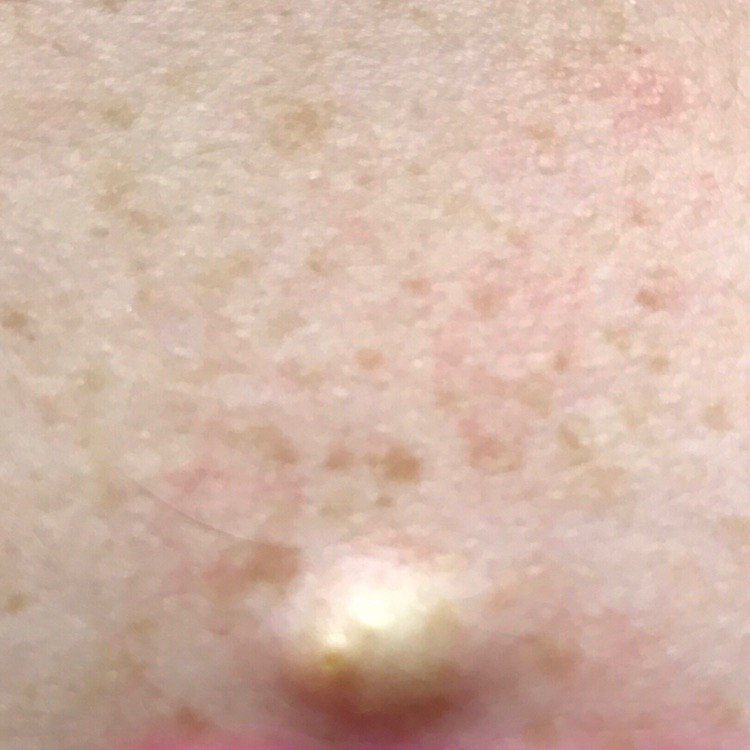
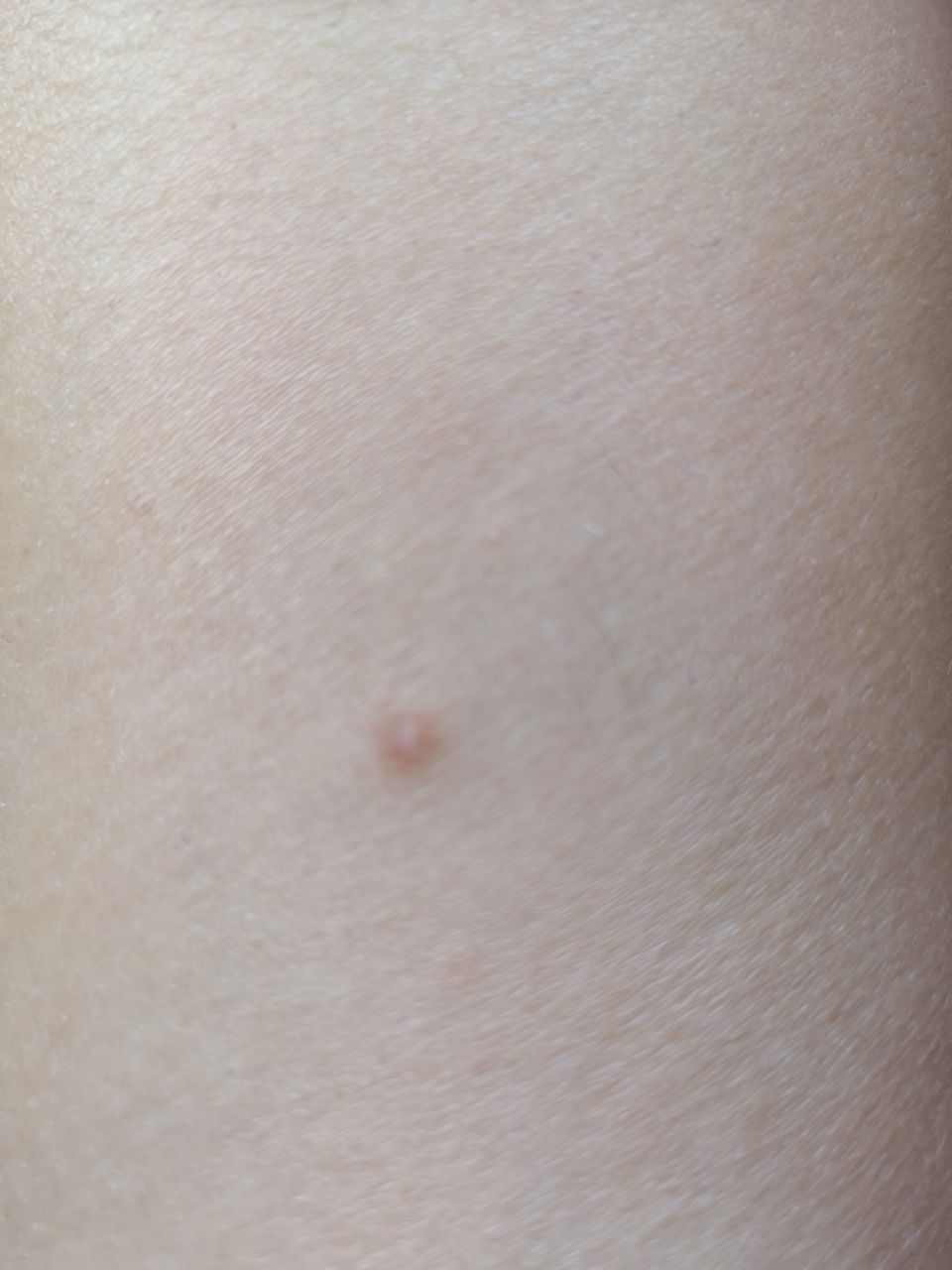
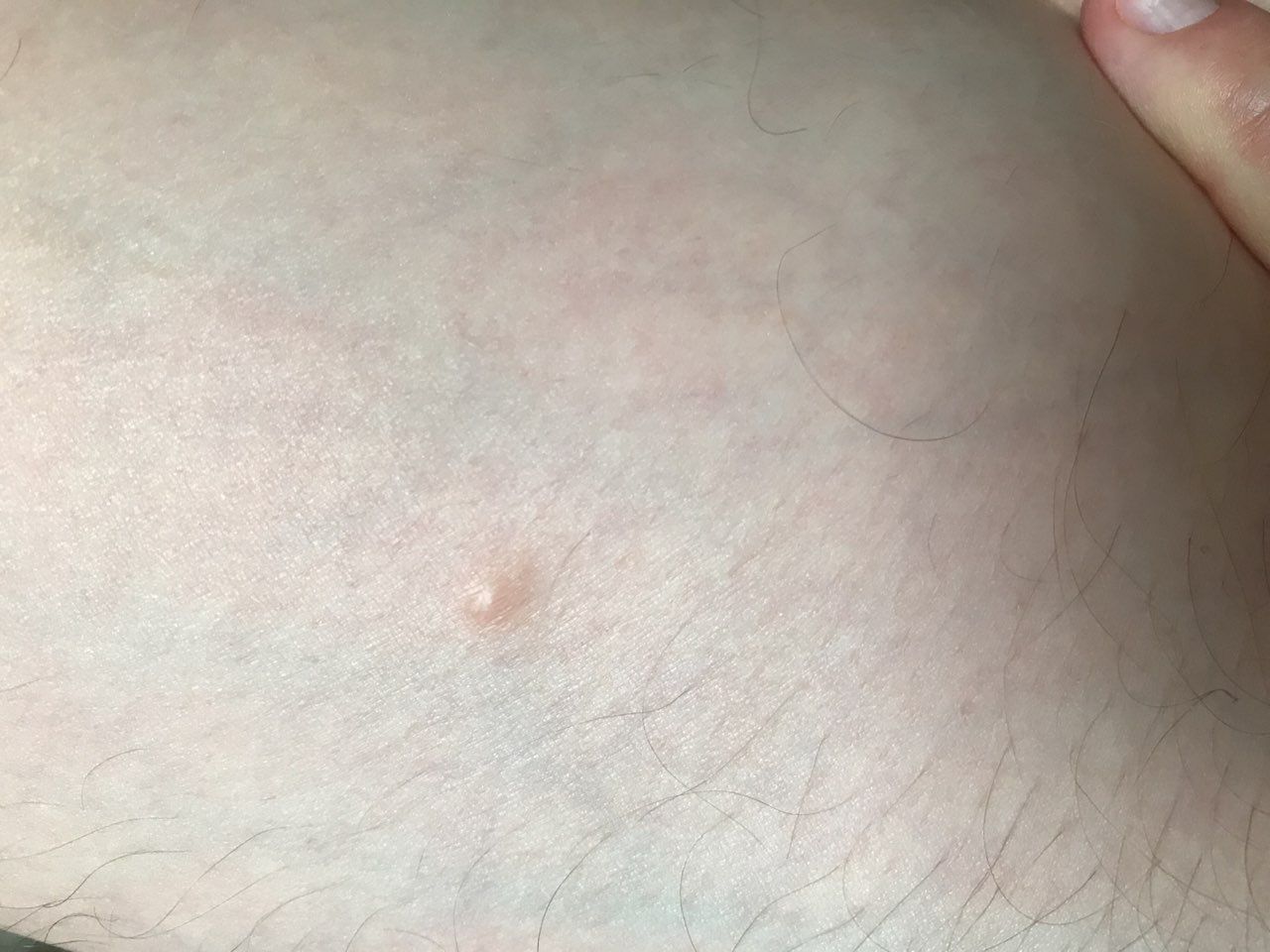
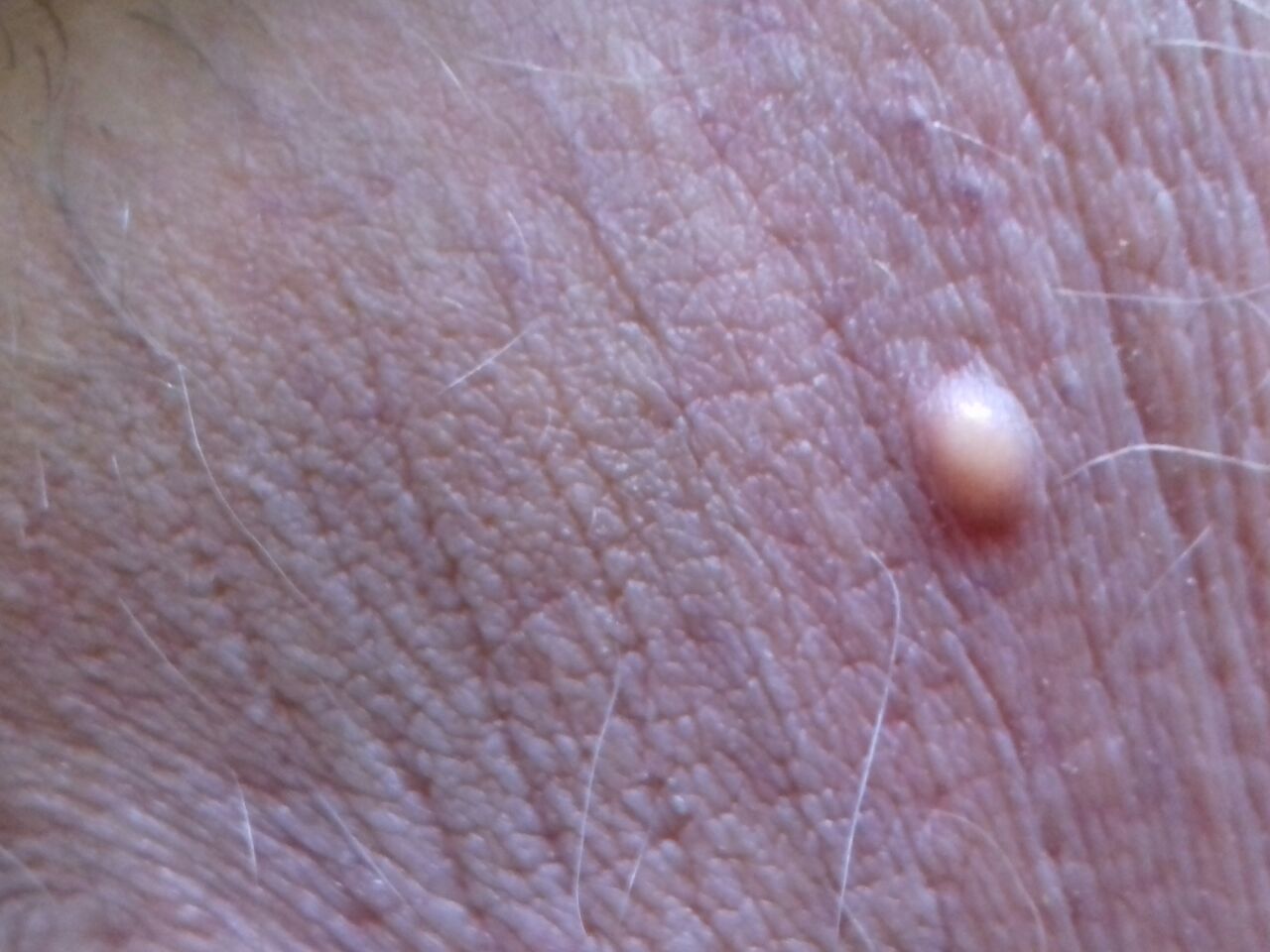
On visual inspection of a closed comedone, a hemispherical formation, a tubercle, most often symmetrical (oval or rounded), rising above the skin is determined. The surface of the comedone does not differ from the texture of normal skin.
The boundaries are fuzzy, as the skin smoothly passes from the comedone zone to the healthy area. The color is unchanged or somewhat paler than the surrounding healthy skin, especially in the center, where