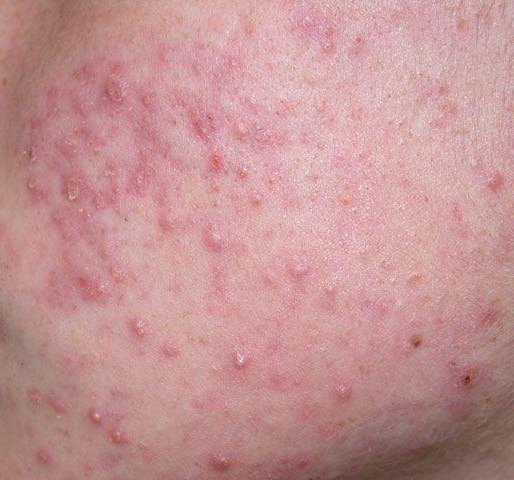
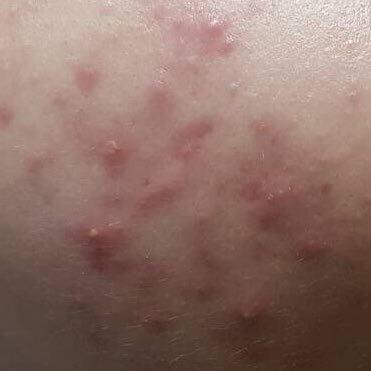
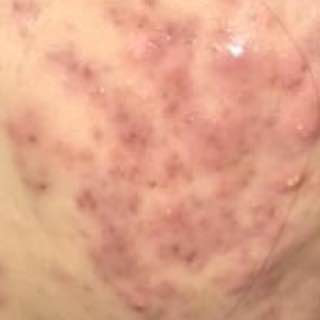
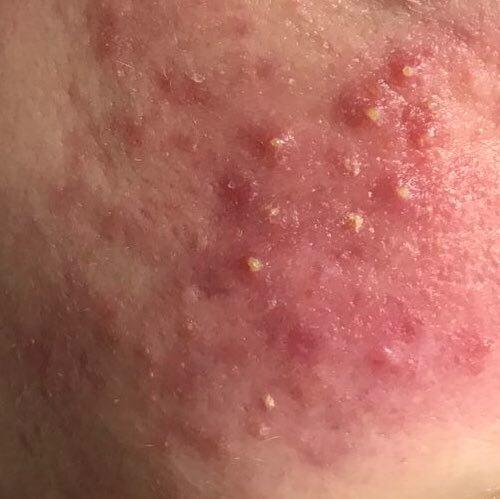
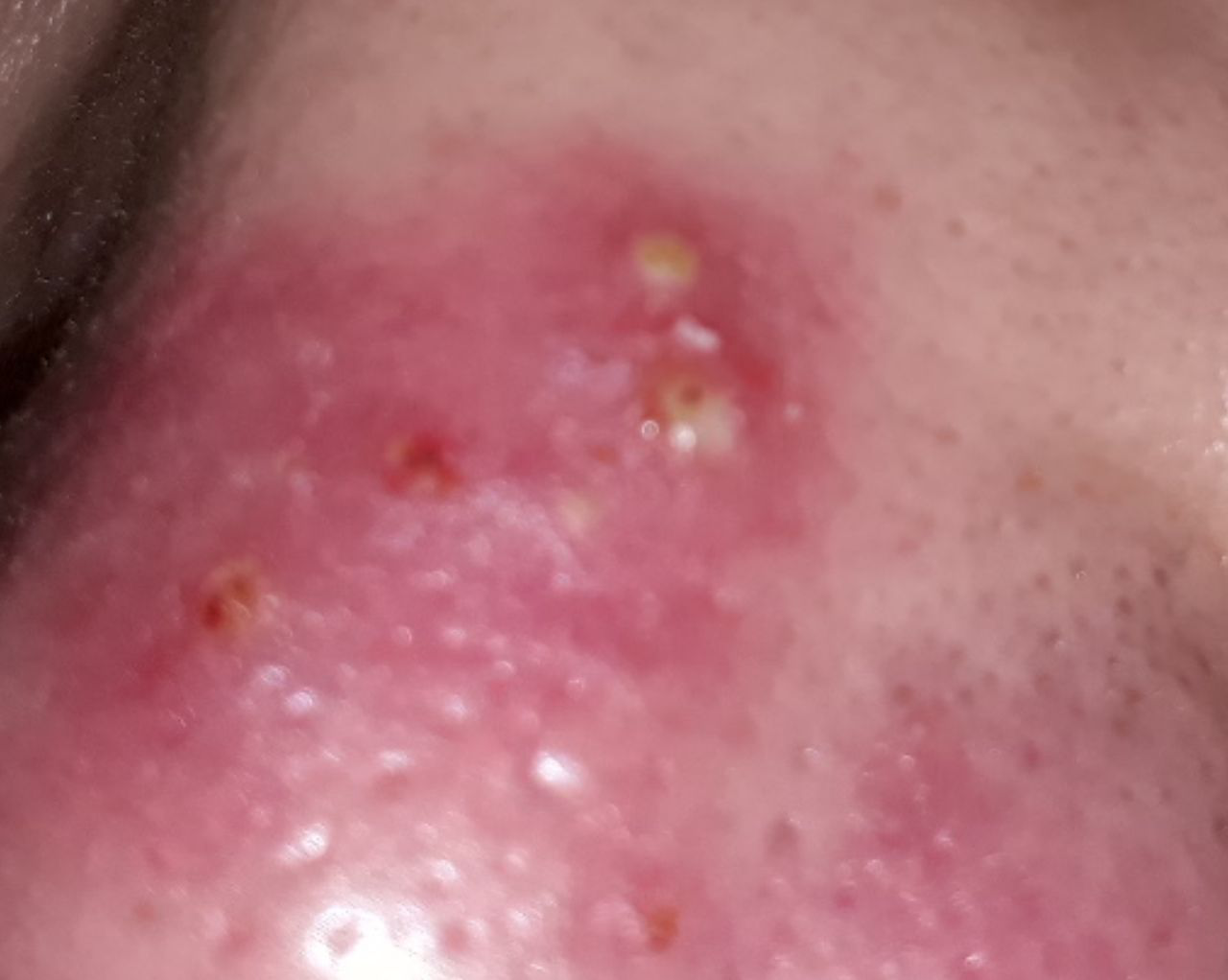
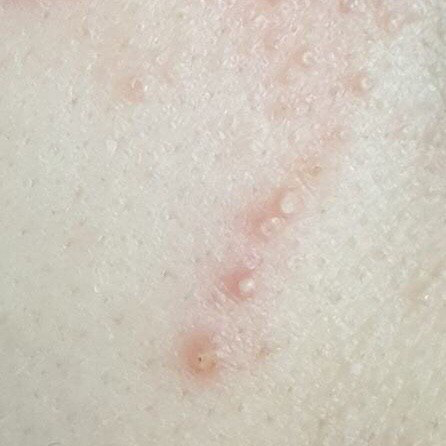
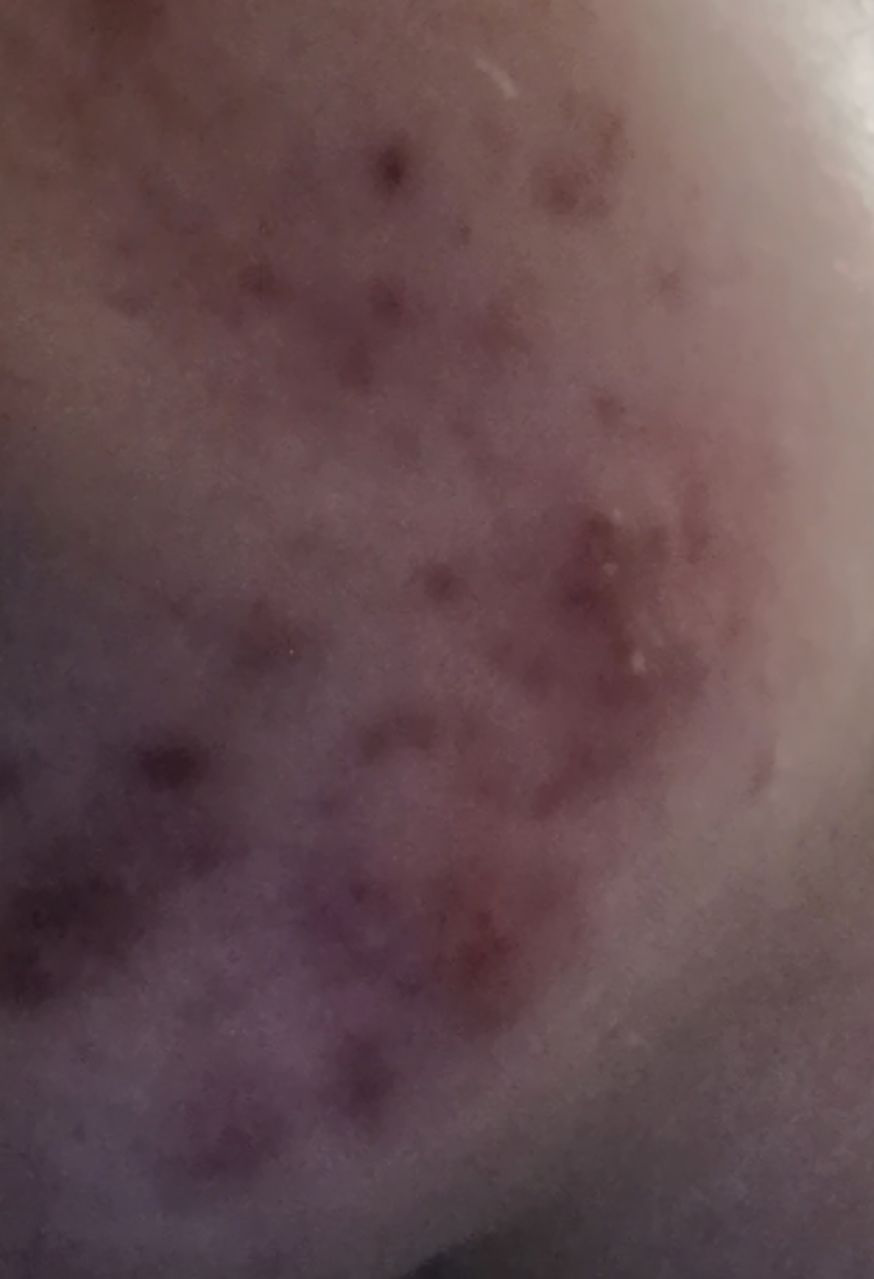
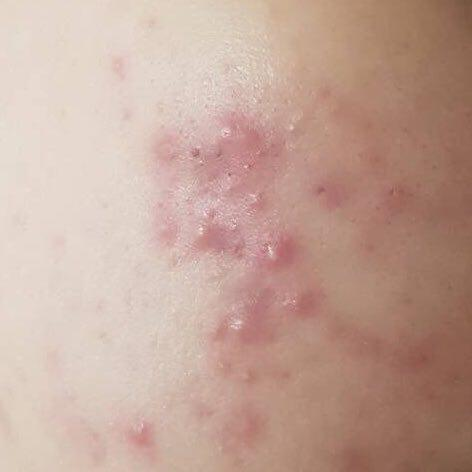
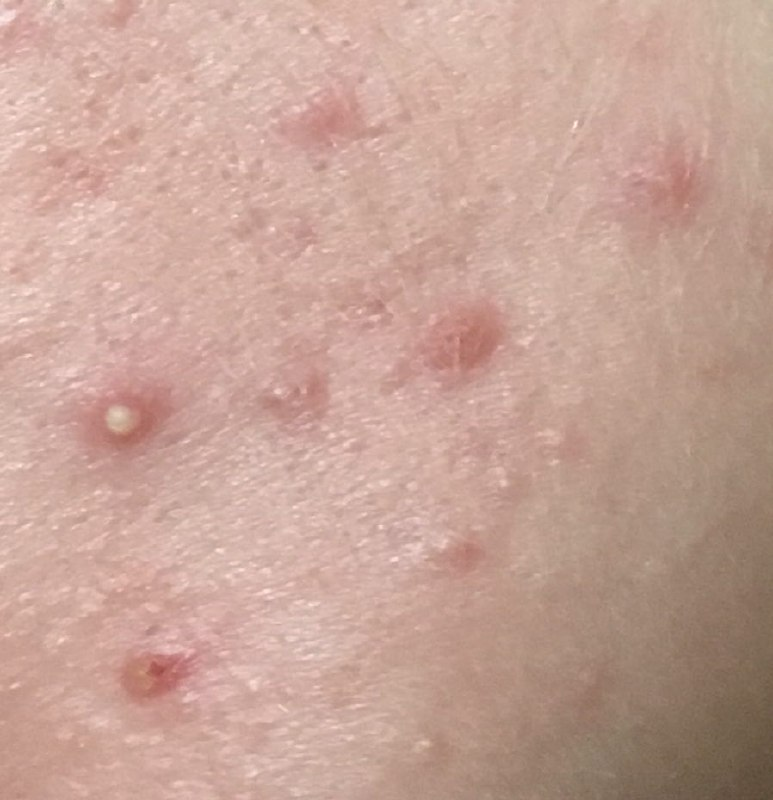
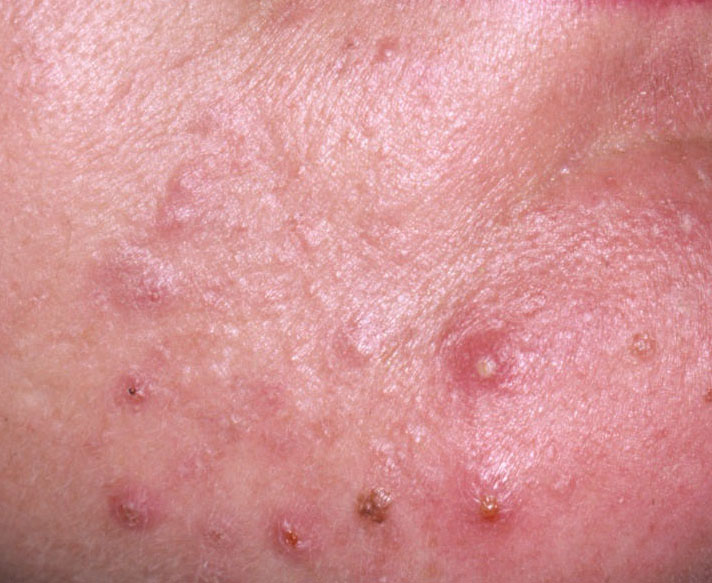
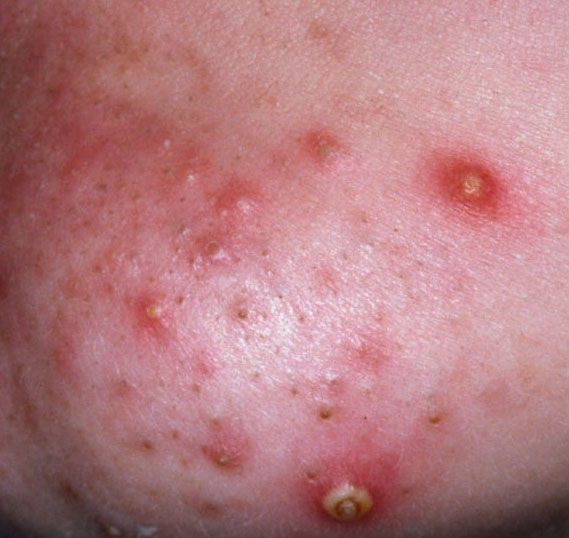
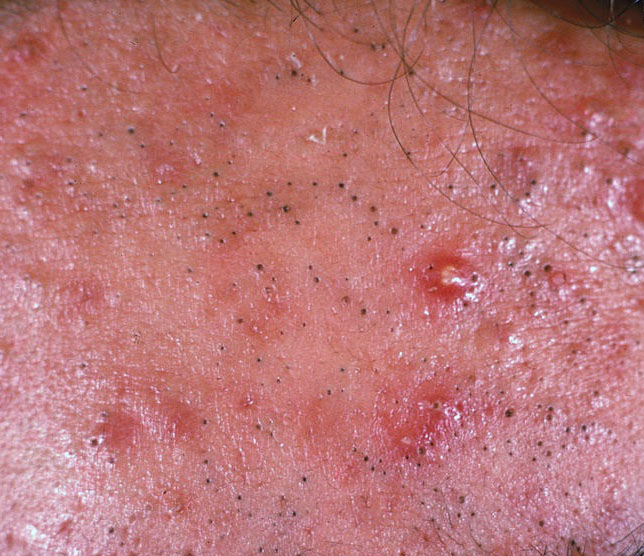
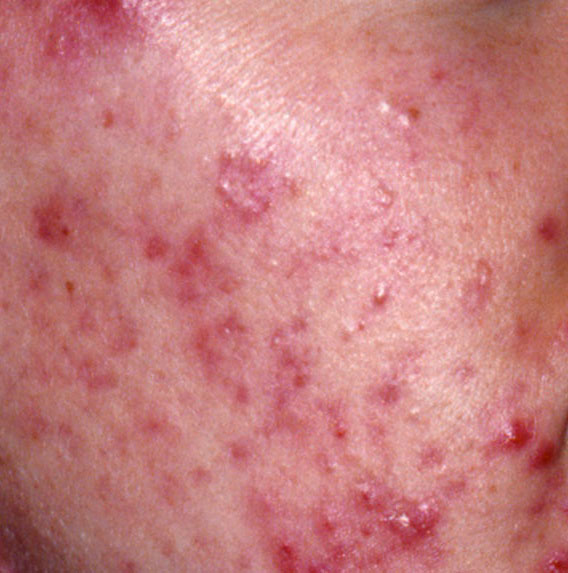