the skin is thinned (the white contents of the clogged sebaceous gland can be seen through the thin skin).
As a rule, hair does not grow from the comedone itself. But if the comedone is large and forms a large subcutaneous cyst without affecting the skin covering it, then the hair growth zone is not disturbed.
Closed comedones are usually 2–3 mm in size, although larger forms can also occur.
On palpation, the comedone is represented by a dense intradermal formation. There are no subjective sensations.
Neoplasms are located mainly on the face, scalp, neck, trunk, less often on the limbs.
Dermatoscopic description
Dermatoscopy of Closed comedone visualizes:
- Whitish central zone surrounded by a normal skin pattern;
- Fuzzy border between the central whitish zone and the skin;
- Symptom of compression (flattening) of the central zone (the most protruding part of the comedone above the skin).
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out with such neoplasms as:
- Papillomatous nevus;
- Sebaceous gland nevus
- Open comedone;
- Acne (with multiple comedones);
- Molluscum contagiosum;
- Papilloma;
- Nodular form of basal cell skin cancer;
- Non-pigmented melanoma.
Risks
A closed comedone does not pose a major threat to a person’s physical health. At the same time, a large number of these formations may indicate the presence of some kind of rearrangements in the body: from physiological (such as puberty) to pathological (metabolic disorders). Being a kind of mirror, a reflection of the internal state of the body, the appearance of a large number of comedones cannot be ignored, it is necessary to conduct a deep search for the causes and provoking factors. This will contribute not only to the effective treatment of comedones, but also to the timely search for other, possibly more serious, diseases.