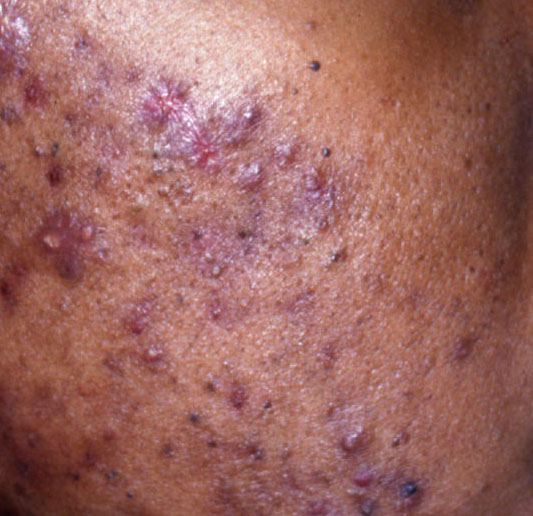
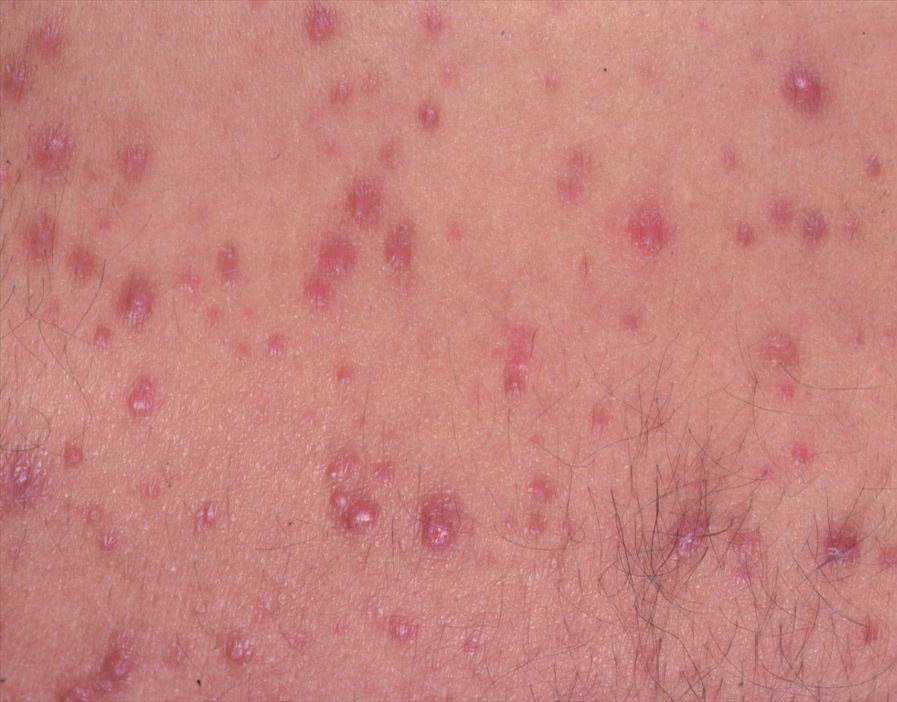
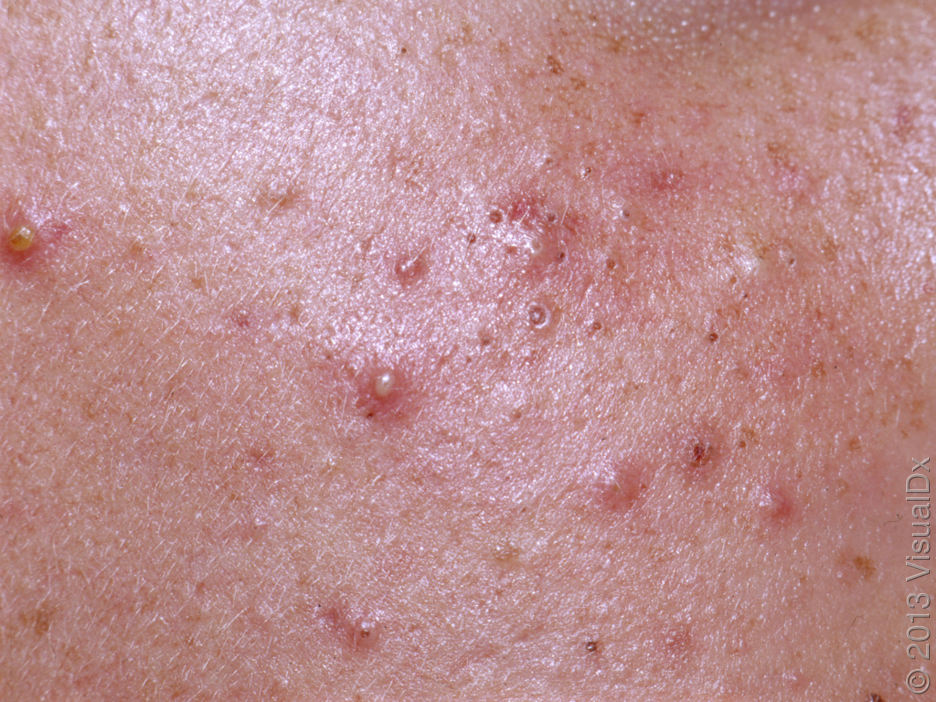
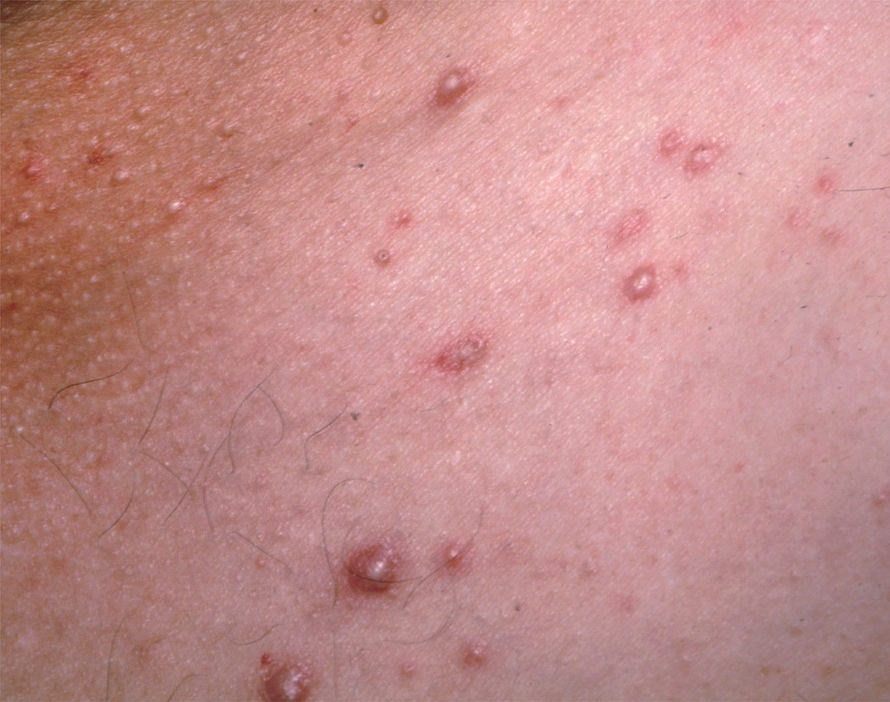
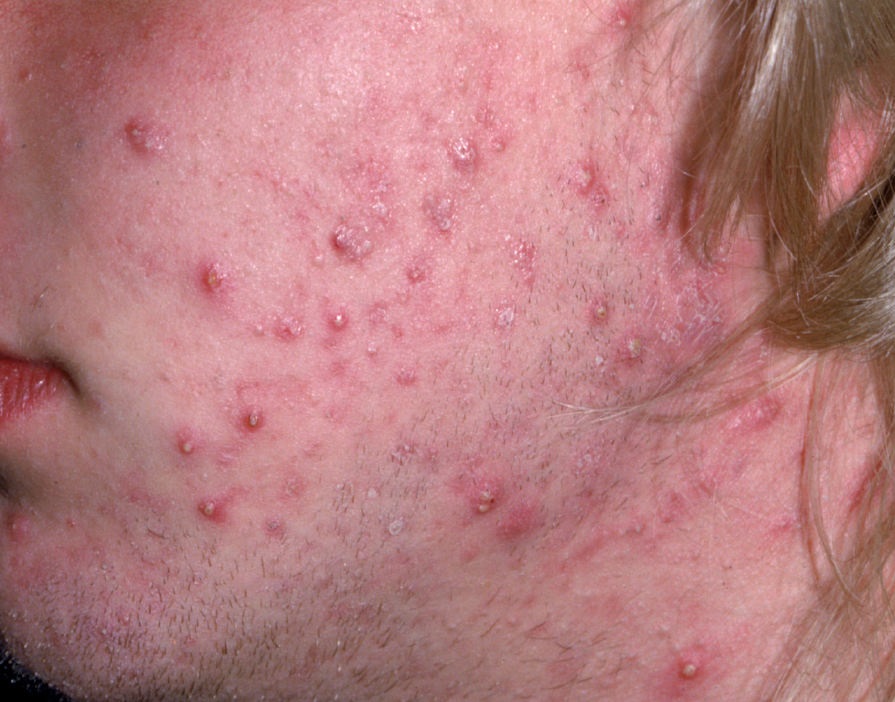
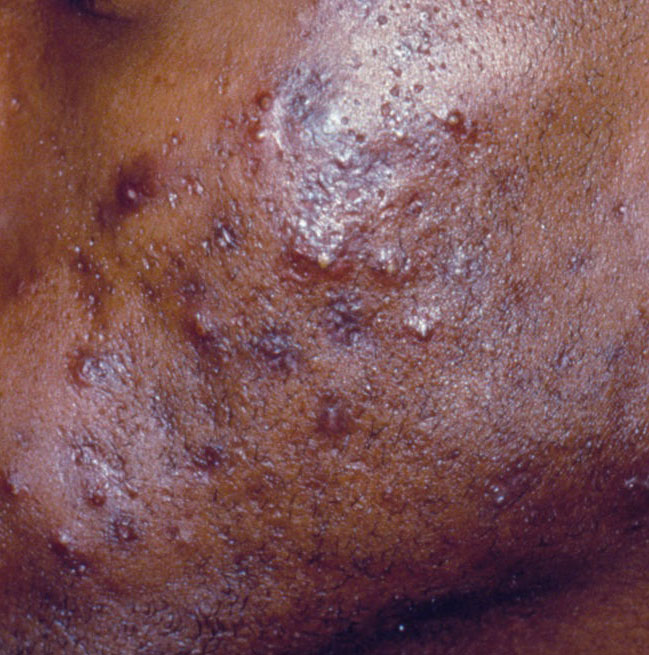
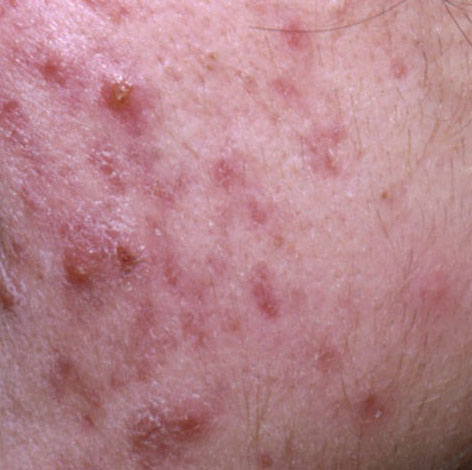
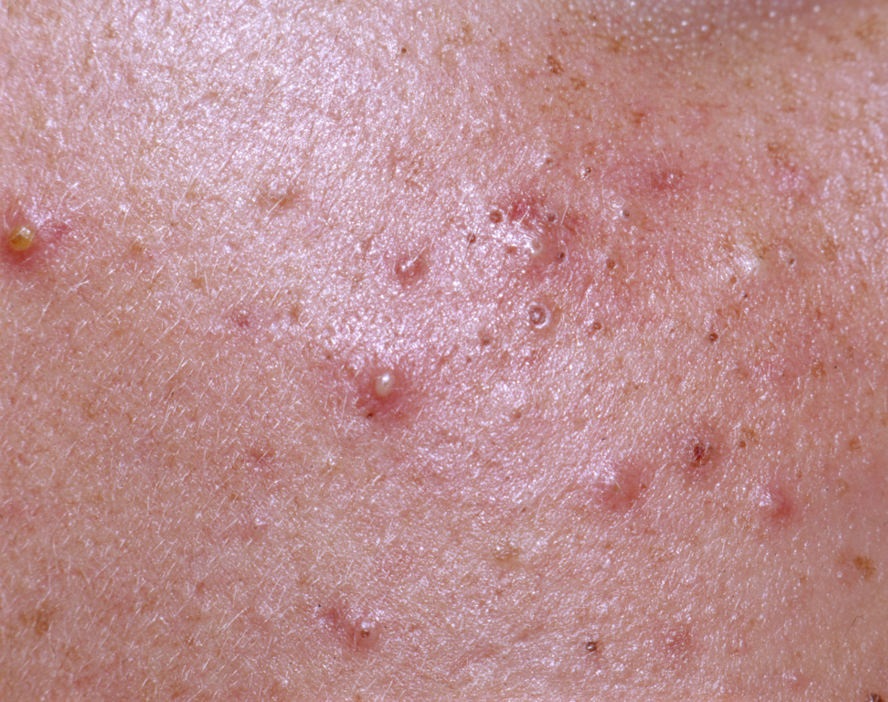
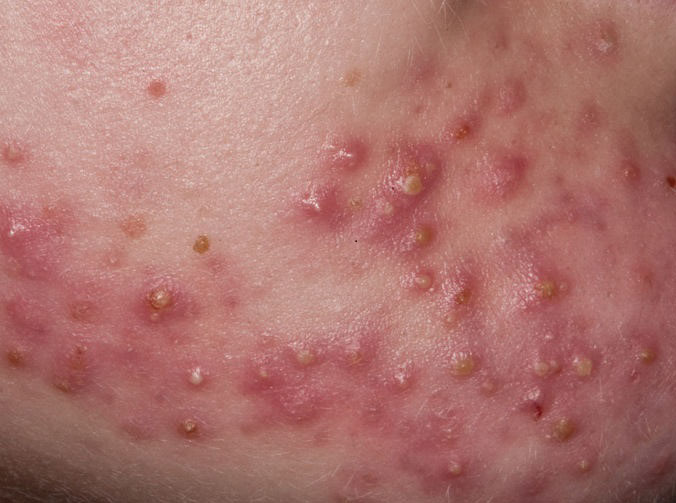
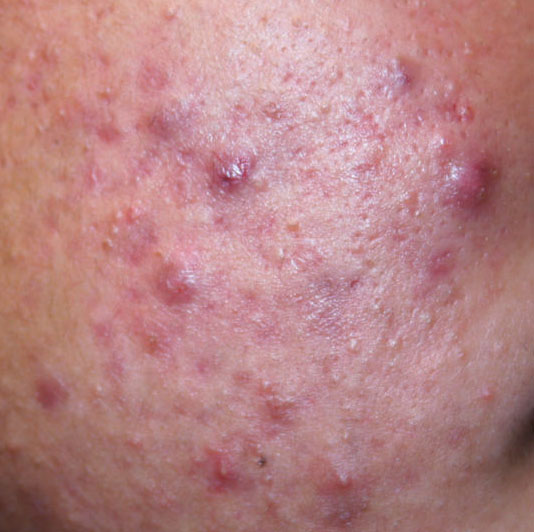
Acne pustular is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with damage to the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. With acne, elements such as comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, cysts, scars and hyperpigmentation lesions appear. The most typical localization of the rash is the face (forehead, cheeks, chin), chest area, back, shoulders.
Depending on the dominance of certain elements, different forms of acne are distinguished. Acne pustular is characterized by the presence of comedones, with a predominance of papules and pustules.
Acne pustular usually occurs during adolescence, starting at the age of 11-13. In males, acne appears a little later (the debut can be observed at the age of 19-20), but it occurs more often. In girls, on the contrary: the first signs can be noted as early as 11 years old, but it happens less often in comparison with males.
The prevalence of Acne pustular is very high. It is believed that this disease is found in 80% of the population. However, due to the absence of special threats to health, not all patients seek medical help, perceiving such a skin condition only as a cosmetic defect and not taking proper measures to eliminate the problem.
Acne pustular formation is associated with excess sebum secretion by the sebaceous glands. The second condition is blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands with the accumulation of secretions in them and the appearance of comedones. These two stages are sufficient for the development of non-inflammatory acne. If microflora begins to actively multiply in comedones (for example, Cutibacterium acnes – a representative of the normal human microflora), followed by the formation of an inflammatory reaction in this place, an inflammatory form of acne develops.
Predisposing factors
There is no specific cause for acne. This is a multifactorial disease, in the development of which many different pathological conditions and changes, both inside and outside the body, take part.
Today, it is believed that the main contribution to the launch of the pathological chain of acne formation is made by heredity. This is supported by scientific research, including observations of twins. A number of genes are already known to increase the risk of developing acne.