On the other hand, comedones can cause significant cosmetic defects and psychological damage to the patient. To avoid serious consequences from these problems, the treatment of comedones should be multi-component with the involvement, if necessary, of different specialists (dermatologists, cosmetologists, nutritionists, endocrinologists, psychologists).
In the absence of timely treatment, in comedones, pathological growth of skin microflora can begin with the development of an inflammatory process, the formation of acne and corresponding complications.
Tactics
With the appearance of the first comedones, as well as with the progression of already existing forms, the ineffectiveness of the previously prescribed treatment, a visit to a dermatologist is indicated.
The initial visit to a specialist is the most important, since it is necessary to carry out the entire range of diagnostic measures, followed by the appointment of individual treatment.
An immediate visit to a specialist is indicated if there has been a mechanical damage to the skin in the area of the comedone, as well as if any changes in the appearance of one of the elements are noticed or previously absent sensations have appeared.
Multiple comedones can be a chronic pathology that lasts for a long time, for many years, with periods of exacerbation and improvement. The course of the disease may depend on various factors occurring in a person’s life, therefore, close contact with a specialist should be maintained, with the help of whom a timely and adequate response to the ongoing changes in the skin will be carried out.
It is also important to realize the need for preventive consultations, especially before the upcoming changes in life: choosing a diet, changing the usual cosmetics, planning trips to zones with a different climate, changing a place of work with a different microclimate, as well as when starting another treatment that affects the human endocrine system.
Treatment
Single comedones that do not manifest themselves in any way and do not cause a cosmetic defect do not require treatment. Over time, spontaneous restoration of the patency of the sebaceous gland duct and the normal functioning of the latter are possible. If desired, single comedones can be removed with special extractors or other devices in a beauty parlor or at a dermatologist.
Multiple comedones require more active participation of specialists, since improper self-treatment can cause significant harm to skin health in the form of the development of severe forms of acne or other infectious dermatitis.
For treatment, various types of skin peels (mechanical, chemical) can be used to remove hyperkeratosis and release the sebaceous gland ducts from blockages. Recently, preference is given to chemical peels, which are less traumatic to the skin. In the fight against comedones, retinoids, azelaic acid and other drugs are used strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
After aggressive cosmetic treatment, topical antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to prevent the development of skin infections.
When treating comedones, attention must also be paid to eliminating the factors that provoke the appearance of these formations: general strengthening of skin health, immunity, timely correction of metabolic and endocrine disorders.
It is important to understand that there is no single miracle remedy that can, in a short time, quickly, without consequences, and absolutely help every person in the fight against comedones. That is why you need to be critical of the advertising of such drugs and self-medication by them. Any new drug should be discussed with a specialist.
Also, in the treatment of multiple comedones, a clear consistency in actions and adherence to the implementation of recommendations are needed. Self-deviation from the prescribed treatment regimen, interruption and non-compliance with therapeutic regimens significantly complicates the achievement of the expected effect.
At the same time, it is necessary to understand the risk of failure in treatment, to accept that the prescribed therapy does not always have the desired effectiveness and speed of achieving results. There should be a readiness for an open dialogue with a dermatologist, tolerance for a possible change in approaches to treatment.
Prevention
The prevention of comedones consists in a gentle and careful attitude to the skin, timely treatment of infectious diseases, strengthening immunity, proper and high-quality personal hygiene, in maintaining a healthy lifestyle, especially in terms of nutrition.
To eliminate negative consequences and complications, it is necessary:
- Limiting ultraviolet exposure (tanning bed, sun tanning);
- Use of protective creams during periods of active sun;
- Exclusion of chronic skin trauma;
- Limitation or elimination of ionizing radiation, occupational hazards;
- Compliance with safety measures when working with factors damaging the skin;
- Personal hygiene and basic skin health awareness.
A regular examination of the skin, timely consultation with a dermatologist are also necessary if any changes appear on it.