Other predisposing factors that, to varying degrees, can influence the formation of acne include:
- Endocrine processes – first of all, this is confirmed by the age of onset of acne. It is during puberty that intense changes in hormonal levels are observed in the body. The main connection is found between acne and androgens – male sex hormones that stimulate the growth of the sebaceous glands and activate the secretion of sebum;
- The role of microorganisms, in particular – Cutibacterium acnes. Despite the fact that this is a normal microflora of human skin, in certain cases it can provoke inflammatory processes. Of course, acne can be caused by the addition of a pathogenic skin infection, as well as the Demodex mite;
- Problems with personal hygiene, improperly selected or poor-quality cosmetics, the effect of external factors on the skin (especially physical ones – chronic injuries by clothing or professional devices) – can provoke the appearance of acne, having a negative effect on the normal functioning of the skin as an organ;
- Decrease in the body’s defenses against the background of stress, immunodeficiency states, poor environmental conditions, the appearance of bad habits, deficiency of vitamins, macro and microelements, poor nutritional quality;
- The nutritional factor has a special role to play. Acne is often observed in adolescents, whose food contains a large amount of sugar, chocolate, coffee, dairy products. Likewise, eliminating or limiting these foods can help you manage your acne problem more quickly and easily. At the same time, there is no scientific evidence describing a direct and reliable relationship between the listed foods and acne.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of acne is based on history and clinical examination. A carefully collected anamnesis allows you to find out the time of the onset of the skin disease, the conditions, the course. On clinical examination, typical elements characteristic of acne are found. If such a need arises, especially in the presence of single elements, unexpressed manifestations, dermatoscopy can be performed.
A thorough diagnosis is necessary to correctly determine the severity of acne, as well as to maximize the identification of provoking factors. All this allows in the future to select an adequate treatment and individually form preventive measures.
Symptoms
On visual inspection of Acne pustular, a skin rash is determined, consisting mainly of elements such as comedones and papules. The proportion of each element may be different, but papules predominate more often.
Comedones – can be closed and open. Closed comedones are slightly raised, whitish or skin-colored, painless, dense formations. Their base diameter does not exceed 1-3 mm. The surface is regular leather or slightly smoothed. Open comedones are distinguished by the presence of a depression on the surface and a black dot in it – this is a sebum plug, oxidized in the open air. Open comedones can be up to 5-7 mm in size, especially on the back.
A papule is a common pimple with no content inside: a slightly elevated, pink-red or red, painful formation on contact with fuzzy boundaries. Their base diameter does not exceed 1-3 mm. A hyperemic skin reaction around the pustule can be up to 10 mm in diameter. In the presence of severe inflammation, the papule may be denser than normal skin. The skin surface is regular or slightly smoothed.
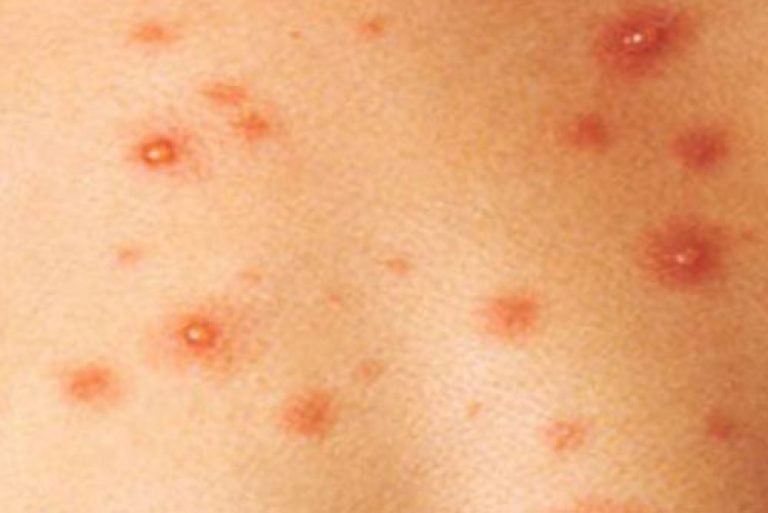
With Acne pustular, a small number of pustules, scars, local foci of hyperpigmentation, nodules can be determined.
A pustule is a common pimple with whitish or yellow-tinged contents inside. It is slightly elevated, pink-red or red around the periphery and whitish in the center, painful on contact, with indistinct boundaries. The pustule is usually denser than the surrounding skin. The diameter at the base does not exceed 1-3 mm. A hyperemic skin reaction around the pustule can be up to 10 mm in diameter. The surface is usually smooth, especially in the center. When squeezed, the pustule is opened and structureless white contents are released from it.
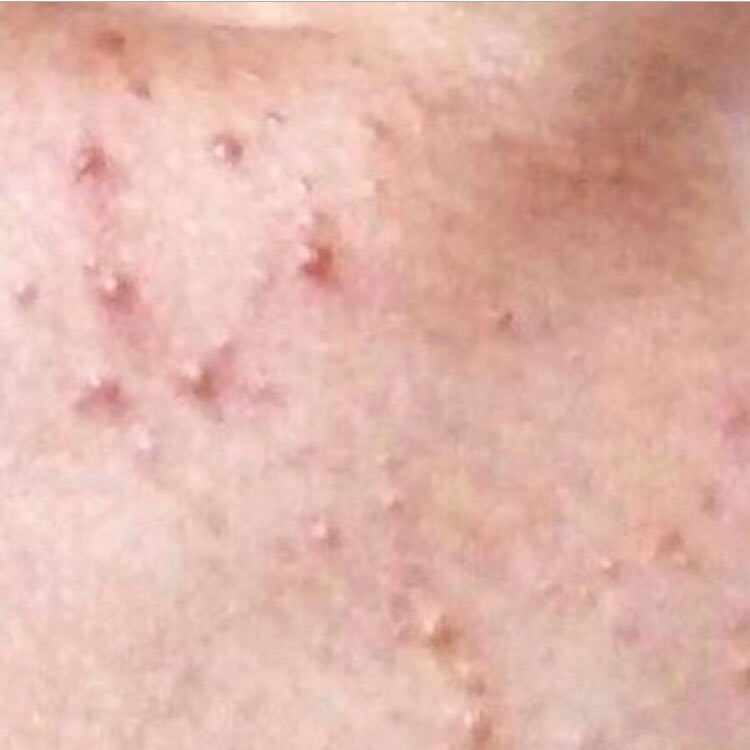
Scars – are formed after the healing of deeply located acne elements in the skin. The likelihood of scarring increases with the severity of the acne. Scars can be atrophic (more common) and hypertrophic. Atrophic scars – a deepening in the skin with clear boundaries, with little or no change in the density of the skin and its pattern, but exceeding the diameter of the original element. Hypertrophic scars are rough, dense formations protruding above the skin, usually corresponding to the diameter of the original element.
Hyperpigmentation – post-inflammatory increase in skin coloration, which forms, like scars, after the disappearance of the original elements of acne. Focuses of hyperpigmentation can exist separately or in combination with scars (in this case, this means the presence of a pigmented scar). By color, pigmentation is represented by various shades of brown.
Nodules are papules, but with a more pronounced inflammatory reaction, larger in size, denser, located deeper in the skin, more painful. After the resolution of the acute process against the background of nodules, the likelihood of scarring is higher. With progression (suppuration), cysts form against the background of the nodules.
The favorite localization of pustular acne is the area of the face, especially the forehead, cheeks and chin, as well as the back (mainly the scapular region), the chest and shoulder joints. For other anatomical areas, the appearance of acne is not typical.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases such as:
- Different degrees of severity and forms of acne;
- Rosacea;
- Isolated comedones;
- Milium;
- Dermatitis;
- Rashes and dermatoses;
- Against the background of severe forms of acne, especially in adults – nodular forms of basal cell carcinoma and non-pigmented melanoma.
Risks
Acne pustular does not pose a major threat to a person’s physical health. At the same time, the presence of this pathology may indicate the presence of some kind of rearrangements in the body: from physiological (such as puberty) to pathological (metabolic disorders, decreased immunity). Being a kind of mirror, a reflection of the internal state of the body, the appearance of acne cannot be ignored, it is necessary to conduct a deep search for the causes and provoking factors. This will contribute not only to the effective treatment of acne, but also to the timely search for other, possibly more serious diseases.
On the other hand, acne can cause significant cosmetic defects and psychological damage to the patient. To avoid serious consequences from these problems, acne treatment should be multi-component with the involvement, if necessary, of different specialists (dermatologists, cosmetologists, nutritionists, endocrinologists, psychologists).
In the absence of timely treatment, the progression of acne leads to severe infectious skin lesions with the risk of generalization of the infection with corresponding complications. In addition, elements of severe acne can be injured, ulcerated, followed by bleeding.
Tactics
When the first signs of acne appear, as well as with the progression of existing forms, the ineffectiveness of the previously prescribed treatment, a visit to a dermatologist is indicated.
The initial visit to a specialist is the most important, since it is necessary to carry out the entire range of diagnostic measures, followed by the appointment of individual treatment.
An immediate visit to a specialist is indicated if there has been a mechanical damage to the skin in the acne area, as well as if any changes in the appearance of one of the elements are noticed or previously absent sensations have appeared.
Acne is a chronic pathology that lasts for a long time, for many years, with periods of exacerbation and improvement. The course of the disease may depend on various factors occurring in a person’s life, therefore, close contact with a specialist should be maintained, with the help of whom a timely and adequate response to the ongoing changes in the skin will be carried out.
It is also important to realize the need for preventive consultations on the management of acne, especially before the upcoming changes in life: choosing a diet and diet, before changing the usual cosmetics, planning travel to zones with a different climate, changing a place of work with a different microclimate, as well as when starting another treatment affecting the human endocrine system.
Treatment
Acne treatment is multicomponent and individual. Includes:
- Drug therapy;
- Local cosmetic treatment;
- Phototherapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Correction and elimination of provoking factors;
- Treatment accompanying pathologies;
- A therapy aimed at reducing emotional distress.
Topical antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are usually used to treat pustular acne. Rarely, if they are ineffective, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Hormone therapy can be prescribed for treatment, however, there must be clear and unambiguous indications for this.
In order to normalize the life cycle of cells in the upper layers of the skin, to ensure normal processes of keratinization and desquamation (exfoliation of the uppermost layers of epithelial cells), topical retinoids are prescribed, as well as cosmetic treatment. Mechanical extraction of comedones using special devices can also be used.
To stop the inflammatory process, local anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy and phototherapy are used.
After the elimination of acute processes and the appearance of scars, various methods of laser resurfacing and dermabrasion are used, as well as other cosmetic procedures aimed at eliminating this defect.
It is important to understand that there is no single miracle remedy that can, in a short time, quickly, without consequences, and absolutely help every person in the fight against acne. That is why you need to be critical of the advertising of such drugs and self-medication by them. Any new drug should be discussed with a specialist.
Also, when treating acne, you need a clear consistency in actions and adherence to the implementation of recommendations. Self-deviation from the prescribed treatment regimen, interruption and non-compliance with therapeutic regimens significantly complicates the achievement of the expected effect.
At the same time, it is necessary to understand the risk of failure in treatment, to accept that the prescribed therapy does not always have the desired effectiveness and speed of achieving results. There should be a readiness for an open dialogue with a dermatologist, tolerance for a possible change in treatment approaches.
Prevention
Prevention of acne consists in a gentle and careful attitude to the skin, timely treatment of infectious diseases, strengthening the immune system, proper and high-quality personal hygiene, in maintaining a healthy lifestyle, especially in terms of nutrition.
To eliminate negative consequences, it is necessary:
- Limiting ultraviolet exposure (tanning bed, sun tanning);
- Use of protective creams during periods of active sun;
- Exclusion of chronic skin trauma;
- Limitation or elimination of ionizing radiation, occupational hazards;
- Compliance with safety measures when working with damaging skin factors;
- Personal hygiene and basic skin health awareness.
A regular examination of the skin, timely consultation with a dermatologist are also necessary if any changes appear on it.]